C# 迭代器,索引器
人气:01、迭代器
- 迭代器(iterator)解决的是集合访问的问题,提供一种方法顺序访问一个集合对象中的各个元素,而不暴露对象内部标识。迭代器还有一个别名:游标(cursor)
- foreach语句与迭代器的关系:Foreach循环语句可以用来迭代枚举的集合中的所有元素,又称foreach迭代语句
- 可枚举的:C#中,如果某个类型继承了接口IEnumerable,或者继承了泛型接口IEnumerable或者继承了泛型接口IEnumerable的任何构造类型,那么久成这个类型时可枚举的
- 常见的可枚举类型:集合,数组,字符串类String,标识动态列表的泛型类List等

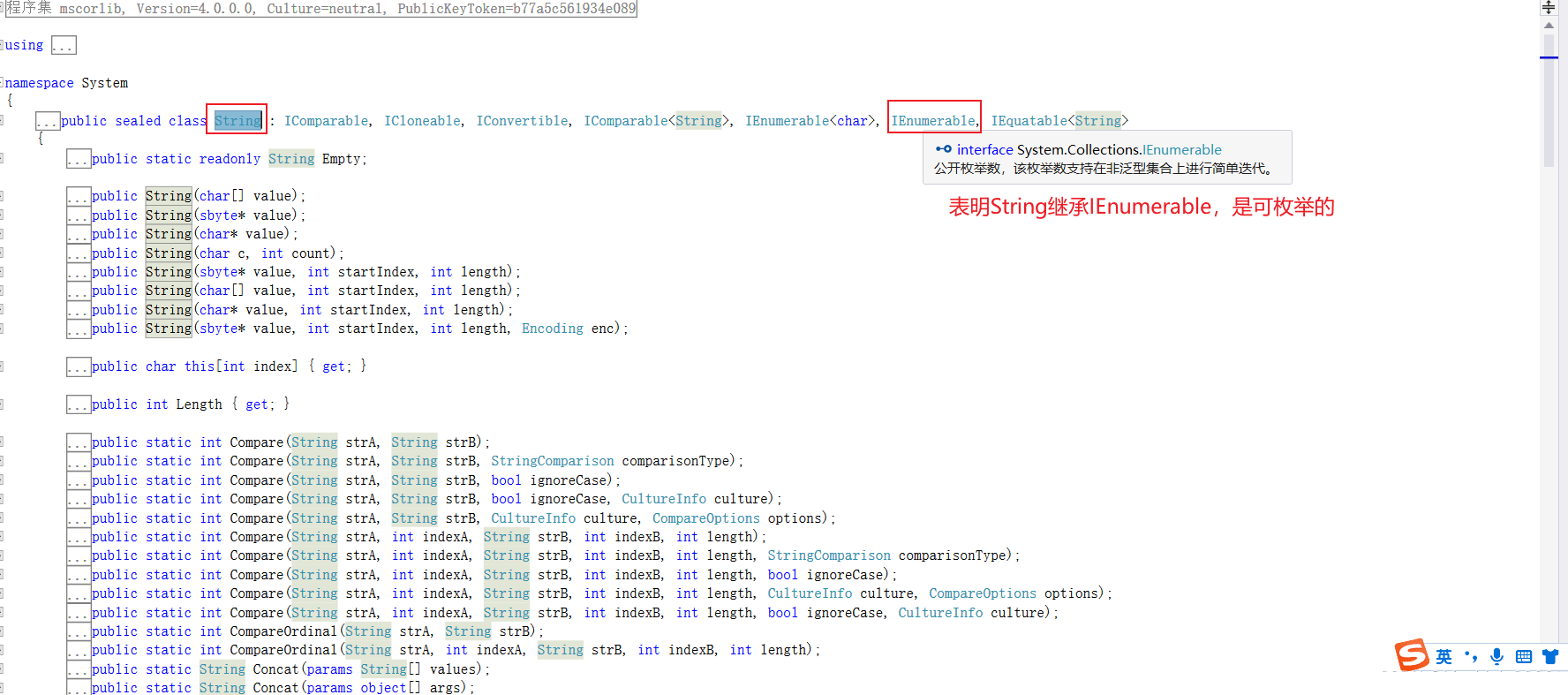
- Foreach语句可以简化C#内置迭代器的使用复杂性,编译froeach语句,会生成调用GetEnumerator和MoveNext方法以及Current属性的代码,这些方法和属性恰是C#内置迭代器所提供的。
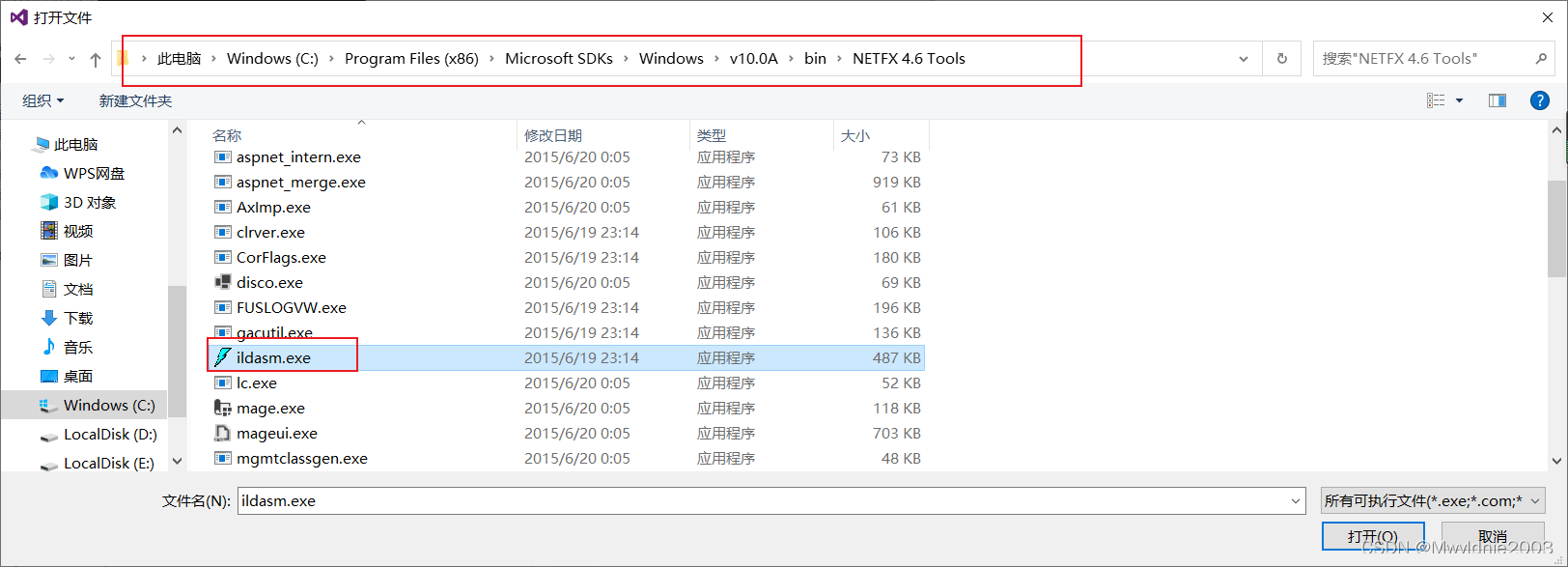
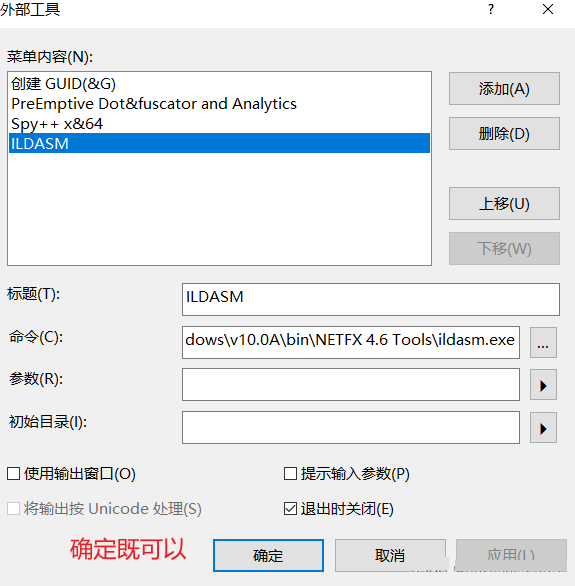
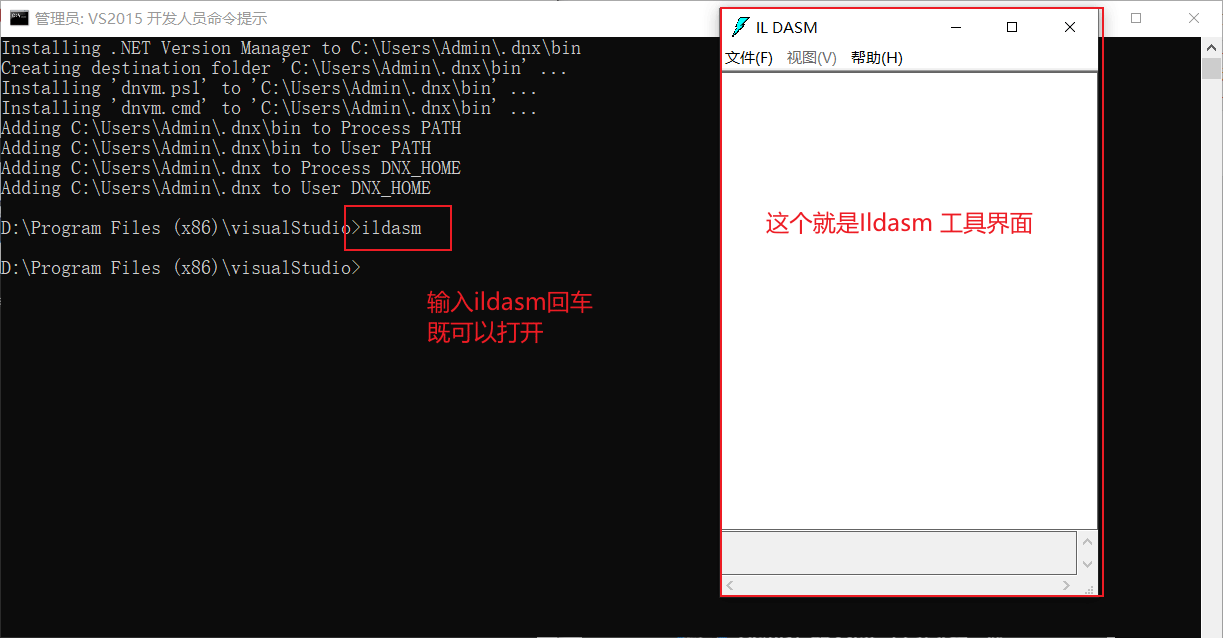
- ILDASM外部工具的添加方法(中间语言反汇编的工具)
方法1:
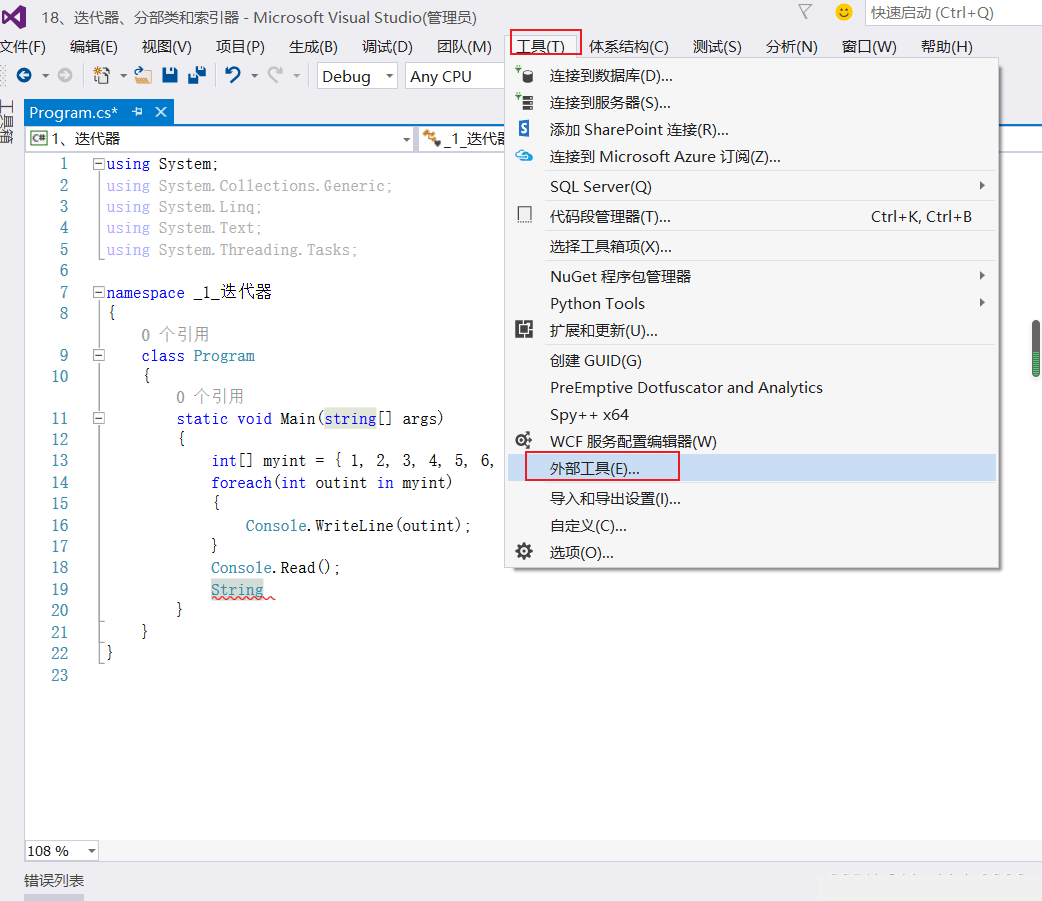
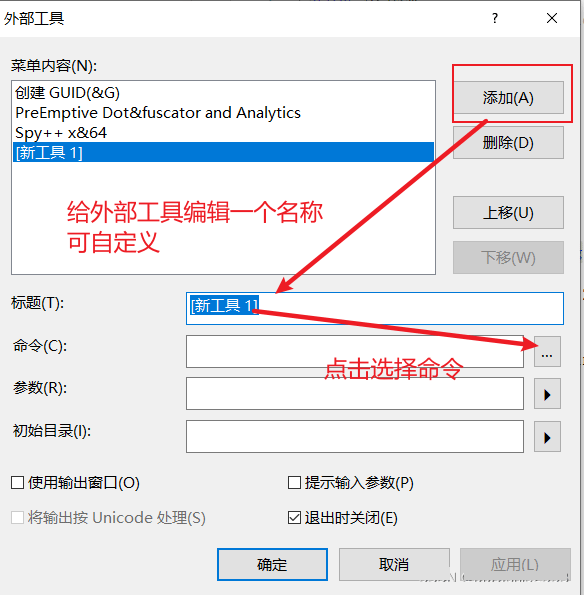
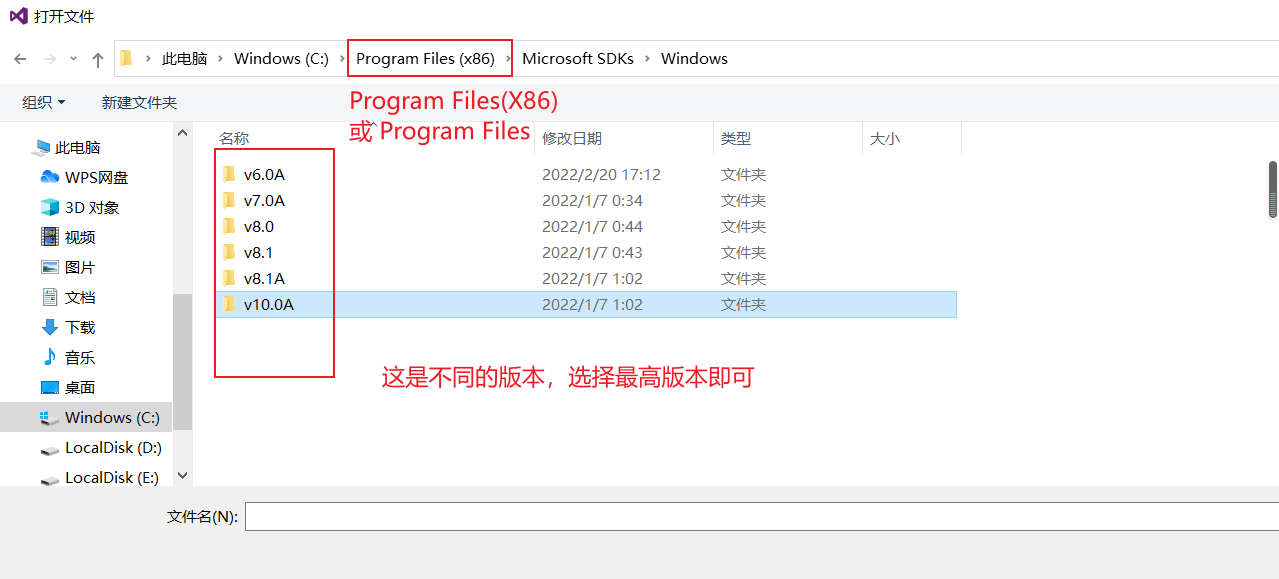
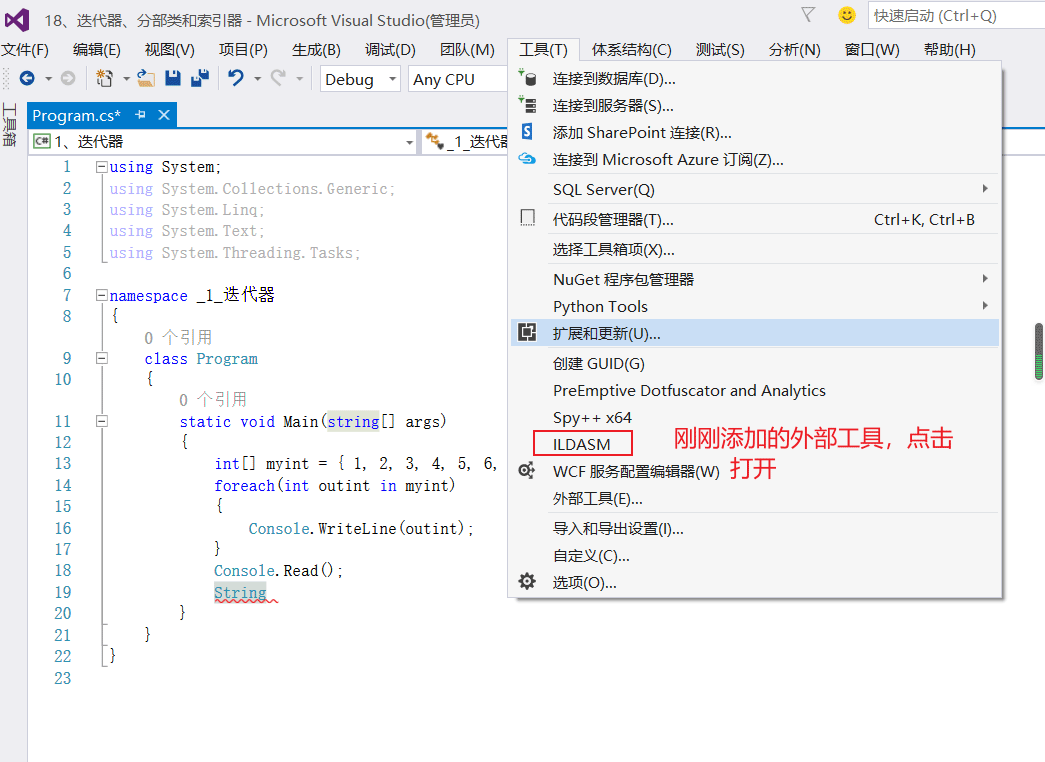
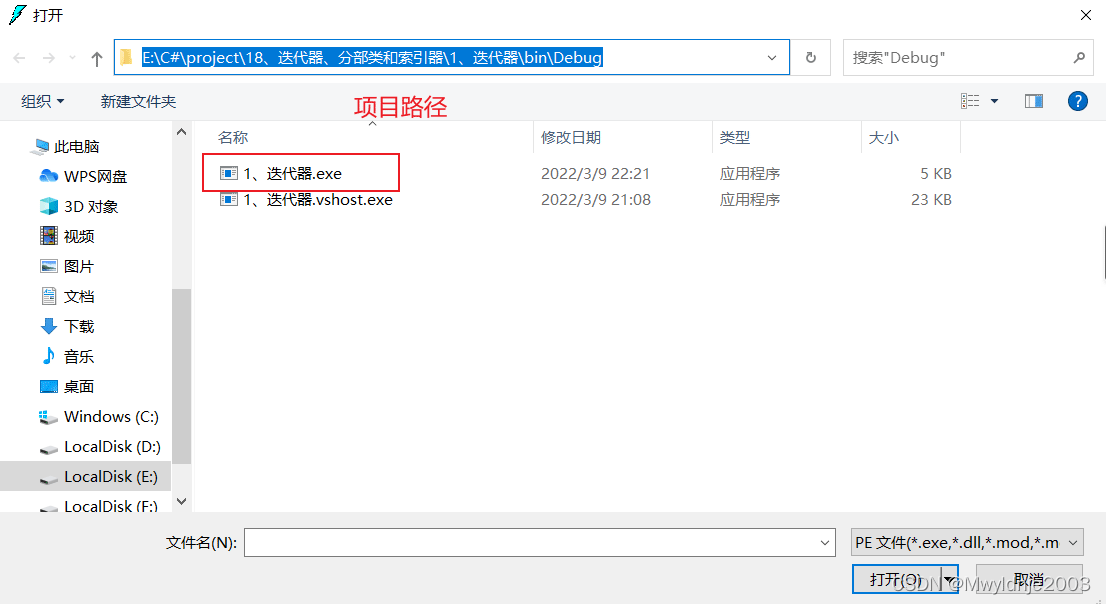
打开新添加的外部工具:
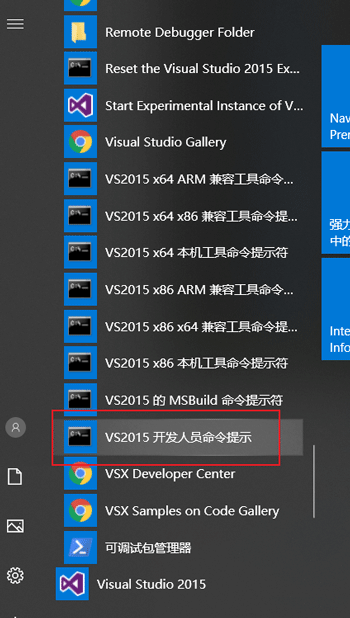
方法2
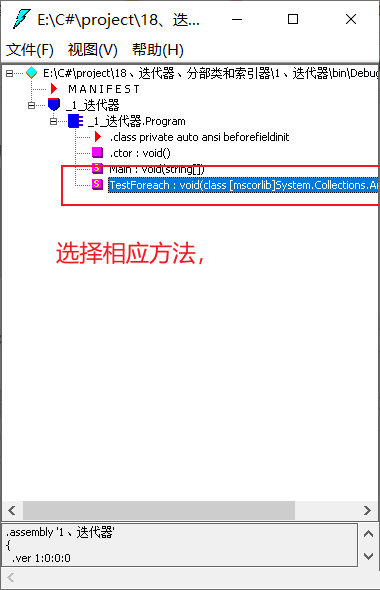
查看Foreach执行中间语言
- 中间语言:intermediate language
- ILDASM: intermediate language decompile assembly

