ahooks useVirtualList封装
Gopal 人气:0简介
提供虚拟化列表能力的 Hook,用于解决展示海量数据渲染时首屏渲染缓慢和滚动卡顿问题。
实现原理
其实现原理监听外部容器的 scroll 事件以及其 size 发生变化的时候,触发计算逻辑算出内部容器的高度和 marginTop 值。
具体实现
其监听滚动逻辑如下:
// 当外部容器的 size 发生变化的时候,触发计算逻辑
useEffect(() => {
if (!size?.width || !size?.height) {
return;
}
// 重新计算逻辑
calculateRange();
}, [size?.width, size?.height, list]);
// 监听外部容器的 scroll 事件
useEventListener(
'scroll',
e => {
// 如果是直接跳转,则不需要重新计算
if (scrollTriggerByScrollToFunc.current) {
scrollTriggerByScrollToFunc.current = false;
return;
}
e.preventDefault();
// 计算
calculateRange();
},
{
// 外部容器
target: containerTarget,
},
);其中 calculateRange 非常重要,它基本实现了虚拟滚动的主流程逻辑,其主要做了以下的事情:
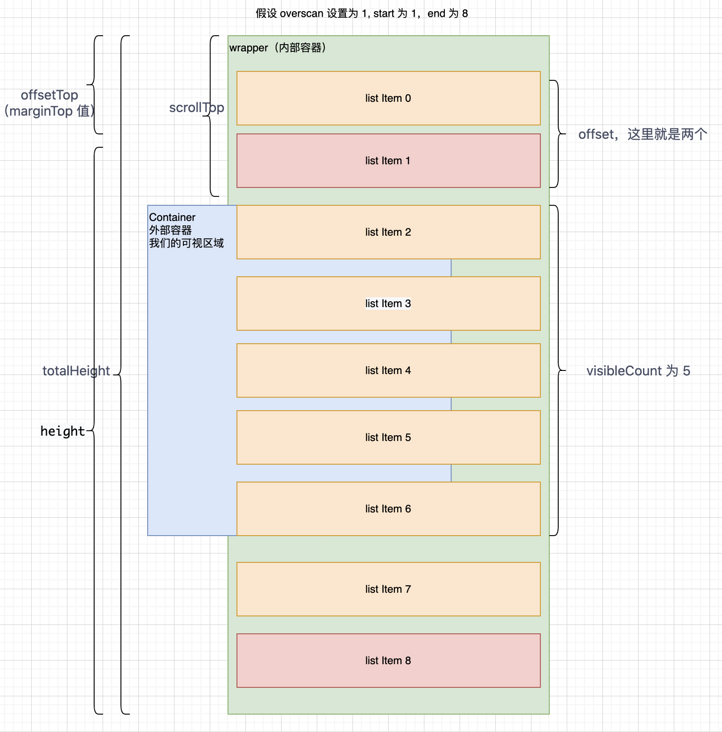
- 获取到整个内部容器的高度 totalHeight。
- 根据外部容器的 scrollTop 算出已经“滚过”多少项,值为 offset。
- 根据外部容器高度以及当前的开始索引,获取到外部容器能承载的个数 visibleCount。
- 并根据 overscan(视区上、下额外展示的 DOM 节点数量)计算出开始索引(start)和(end)。
- 根据开始索引获取到其距离最开始的距离(offsetTop)。
- 最后根据 offsetTop 和 totalHeight 设置内部容器的高度和 marginTop 值。
变量很多,可以结合下图,会比较清晰理解:
代码如下:
// 计算范围,由哪个开始,哪个结束
const calculateRange = () => {
// 获取外部和内部容器
// 外部容器
const container = getTargetElement(containerTarget);
// 内部容器
const wrapper = getTargetElement(wrapperTarget);
if (container && wrapper) {
const {
// 滚动距离顶部的距离。设置或获取位于对象最顶端和窗口中可见内容的最顶端之间的距离
scrollTop,
// 内容可视区域的高度
clientHeight,
} = container;
// 根据外部容器的 scrollTop 算出已经“滚过”多少项
const offset = getOffset(scrollTop);
// 可视区域的 DOM 个数
const visibleCount = getVisibleCount(clientHeight, offset);
// 开始的下标
const start = Math.max(0, offset - overscan);
// 结束的下标
const end = Math.min(list.length, offset + visibleCount + overscan);
// 获取上方高度
const offsetTop = getDistanceTop(start);
// 设置内部容器的高度,总的高度 - 上方高度
// @ts-ignore
wrapper.style.height = totalHeight - offsetTop + 'px';
// margin top 为上方高度
// @ts-ignore
wrapper.style.marginTop = offsetTop + 'px';
// 设置最后显示的 List
setTargetList(
list.slice(start, end).map((ele, index) => ({
data: ele,
index: index + start,
})),
);
}
};其它就是这个函数的辅助函数了,包括:
- 根据外部容器以及内部每一项的高度,计算出可视区域内的数量:
// 根据外部容器以及内部每一项的高度,计算出可视区域内的数量
const getVisibleCount = (containerHeight: number, fromIndex: number) => {
