java try-with-resources
悟空不买菜了 人气:0前言:
这个语句的作用是,确保该语句执行之后,关闭每一个资源,也就是说它确保了每个资源都在生命周期结束之后被关闭,因此,比如读写文件,我们就不需要显示的调用close()方法
这个语句的大致模板如下:
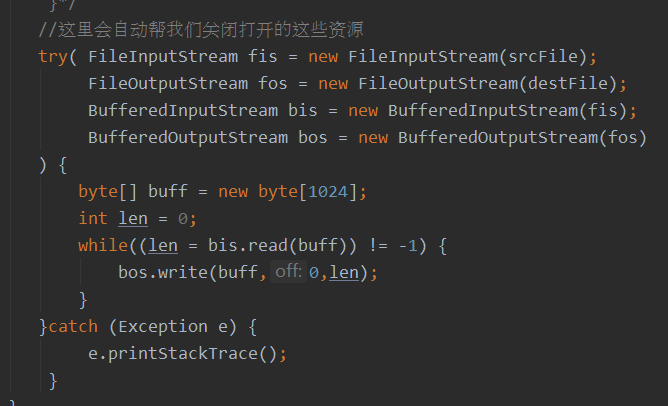
我们可以看到我们把需要关闭的资源都放到try()这个括号里面去了,之前都是对异常的捕获,怎么还可以写资源语句,这就是奇妙之处,注意分号啊,最后一个资源可以不用加分号,中间的都要加分号,并且,对于java7来说,变量的声明必须放在括号里面。
下面来说一下具体实现原理:
首先在try()里面的类,必须实现了如下这个接口

这个接口也叫自动关闭资源接口.我们想要写这样的语句,必须去实现它里面的close()方法

对于这个类,很多类都已经做了默认实现,所以我们没有必要显示去山实现这样一个东西,直接拿来用就可以了,比如:
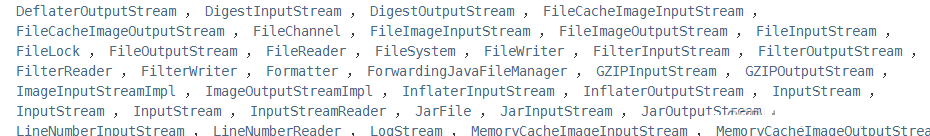
我们这些常见的文件操作类,都已经做了实现。
这样的做法有助于我们写非常复杂的finally块,话不多说,直接上代码:
ImageCopy.java
import java.io.*;
public class ImageCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File srcFile = new File("F:\\java课程资料\\王也.png");
File destFile = new File("E:\\717.png");
copyImage(srcFile,destFile);
}
//这个采用一边读,一边写的思路来做
public static void copyImage(File srcFile, File destFile) {
//这个太繁琐了,我们把它进行改进
/* FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = fis.read(buff)) != -1) {
fos.write(buff,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}*/
//这里会自动帮我们关闭打开的这些资源
try( FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos)
) {
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = bis.read(buff)) != -1) {
bos.write(buff,0,len);
}
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//采用字符流来读取文本操作
public static void copyText(File srcFile,File destFile) {
InputStreamReader fr = null;
OutputStreamWriter fw = null;
try {
fr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(srcFile),"gbk");
// fw = new FileWriter(destFile);
fw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(destFile),"gbk");
char[] buff = new char[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = fr.read(buff)) != -1) {
System.out.println("读取到的长度:" + len);
fw.write(buff,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}加载全部内容