ASP.NET Core中Grpc通信基础
奋斗的大橙子 人气:0目录:
- 一、简单介绍DotnetCore3.0如何将.proto文件生成对应的服务端和客户端类
- 二、介绍如何在服务端使用Grpc,以及Grpc需要的条件(HTTP2、TLS)
- 三、介绍如何创建GrpcClient,以及Grpc通讯的四种模式
- 四、举例如何使用Grpc
一、如何使用protobuf生成服务类
Grpc中使用协议缓冲区 (protobuf) 用作接口设计语言 (IDL),它的主要内容包含:
- GRPC 服务的定义。
- 客户端和服务器之间发送的消息。
Grpc.Tools 这个工具,在每次编译的时候,都能将.proto文件生成为对于的cs文件。 服务端和客户端都需要添加。Grpc.AspNetCore这个包会对Grpc.Tools 进行使用。引用了这个包之后。还有注意在Server和Client,都要在对应.csproj下面,修改GrpcServices这个配置的值,如果是服务端就写Server,如果是客户端就写Client。
<ItemGroup>
<Protobuf Include="Protos\xxxx.proto" GrpcServices="Server" />
</ItemGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<Protobuf Include="Protos\xxxx.proto" GrpcServices="Client" />
</ItemGroup>二、服务端使用Grpc
1.添加引用
需要添加 Grpc.AspNetCore 的引用
2.配置Grpc
在Startup.cs中需要配置如下信息:
①ConfigureServices 中需要配置
services.AddGrpc();
②Configure 中需要配置endpoints
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
// Communication with gRPC endpoints must be made through a gRPC client.
// To learn how to create a client, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2086909
endpoints.MapGrpcService<GreeterService>();
});3.Kestrel的配置
Grpc中的endpoints需要下面的支持:
HTTP/2
gRPC 要求 HTTP/2。gRPC for ASP.NET Core 验证HttpRequest为HTTP/2。在大多数现代操作系统上,Kestrel支持 HTTP/2。默认情况下,Kestrel 终结点配置为支持 HTTP/1.1 和 HTTP/2 连接。
传输安全性Transport Layer Security (TLS).
用于 gRPC 的 Kestrel 终结点应使用 TLS 进行保护。
在开发版中,将在存在 ASP.NET Core 开发证书https://localhost:5001时,自动创建一个使用 TLS 保护的终结点。不需要配置。https前缀验证 Kestrel 终结点是否正在使用 TLS。
在生产环境如果使用TLS中,必须显式配置 TLS。
两种方式配置对应的TLS:
1.在AppSettings下面添加配置节点:
{
"Kestrel": {
"Endpoints": {
"HttpsInlineCertFile": {
"Url": "https://localhost:5001",
"Protocols": "Http2",
"Certificate": {
"Path": "<path to .pfx file>",
"Password": "<certificate password>"
}
}
}
}
}2.直接在代码中添加
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.ConfigureKestrel(options =>
{
options.Listen(IPAddress.Any, 5001, listenOptions =>
{
listenOptions.Protocols = HttpProtocols.Http2;
listenOptions.UseHttps("<path to .pfx file>",
"<certificate password>");
});
});
webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>();
});此外TLS不仅仅适用于Client和Server间的安全传输,还可以用于服务协商。
我在看官网的关于服务协商时候,有些发懵,因为又说了grpc 需要Http/2 、又需要TLS,但是后面又说在不配置TLS的endpoint的时候...... 那么到底是需要TLS还是不需要TLS,Grpc到底是仅仅支持HTTP2还是会兼容HTTP1?
首先要明确几个概念:
- 什么是EndPoint
- 什么是Grpc endpoint
- 什么是TLS
TLS 和 HTTP1、HTTP2
以下是我的理解:
Endpoint是一个大概念,不仅仅是grpc有endpoint,以前我们用的webservice、wcf都有,他可以是HTTP1的,也可以是HTTP2的,也可以都支持。仅仅是当我们要用Grpc的时候我们需要使用HTTP2协议。
TLS是一种安全协议,是在传输层上的安全协议,具体是什么样的可以不用了解,只是在.Net Core 中配置TLS,不仅仅作用于安全传输,还有作用于协议的选择,当我们的endpoint使用的是HTTP2,且不用TLS的时候,我们需要配置我们的Kestrel服务器的ListenOptions.Protocols 必须设置为HttpProtocols.Http2 ,换句话说 如果ListenOptions.Protocols= HttpProtocols.Http1AndHttp2,那么就不能使用TLS。
总结一下就是:
你配置你的Kestrel 为使用HTTP2协议的时候,你可以使用TLS作为安全传输,也可以不用
你配置你的Kestrel 为使用兼容HTTP1协议的时候,那么你就不能用TLS
那么对于GPRC来讲,他的endpoint 必须使用HTTP2协议,TLS也不是必须要配置的。
4.将Grpc像Api一样提供出去
public class GreeterService : Greeter.GreeterBase
{
private readonly ILogger<GreeterService> _logger;
public GreeterService(ILogger<GreeterService> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
public override Task<HelloReply> SayHello(HelloRequest request, ServerCallContext context)
{
return Task.FromResult(new HelloReply
{
Message = "Hello " + request.Name
});
}
}- ①继承一下生成出来的抽象类 Greeter.GreeterBase
- ②根据自己的需要,依赖注入一些必要的Service类
- ③实现生成出来的Virtual方法
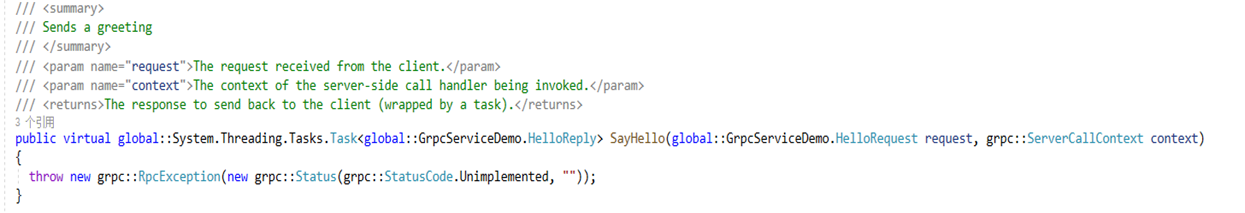
备注:
- 1.发生的问题

