Java ArrayList
niuyongzhi 人气:01.ArrayList 是基数组结构的,需要连续的内存空间
从构造函数可以看出,ArrayList内部用一个Object数组来保存数据。
对于无参构造,ArrayList会创建一个大小为10的初始数组,第一次扩容时会创建默认大小数组。
//无参构造函数,会构造一个空数组。第一次扩容时会创默认大小为10的数组
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
transient Object[] elementData;
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
//如果给定集合大小,会创建一个对应大小的数组
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}2.对于set和get方法ArrayList效率高,因为可以直接通过下标获取存储对象。
//直接通过角标从数组中取出元素
public E get(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
return (E) elementData[index];
}
//set 方法,直接通过index 拿到元素,进行修改就行。
public E set(int index, E element) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
E oldValue = (E) elementData[index];
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}3.对于add方法,有两种情况:
第一种是在尾部添加,不需要移动数组。
//Add 方法 ,在末端插入不需要
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}第二种情况在指定位置添加或插入数据,则需要移动数组,效率比较低。如果插入在第0个位置则需要移动整个数组。
public void add(int index, E element) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//被插入的元素在index。则移动的数组应该从index开始,向后移动一个,
//移动的数组长度 size-index 从index开始的数组长度
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}在add时还需要考虑到数组的扩容问题,看ensureCapacityInternal方法
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
//通过无参构造创建为设置初始大小时,判断条件为true
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
//创建默认大小的数组,初始大小是10
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}添加元素后,元素数量大于数组长度时,进行扩容grow,扩容大小是原数组的1.5倍
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
//新增后,数组容量已经大于了数组长度,则进行扩容
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//新的数组大小是原来的1.5倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
//创建一个新长度的数组。
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}4.对应remove 删除元素操作。如果删除元素在最后一个,不需要移动数组,否则会将被删除元素之后的所有元素都要向前移动,效率比较低。
//删除
public E remove(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
modCount++;
//取出被删除的元素
E oldValue = (E) elementData[index];
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
//移动的数组长度,大于0才需要移动,小于0说明被删元素在最后一个
if (numMoved > 0)
//第一个参数是源数组,
//第二个参数是移动的起始位置:index+1,从被删元素的后一个位置开始
//第三个参数是目标数组
//第四个参数是移动目标位置:index,被删除元素的位置
//第五个参数是移动的数组长度 size - index - 1,从index+1位置开始之后的数组长度
//最终会调用到native方法进行移动。
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}5.System.arraycopy方法参数分析。
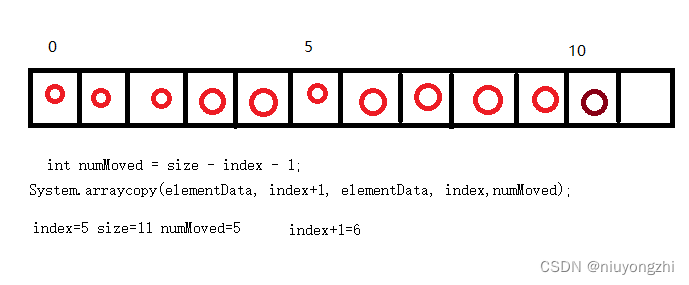
第二个参数 index+1是被移动数组的起始位置,即被删元素后一个位置
第四个参数index,是被移动数组的起始位置,即被删元素的位置。
最后一个参数size-index-1,被移动数组的长度,即被删元素后一个位置到元素末尾的长度
public static native void arraycopy(java.lang.Object src, int srcPos, java.lang.Object dest, int destPos, int length);
通过对源码的阅读,也许会对ArrayList有一个更加直接的了解。
加载全部内容