foreach实现过程总结
foreach语句是微软提供的支持内置迭代器的语句法糖,编译foreach语句后生产的代码与使用迭代器的代码完全一致
调用GetEnumerator()方法获得迭代器——调用IEnumerator.MoveNext()——调用IEnumerator.Current()
Foreach循环迭代可枚举类型的过程:
1、通过调用IEnumerator接口和IEnumerator的引用
2、IEnuerator调用MoveNext方法
3) ①True:IEnumerator的Current属性获取对象的应用,用于foreach循环
②false 结束
4、重复2、3步知道MoveNext返回false
实现迭代器最常用的方法
迭代器可用于方法、属性访问器或其他代码块,使用户能够在类或结构中支持Foreach迭代,而不必实现整个IEnumerable接口,只需要一个类型化的方法GetEnumerator(),不需要处理设计模式
- 迭代器是C#可以提供的最简单的设计模式。
- 设计模式(Design pattern/behavorial pattern)是一套被反复使用、多数人知晓的、经过分类编目的、典卖设计经验总结。使用设计模式是为了可重用代码、让代码更容易被他人理解、保证代码可靠性。
- .Net Framework有自己的IEnumerator接口,使用的迭代器的作用很明确,及可以做到不暴露集合的内部接口,又可让外部代码同名地方访问集合内部的数据。 2.1 创建迭代器最常用的方法 是对IEnumerable接口实现GetEnumerator方法创建最简单的迭代块说明:迭代器返回值类型必须为IEnumerable(迭代类成员)和IEnumerator(迭代类)一个迭代器会出现一个或者多个yield语句,与一般语句块的区别:yield return 一次返回迭代的下一个袁旭yield break 指出这个迭代的结束
```csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Collections; // 需要引用的命名空间
namespace 实现迭代器常用的方法
{
class Program
{
public static IEnumerable SimpleDemo()
{
