Python+OpenCV实现单个圆形孔和针检测
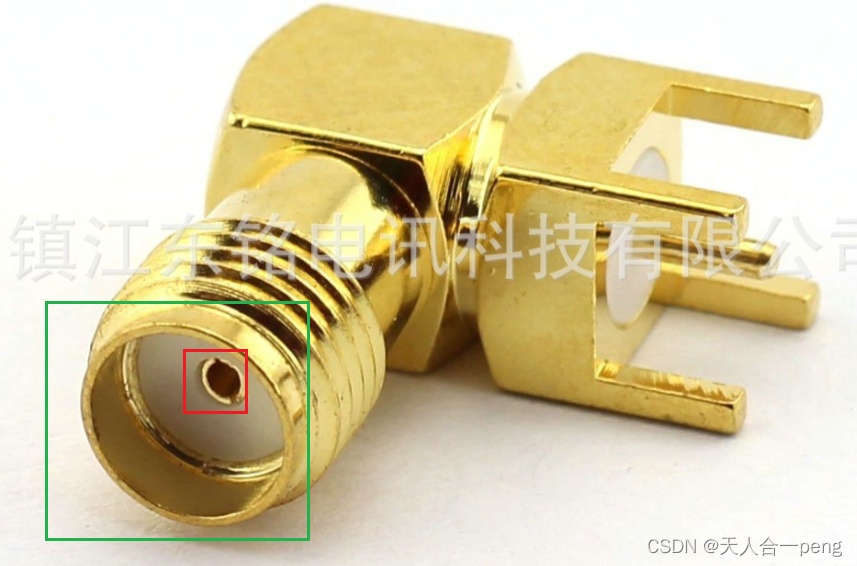
天人合一peng 人气:0如果中间红色区域是针则可以用下面的代码检测,其阈值和斑点检测的参数根据图像像素值做相应修改
检测的主要思路是先通过找到外面的大圆,再通过圆心定位出一个ROI区域,在ROI区域中检测中心的检测对象
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
import math
# 检测针脚位置
def needelCenter_detect(img):
params = cv2.SimpleBlobDetector_Params()
# Setup SimpleBlobDetector parameters.
# print('params')
# print(params)
# print(type(params))
# Filter by Area.
params.filterByArea = True
params.minArea = 100
params.maxArea = 10e3
params.minDistBetweenBlobs = 50
# params.filterByColor = True
params.filterByConvexity = False
# tweak these as you see fit
# Filter by Circularity
params.filterByCircularity = False
params.minCircularity = 0.2
# params.blobColor = 0
# # # Filter by Convexity
# params.filterByConvexity = True
# params.minConvexity = 0.87
# Filter by Inertia
# params.filterByInertia = True
# params.filterByInertia = False
# params.minInertiaRatio = 0.01
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Detect blobs.
minThreshValue = 110
_, gray = cv2.threshold(gray, minThreshValue, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# gray = cv2.resize(gray, dsize=None, fx=2, fy=2, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
# plt.imshow(gray)
# cv2.imshow("gray",gray)
# 找到距离原点(0,0)最近和最远的点
detector = cv2.SimpleBlobDetector_create(params)
keypoints = detector.detect(gray)
# print(len(keypoints))
# print(keypoints[0].pt[0])
# 如果这儿没检测到可能会出错
if len(keypoints) == 0:
print("没有检测到针角坐标,可能需要调整针角斑点检测参数")
return keypoints
else:
print(len(keypoints))
im_with_keypoints = cv2.drawKeypoints(gray, keypoints, np.array([]), (255, 0, 0),
cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS)
# if keypoints is not None:
color_img = cv2.cvtColor(im_with_keypoints, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 画出圆的圆心
cv2.circle(color_img, (int(keypoints[0].pt[0]), int(keypoints[0].pt[1])), 5, (0, 255, 0), -1)
cv2.imshow("color_img",color_img)
# cv2.waitKey()
return keypoints
# 检测连接器圆形位置
def circle_detect(image):
# 灰度化
circle_img = image.copy()
gray = cv2.cvtColor(circle_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 输出图像大小,方便根据图像大小调节minRadius和maxRadius
# print(image.shape)
# 进行中值滤波
img = cv2.medianBlur(gray, 3)
# 针角圆心坐标
out_x = 0
out_y = 0
# 霍夫变换圆检测
circles = cv2.HoughCircles(img, cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, 10e10, param1=100, param2=30, minRadius=10, maxRadius=100)
# 如果没检测到会报错
# 这种判断方式过于简单
if circles is None:
