c++ sort排序
爱钻研的小铭 人气:01. 引言
在C++中,sort()函数常常用来对容器内的元素进行排序,先来了解一下sort()函数。
sort()函数有三个参数:
- 第一个是要排序的容器的起始迭代器。
- 第二个是要排序的容器的结束迭代器。
- 第三个参数是排序的方法,是可选的参数。默认的排序方法是从小到大排序,也就是
less<Type>(),还提供了greater<Type>()进行从大到小排序。这个参数的类型是函数指针,less和greater实际上都是类/结构体,内部分别重载了()运算符,称为仿函数,所以实际上less<Type>()和greater<Type>()都是函数名,也就是函数指针。我们还可以用普通函数来定义排序方法。
如果容器内元素的类型是内置类型或string类型,我们可以直接用less<Type>()或greater<Type>()进行排序。但是如果数据类型是我们自定义的结构体或者类的话,我们需要自定义排序函数,
有三种写法:
- 重载 < 或 > 运算符:重载
<运算符,传入less<Type>()进行升序排列。重载>运算符,传入greater<Type>()进行降序排列。这种方法只能针对一个维度排序,不灵活。 - 普通函数:写普通函数cmp,传入
cmp按照指定规则排列。这种方法可以对多个维度排序,更灵活。 - 仿函数:写仿函数cmp,传入
cmp<Type>()按照指定规则排列。这种方法可以对多个维度排序,更灵活。
2. 自定义排序规则
2.1 重写 < 或 > 运算符
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Person {
int id;
int age;
Person(int id,int age):id(id),age(age){}
//重载<运算符,进行升序排列
bool operator < (const Person& p2) const {
return id < p2.id;
}
//重载>运算符,进行降序排列
bool operator > (const Person& p2) const {
return id > p2.id;
}
};
int main()
{
Person p1(1, 10), p2(2, 20), p3(3, 30);
vector<Person> ps;
ps.push_back(p2);
ps.push_back(p1);
ps.push_back(p3);
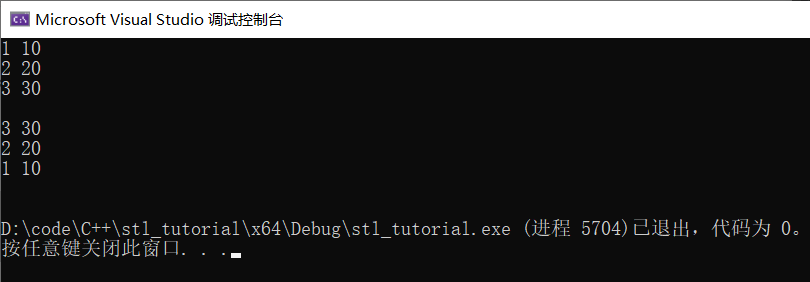
sort(ps.begin(), ps.end(), less<Person>());
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
cout << ps[i].id << " " << ps[i].age << endl;
}
cout << endl;
sort(ps.begin(), ps.end(), greater<Person>());
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
cout << ps[i].id << " " << ps[i].age << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
2.2 普通函数
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Person {
int id;
int age;
Person(int id,int age):id(id),age(age){}
};
//普通函数
bool cmp(const Person& p1, const Person& p2) {
if (p1.id == p2.id) return p1.age >= p2.age;
return p1.id < p2.id;
}
int main()
{
Person p1(1, 10), p2(2, 20), p3(3, 30), p4(3, 40);
vector<Person> ps;
ps.push_back(p2);
ps.push_back(p1);
ps.push_back(p3);
ps.push_back(p4);
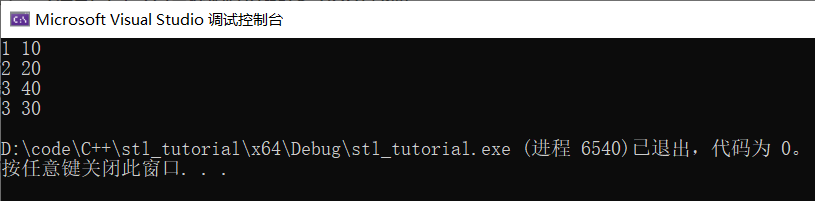
sort(ps.begin(), ps.end(), cmp);//传入函数指针cmp
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
cout << ps[i].id << " " << ps[i].age << endl;
}
}
2.3 仿函数
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Person {
int id;
int age;
Person(int id, int age) :id(id), age(age) {}
};
//仿函数
struct cmp {
bool operator()(const Person& p1, const Person& p2) {
if (p1.id == p2.id) return p1.age >= p2.age;
return p1.id < p2.id;
}
};
int main()
{
Person p1(1, 10), p2(2, 20), p3(3, 30), p4(3, 40);
vector<Person> ps;
ps.push_back(p2);
ps.push_back(p1);
ps.push_back(p3);
ps.push_back(p4);
sort(ps.begin(), ps.end(), cmp()); //传入函数指针cmp()
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
cout << ps[i].id << " " << ps[i].age << endl;
}
}
加载全部内容