yield return "string1";
yield return "string2";
yield return "string3";
yield break; //运行到此处就终止了迭代
yield return "string4";
yield return "string5";
}
//月份迭代
public class Months : IEnumerable //为了使用Foreach遍历,要保证是可枚举类型的
{
string[] month = { "Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "Apr", "May", "June", "July", "Aug", "Nov", "Dec" };
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
for(int i=0;i<month.Length;i++)
{
yield return month[i];
}
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
foreach (string item in SimpleDemo())
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
Months mon = new Months();
foreach(string m in mon)
{
Console.WriteLine(m);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
分布类概述及其使用
分布类定义:将类的定义拆分到两个或多个资源文件中。每个源文件包含类定义的一部分,编译应用程序时将把所有部分组合起来,这就是分布类。
应用场合(partial):
- 处理大型项目时,使一个类分布于多个独立文件中,可以让多位程序员同时对该类进行处理;
- 使用自动生成的源时,无需重新创建源文件便可将代码添加到类中。
vs在创建windows窗体和web服务包装代码等时都是用此方法。开发人员无须编译vs所创建的文件,即可创建使用这些类的代码。
实现过程:
- 通过多个部分来定义一个类
- partial关键字:必须直接放在class的前面
- 分部类声明的每个部分都必须包含partial修饰符,并且器声明必须与其他部分位于同一命名空间。
- partial修饰符说明在其他位置可能还有同一个类型声明的其他部分。但是这些其他部分并非必须存在:如果只有一个类型声明,包含partial修饰符也是有效的。
- 当分部类声明指定了可访问性(借助访问修饰符:public、protected、internal private)时,它必须与其他部分所指定的可访问性一致。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _3_分部类
{
//利用分部类实现阶乘与幂指数运算
partial class arithmetic //阶乘
{
public int factorial(int num)
{
int factorialval = 1;
for(int i = num; i>0;i--)
{
factorialval *= i;
}
return factorialval;
}
}
partial class arithmetic //幂指数运算
{
public int power(int num, int index)
{
int result = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
{
result *= num;
}
return result;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
arithmetic a = new arithmetic();
int num = 5;
Console.WriteLine("调用分部类的第一部分——阶乘计算结果:{0}", a.factorial(num));
int index = 3;
Console.WriteLine("调用分部类的第二部分——幂指函数计算结果:{0}", a.power(num, index));
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}注意事项 :
- 分部类时,同一个类型各个部分的所有分部类类型定义都必须使用partial进行修饰,必须具有相同的可访问性。