print("没有检测到连接器外圆")
else:
for circle in circles[0]:
# 圆的基本信息
# print(circle[2])
# 坐标行列-圆心坐标
out_x = int(circle[0])
out_y = int(circle[1])
# 半径
r = int(circle[2])
# 在原图用指定颜色标记出圆的边界
cv2.circle(circle_img, (out_x, out_y), r, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# # 画出圆的圆心
cv2.circle(circle_img, (out_x, out_y), 3, (0, 255, 255), -1)
# 记录外圆坐标
out_xpoint = out_x
out_ypoint = out_y
# 只框出单个针角的位置区域
step_center = 30
step_rect = 60
out_x -= step_center
out_y -= step_center
needleRect = image[out_y: out_y + step_rect, out_x: out_x + step_rect]
# cv2.imshow("needleRect", needleRect)
# 根据检测到的圆形连接器中心找针角位置
centerPoint = needelCenter_detect(needleRect)
if len(centerPoint) == 0:
print("调整位置")
else:
# 将针角的坐标原还至原图
in_x = int(centerPoint[0].pt[0])
in_y = int(centerPoint[0].pt[1])
in_x += out_x
in_y += out_y
# 画出针角的圆心
cv2.circle(circle_img, (in_x, in_y), 3, (0, 255, 0), -1)
# 计算两者的距离
# 假设通过标定其一个像素代表0.0056mm
DPI = 0.00568
dis = math.sqrt(math.pow(out_xpoint - in_x,2) + math.pow(out_ypoint - in_y,2))
print("两者相互之间的距离为(mm):", dis*DPI)
cv2.imshow("image",circle_img)
cv2.waitKey(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# # 测试0 如果是小图 需要将检测程序中的cv2.waitKey(1)修改为cv2.waitKey()不然看到图片
# image = cv2.imread("images/CircleLinker/CLinker01.jpg")
# # cv2.imshow("show",image)
# # cv2.waitKey()
# roi = image
# circle_detect(roi)
# 测试1 从原图中换到连接器位置
image = cv2.imread("SingleImages/src/single.jpg")
# cv2.imshow("show",image)
# cv2.waitKey()
# 如何准确找到圆形连接器 ---》用yolo训练后能准备找到
roi = image[1800:2300, 1800:2300 ]
# cv2.imshow("show",roi)
# cv2.waitKey()
circle_detect(roi)
# # 测试2 如果是小图 需要将检测程序中的cv2.waitKey(1)修改为cv2.waitKey()不然看到图片
# image = cv2.imread("SingleImages/single04.jpg")
# # cv2.imshow("show",image)
# # cv2.waitKey()
# roi = image
# circle_detect(roi)
# # 测试3 检测文件夹下所有图片
# path = r"D:\BUFFER\Pycharm\ZhenJiaoDect\SingleImages"
# for filename in os.listdir(path): # listdir的参数是文件夹的路径
# filenames = path + '\\' + filename
# # print(filenames)
# img_orig = cv2.imread(filenames, 1)
# print(filenames)
#
# if img_orig is None:
# print("Warning: No Pictures")
# else:
# circle_detect(img_orig)
# # # 测试4 打开相机测试
# # 需要将检测程序中的cv2.waitKey()修改为cv2.waitKey(1)
# # 否则看到不视频实时检测结果
# capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
#
# while (True):
# # 获取一帧
# ret, frame = capture.read()
# circle_detect(frame)
#
# # cv2.imshow('frame', frame)
#
# if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):
# break加载全部内容