OpenCV车道线识别
獜洛橙 人气:0一、首先进行canny边缘检测,为获取车道线边缘做准备
import cv2
gray_img = cv2.imread('img.jpg',cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
canny_img = cv2.Canny(gray_img,50,100)
cv2.imwrite('canny_img.jpg',canny_img)
cv2.imshow('canny',canny_img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
二、进行ROI提取获取确切的车道线边缘(红色线内部)
方法:在图像中,黑色表示0,白色为1,那么要保留矩形内的白色线,就使用逻辑与,当然前提是图像矩形外也是0,那么就采用创建一个全0图像,然后在矩形内全1,之后与之前的canny图像进行与操作,即可得到需要的车道线边缘。

import cv2
import numpy as np
canny_img = cv2.imread('canny_img.jpg',cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
roi = np.zeros_like(canny_img)
roi = cv2.fillPoly(roi,np.array([[[0, 368],[300, 210], [340, 210], [640, 368]]]),color=255)
roi_img = cv2.bitwise_and(canny_img, roi)
cv2.imwrite('roi_img.jpg',roi_img)
cv2.imshow('roi_img',roi_img)
cv2.waitKey(0)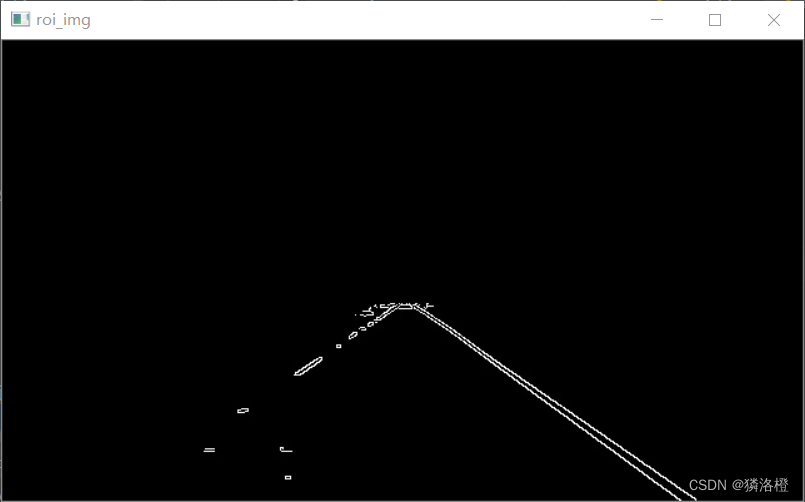
三、利用概率霍夫变换获取直线,并将斜率正数和复数的线段给分割开来
TIPs:使用霍夫变换需要将图像先二值化
概率霍夫变换函数:
- lines=cv2.HoughLinesP(image, rho,theta,threshold,minLineLength, maxLineGap)
- image:图像,必须是8位单通道二值图像
- rho:以像素为单位的距离r的精度,一般情况下是使用1
- theta:表示搜索可能的角度,使用的精度是np.pi/180
- threshold:阈值,该值越小,判定的直线越多,相反则直线越少
- minLineLength:默认为0,控制接受直线的最小长度
- maxLineGap:控制接受共线线段的最小间隔,如果两点间隔超过了参数,就认为两点不在同一直线上,默认为0
- lines:返回值由numpy.ndarray构成,每一对都是一对浮点数,表示线段的两个端点
import cv2
import numpy as np
#计算斜率
def calculate_slope(line):
x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2 = line[0]
return (y_2 - y_1) / (x_2 - x_1)
edge_img = cv2.imread('masked_edge_img.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
#霍夫变换获取所有线段
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(edge_img, 1, np.pi / 180, 15, minLineLength=40,
maxLineGap=20)
#利用斜率划分线段
left_lines = [line for line in lines if calculate_slope(line) < 0]
right_lines = [line for line in lines if calculate_slope(line) > 0]四、离群值过滤,剔除斜率相差过大的线段
流程:
- 获取所有的线段的斜率,然后计算斜率的平均值
- 遍历所有斜率,计算和平均斜率的差值,寻找最大的那个斜率对应的直线,如果差值大于阈值,那么就从列表中剔除对应的线段和斜率
- 循环执行操作,直到剩下的全部都是小于阈值的线段
def reject_abnormal_lines(lines, threshold):
slopes = [calculate_slope(line) for line in lines]
while len(lines) > 0:
mean = np.mean(slopes)
diff = [abs(s - mean) for s in slopes]
idx = np.argmax(diff)
if diff[idx] > threshold:
slopes.pop(idx)
lines.pop(idx)
else:
break
return lines
reject_abnormal_lines(left_lines, threshold=0.2)
reject_abnormal_lines(right_lines, threshold=0.2)五、最小二乘拟合,实现将左边和右边的线段互相拟合成一条直线,形成车道线
流程:
- 取出所有的直线的x和y坐标,组成列表,利用np.ravel进行将高维转一维数组
- 利用np.polyfit进行直线的拟合,最终得到拟合后的直线的斜率和截距,类似y=kx+b的(k,b)
- 最终要返回(x_min,y_min,x_max,y_max)的一个np.array的数据,那么就是用np.polyval求多项式的值,举个example,np.polyval([3,0,1], 5) # 3 * 5**2 + 0 * 5**1 + 1,即可以获得对应x坐标的y坐标。
def least_squares_fit(lines):
# 1. 取出所有坐标点
x_coords = np.ravel([[line[0][0], line[0][2]] for line in lines])
y_coords = np.ravel([[line[0][1], line[0][3]] for line in lines])
# 2. 进行直线拟合.得到多项式系数
poly = np.polyfit(x_coords, y_coords, deg=1)
print(poly)
# 3. 根据多项式系数,计算两个直线上的点,用于唯一确定这条直线
point_min = (np.min(x_coords), np.polyval(poly, np.min(x_coords)))
point_max = (np.max(x_coords), np.polyval(poly, np.max(x_coords)))
return np.array([point_min, point_max], dtype=np.int)
print("left lane")
print(least_squares_fit(left_lines))
print("right lane")
print(least_squares_fit(right_lines))六、绘制线段

cv2.line(img, tuple(left_line[0]), tuple(left_line[1]), color=(0, 255, 255), thickness=5) cv2.line(img, tuple(right_line[0]), tuple(right_line[1]), color=(0, 255, 255), thickness=5)
全部代码(视频显示)
import cv2