- 同一个类型的各个部分的所有分部类型定义都必须在同一程序集合同一模块中进行定义。分部类定义不能跨越多个模块。
- 使用partial关键字表明可在命名空间内定义该类、结构或接口的其他部分,各个部分可以指定不同的基接口,最终类型将实现,所有分部声明所列出的全部接口。
索引器概述及声明
可以通过小标访问数组中的元素的方式就是索引器
索引器允许类或结构的实例按照与数组相同的方式进行索引。索引器的声明和属性的声明非常相似,不同的是他们的访问器采用参数——索引器的声明除了包括索引关键字(index)的声明外,还包括this关键字。使得向数组那样对对象使用下标,并提供了通过索引方式方便第访问类的数据信息的方法。(属性的作用就是保护字段,对字段的取值和赋值进行限定)
- 虚拟索引器:virtual
- 外部索引器:extern 因为外部索引器声明不提供任何实际的实现,所以他的每个访问器生摩纳哥都由一个分号组成。
- 抽象索引器:abstract 当要定义为抽象索引器时,必须提供空的get和set,必须在抽象类中声明抽象索引器
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _4_索引器概述及声明
{
//属性声明
public class Clerk
{
private string name; //字段声明,专供类内部使用,所以声明为私有的
public string Name //属性为外部事务,可以供其他类进行交流使用,所以声明为公共的
{
get { return name; }
set { name = value; }
}
private char gender;
public char Gender
{
get
{
if (gender != '男' && gender != '女') gender = '男';
return gender;
}
set
{
gender = value;
}
}
//索引器声明1
//private int[] myint = new int[10];
//public int this[int index]
//{
// get { return myint[index]; } //单独存在为只读
// set { myint[index] = value; } //单独存在为只写 ,两个同时存在为读写
//}
