Maven依赖管理
mzz124 人气:0一、依赖传递
1. 直接依赖与间接依赖
pom.xml 声明了的依赖是直接依赖,依赖中又包含的依赖就是间接依赖(直接依赖的直接依赖),间接依赖虽然未被声明,但也是依赖所必须的依赖,同时间接依赖中的资源也可以直接使用
比如 A 依赖了 B,B 依赖了 C,那么 A 也就间接的依赖了 C,如果没有 C,那么 A 和 B 都无法正常运行,A 也可以直接使用 C 的内容,而可以不必再声明 C
实例如 spring-webmvc:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version> </dependency>
学习 Spring 时需要导入 spring-context 依赖,但学习 SpringMVC 时,我们会导入 spring-webmvc,此时即便会用到 Spring 的功能也无需再导入 spring-context。因为 spring-webmvc 依赖了 spring-context,spring-context 作为间接依赖被引入到了项目中,可以直接使用

2. 依赖传递冲突时的优先规则
假如一个项目中或直接或间接的多次导入了同一个依赖,就会产生依赖冲突,此时 Maven 会按照下面三种优先规则确定真正依赖的是哪个包:(主要讨论不同版本的依赖,相同版本没什么所谓)
(1) 路径优先
直接依赖优先级最高,其次是间接依赖,然后是间接依赖的直接依赖,间接依赖的间接依赖 ……
层级越深,优先级越低,或者说就近原则,离项目最近的包就是项目真正所依赖的
如下例:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.1.19.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
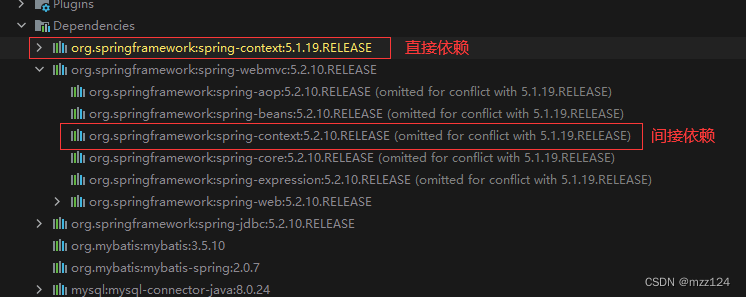
示例中引入了 spring-context 5.1.19 为直接依赖,又引入 spring-webmvc 5.2.10,其中又依赖了 spring-context 5.2.10,但它是间接依赖,所以项目中所使用的 spring-context 资源是 5.1.19 版本的(但并不代表 webmvc 中的 context 版本也被改为了 5.1.19),图中也可以看到 IDEA 在依赖后边给出了冲突标识
(2) 声明优先
相同层级的依赖资源,先被声明的优先
如下例:(和刚才的一样)
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.1.19.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
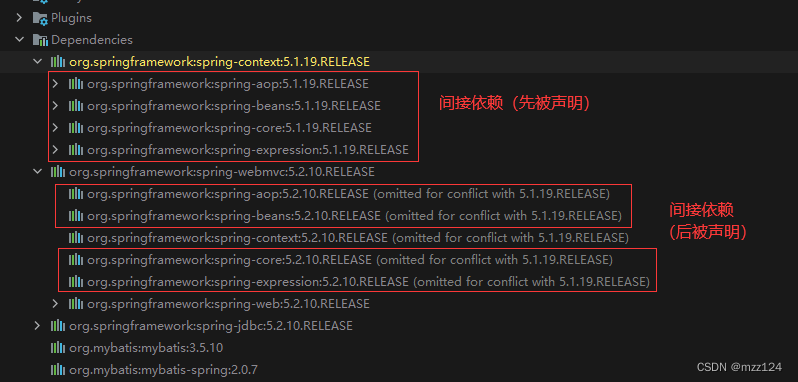
和上面一样导入 spring-context 5.1.19 和 spring-webmvc 5.2.10,可以看到 context 和 webmvc 都又依赖了 aop, beans, core 等几个包,且都是间接依赖,层级相等,但由于先声明的 context 5.1.19,所以其中的 aop, core 等几个包的优先级更高
(3) 后声明覆盖先声明
同时声明了同一个依赖的不同版本,那么先声明的版本会被最后声明的版本覆盖掉(以最后一次声明为准)
如下例:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.1.19.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version> </dependency> </dependencies>

先声明 spring-context 5.1.19,又声明了 spring-context 5.2.10,最后使用的依赖版本为 5.2.10
二、依赖管理
分模块开发时,合理的管理依赖能够避免掉依赖冲突可能带来的麻烦。
1. 可选依赖
用于对外隐藏本项目中使用的依赖。如果项目中将某个依赖设置为可选依赖,那么其他项目引用此项目时不会加载到可选依赖。
只需在声明依赖时加入 optional 标签,设置值为 true 即可(默认为 false)
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.1.19.RELEASE</version> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>
如上设置后,其他项目引入此项目时,不会加载到此项目中的 spring-context 5.1.19
2. 排除依赖
引入依赖时,用于排除掉该依赖中传递来的指定依赖。
需要在声明依赖时加入 exclusions 标签,内含多个 exclusion,设置 要排除的依赖坐标,不必指定版本
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>如上设置后,本项目不会加载 spring-webmvc 依赖中包含的 spring-aop 和 spring-core
3. 可选依赖与排除依赖的异同点
相同点:
- 功能相同:都用于阻断依赖的传递
不同点:
- 原理不同:可选依赖对外不透明,排除依赖有传递但不采用
- 生效时机不同:可选依赖生效在项目被引入时,排除依赖生效在引入其他项目时
加载全部内容