import numpy as np
def get_edge_img(color_img, gaussian_ksize=5, gaussian_sigmax=1,
canny_threshold1=50, canny_threshold2=100):
"""
灰度化,模糊,canny变换,提取边缘
:param color_img: 彩色图,channels=3
"""
gaussian = cv2.GaussianBlur(color_img, (gaussian_ksize, gaussian_ksize),
gaussian_sigmax)
gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(gaussian, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
edges_img = cv2.Canny(gray_img, canny_threshold1, canny_threshold2)
return edges_img
def roi_mask(gray_img):
"""
对gray_img进行掩膜
:param gray_img: 灰度图,channels=1
"""
poly_pts = np.array([[[0, 368], [300, 210], [340, 210], [640, 368]]])
mask = np.zeros_like(gray_img)
mask = cv2.fillPoly(mask, pts=poly_pts, color=255)
img_mask = cv2.bitwise_and(gray_img, mask)
return img_mask
def get_lines(edge_img):
"""
获取edge_img中的所有线段
:param edge_img: 标记边缘的灰度图
"""
def calculate_slope(line):
"""
计算线段line的斜率
:param line: np.array([[x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2]])
:return:
"""
x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2 = line[0]
return (y_2 - y_1) / (x_2 - x_1)
def reject_abnormal_lines(lines, threshold=0.2):
"""
剔除斜率不一致的线段
:param lines: 线段集合, [np.array([[x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2]]),np.array([[x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2]]),...,np.array([[x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2]])]
"""
slopes = [calculate_slope(line) for line in lines]
while len(lines) > 0:
mean = np.mean(slopes)
diff = [abs(s - mean) for s in slopes]
idx = np.argmax(diff)
if diff[idx] > threshold:
slopes.pop(idx)
lines.pop(idx)
else:
break
return lines
def least_squares_fit(lines):
"""
将lines中的线段拟合成一条线段
:param lines: 线段集合, [np.array([[x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2]]),np.array([[x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2]]),...,np.array([[x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2]])]
:return: 线段上的两点,np.array([[xmin, ymin], [xmax, ymax]])
"""
x_coords = np.ravel([[line[0][0], line[0][2]] for line in lines])
y_coords = np.ravel([[line[0][1], line[0][3]] for line in lines])
poly = np.polyfit(x_coords, y_coords, deg=1)
point_min = (np.min(x_coords), np.polyval(poly, np.min(x_coords)))
point_max = (np.max(x_coords), np.polyval(poly, np.max(x_coords)))
return np.array([point_min, point_max], dtype=np.int)
# 获取所有线段
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(edge_img, 1, np.pi / 180, 15, minLineLength=40,
maxLineGap=20)
# 按照斜率分成车道线
left_lines = [line for line in lines if calculate_slope(line) > 0]
right_lines = [line for line in lines if calculate_slope(line) < 0]
# 剔除离群线段
left_lines = reject_abnormal_lines(left_lines)
right_lines = reject_abnormal_lines(right_lines)
return least_squares_fit(left_lines), least_squares_fit(right_lines)
def draw_lines(img, lines):
left_line, right_line = lines
cv2.line(img, tuple(left_line[0]), tuple(left_line[1]), color=(0, 255, 255),
thickness=5)
cv2.line(img, tuple(right_line[0]), tuple(right_line[1]),
color=(0, 255, 255), thickness=5)
def show_lane(color_img):
edge_img = get_edge_img(color_img)
mask_gray_img = roi_mask(edge_img)
lines = get_lines(mask_gray_img)
draw_lines(color_img, lines)
return color_img
capture = cv2.VideoCapture('video.mp4')
while True:
ret, frame = capture.read()
if not ret:
break
frame = show_lane(frame)
cv2.imshow('frame', frame)
cv2.waitKey(10)总结
加载全部内容