//声明一个虚拟的索引器
//private int[] myint2 = new int[10];
//public virtual int this[int index2]
//{
// get { return myint2[index2]; }
// set { myint2[index2] = value; }
//}
// 声明一个外部索引器
public extern int this[int index]
{ get; set; }
}
// 抽象索引器声明
abstract class indexEaxmple
{
public abstract int this[int index]
{
get;
set;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
}
}
}索引器在类中的使用
- 索引器允许用户按照处理数组的方式索引类,访问时有两种形式
- 使用索引器可直接访问类实例:将数组声明为public成员并直接访问它的成员;
实例:1、访问类实例(容量为10的整型数组为例)2、访问类成员(以星期演示)
using System;
namespace _5_索引器在类中的使用
{
public class indexText //访问类的实例
{
private int[] array = new int[10];
public int this[int index]
{
get
{
if (index < 0 || index > 10) return 0;
else return array[index];
}
set
{
if (index >= 0 && index < 10) array[index] = value;
}
}
}
public class weekIndex //访问类成员
{
string[] week = { "星期一", "星期二", "星期三", "星期四", "星期五", "星期六", "星期日" };
private int getDay(string weekText)
{
int i = 0;
foreach(string day in week)
{
if (day == weekText) return i+1;
i++;
}
return -1;
}