// 知道每一行的高度 - number 类型,则根据容器计算
if (isNumber(itemHeightRef.current)) {
return Math.ceil(containerHeight / itemHeightRef.current);
}
// 动态指定每个元素的高度情况
let sum = 0;
let endIndex = 0;
for (let i = fromIndex; i < list.length; i++) {
// 计算每一个 Item 的高度
const height = itemHeightRef.current(i, list[i]);
sum += height;
endIndex = i;
// 大于容器宽度的时候,停止
if (sum >= containerHeight) {
break;
}
}
// 最后一个的下标减去开始一个的下标
return endIndex - fromIndex;
};- 根据 scrollTop 计算上面有多少个 DOM 节点:
// 根据 scrollTop 计算上面有多少个 DOM 节点
const getOffset = (scrollTop: number) => {
// 每一项固定高度
if (isNumber(itemHeightRef.current)) {
return Math.floor(scrollTop / itemHeightRef.current) + 1;
}
// 动态指定每个元素的高度情况
let sum = 0;
let offset = 0;
// 从 0 开始
for (let i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
const height = itemHeightRef.current(i, list[i]);
sum += height;
if (sum >= scrollTop) {
offset = i;
break;
}
}
// 满足要求的最后一个 + 1
return offset + 1;
};- 获取上部高度:
// 获取上部高度
const getDistanceTop = (index: number) => {
// 每一项高度相同
if (isNumber(itemHeightRef.current)) {
const height = index * itemHeightRef.current;
return height;
}
// 动态指定每个元素的高度情况,则 itemHeightRef.current 为函数
const height = list
.slice(0, index)
// reduce 计算总和
// @ts-ignore
.reduce((sum, _, i) => sum + itemHeightRef.current(i, list[index]), 0);
return height;
};- 计算总的高度:
// 计算总的高度
const totalHeight = useMemo(() => {
// 每一项高度相同
if (isNumber(itemHeightRef.current)) {
return list.length * itemHeightRef.current;
}
// 动态指定每个元素的高度情况
// @ts-ignore
return list.reduce(
(sum, _, index) => sum + itemHeightRef.current(index, list[index]),
0,
);
}, [list]);最后暴露一个滚动到指定的 index 的函数,其主要是计算出该 index 距离顶部的高度 scrollTop,设置给外部容器。并触发 calculateRange 函数。
// 滚动到指定的 index
const scrollTo = (index: number) => {
const container = getTargetElement(containerTarget);
if (container) {
scrollTriggerByScrollToFunc.current = true;
// 滚动
container.scrollTop = getDistanceTop(index);
calculateRange();
}
};思考总结
对于高度相对比较确定的情况,我们做虚拟滚动还是相对简单的,但假如高度不确定呢?
或者换另外一个角度,当我们的滚动不是纵向的时候,而是横向,该如何处理呢?
加载全部内容