public int this[string week]
{
get { return getDay(week); }
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("访问类实例的结果");
indexText Arr = new indexText();
Arr[-5] = 5;
Arr[0] = 15;
Arr[2] = 60;
Arr[11] = 65;
Console.WriteLine("Arr[-5]={0}", Arr[-5]);
Console.WriteLine("Arr[0]={0}", Arr[0]);
Console.WriteLine("Arr[1]={0}", Arr[1]);
Console.WriteLine("Arr[2]={0}", Arr[2]);
Console.WriteLine("Arr[11]={0}", Arr[11]);
Console.WriteLine("访问累成员结果");
weekIndex we = new weekIndex();
Console.WriteLine(we["星期三"]);
Console.WriteLine(we["星期四"]);
Console.WriteLine(we["星期八"]);
Console.WriteLine(we["星期0"]);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}索引器在接口中的使用
索引器可以作为接口成员来声明,单接口中的索引器声明不包括任何访问修饰符,这是因为接口不包括任何编程程序语句,所以get和set访问器没有程序主题,因此,访问索引器的用途是指示索引器时读写、只读还是只写
using System;
namespace _6_索引器在接口中的使用
{
public interface iTextIndex
{
int this[int index]
{
get;
set;
}
}
class indexText:iTextIndex
{
// 演示容量为10的数组,对实例成员的访问
private int[] array = new int[10];
public int this[int index]
{
get
{
if (index < 0 || index >= 10) return 0;
else return array[index];
}
set
{
if (index > 0 && index < 10) array[index] = value;
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
indexText Arr = new indexText();
Arr[-1] = 5;
Arr[4] = 10;
Arr[9] = 20;
Arr[14] = 30;
for(int i=-1;i<15;i=i+5)
{
Console.WriteLine("Arr[{0}]={1}", i, Arr[i]);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}小结及任务实施
索引器实现QQ状态的访问,利用类成员进行访问,得出QQ状态对应的索引值
using System;
namespace 本章小结及任务实施
{
public class QQStateIndex
{
string [] qqState = { "在线", "离线", "忙碌", "Q我", "隐身" };
private int getState(string stateText)
{
int i= 0;
foreach(string stateString in qqState)
{
if (stateString == stateText) return i;
i++;
}
return -1;
}
public int this[string stateString]
{
get { return getState(stateString); }
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
QQStateIndex qs = new QQStateIndex();
Console.WriteLine(qs["在线"]);
Console.WriteLine(qs["忙碌"]);
Console.WriteLine(qs["睡眠"]);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}加载全部内容