- 2.Status(StatusCode=Internal, Detail="Error starting gRPC call: The SSL connection could not be established, see inner exception.")
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/core/grpc/troubleshoot?view=aspnetcore-3.0
- 3.Grpc.Core.RpcException:“Status(StatusCode=Internal, Detail="Bad gRPC response. Response protocol downgraded to HTTP/1.0.")”
先按照下面的做
https://github.com/grpc/grpc-dotnet/issues/654
如果不行的话,检查一下是否本地一直在开着抓包工具之类的代理软件,我之前一直不行,是因为本地运行着Fiddler

三、客户端使用Grpc
1.创建Gprc客户端
和上面不一样,grpc client 是通过 xxx.proto 文件生成的具体的类型。里面包含了我们要调用的所有的方法。一般情况下,我们都是创建一个Channel类,然后通过Channel类在创建一个Client。
如下图所示。
var channel = GrpcChannel.ForAddress("https://localhost:5001");
var client = new Greet.GreeterClient(channel);ForAddress方法:

注:
gRPC的Channel维持了一个到远程服务的长连接。
客户端对象可以重用相同的通道。
与调用远程方法相比,创建通道是一项昂贵的操作,因此通常应该为尽可能多的调用重用单个通道。
2.Grpc方法调用
Grpc具有多种不同的方式:
- Unary (一元模式)
- Server streaming (服务器流)
- Client streaming (客户端流)
- Bi-directional streaming (双向流)
① Unary方式
从客户端发送请求到服务端开始,服务端响应请求回来结束。每一个Unary 服务都会从*.proto文件中生成两个具体的调用方法,一个异步方法,一个同步方法。例如下面的代码:
var reply1 = await client.SayHelloAsync(new HelloRequest { Name = "GreeterClient" });
var reply2 = client.SayHello(new HelloRequest { Name = "GreeterClient" });②Server streaming 方式
从客户端发送请求到服务端开始,利用ResponseStream.MoveNext()方法读取服务端返回的数据,知道ResponseStream.MoveNext() 返回false说明读取结束。
var client = new Greet.GreeterClient(channel);
using (var call = client.SayHellos(new HelloRequest { Name = "World" }))
{
while (await call.ResponseStream.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine("Greeting: " + call.ResponseStream.Current.Message);
// "Greeting: Hello World" is written multiple times
}
}
//或者C# 8以上通过await foreach来处理返回信息
using (var call = client.SayHellos(new HelloRequest { Name = "World" }))
{
await foreach (var response in call.ResponseStream.ReadAllAsync())
{
Console.WriteLine("Greeting: " + response.Message);
// "Greeting: Hello World" is written multiple times
}
}③Client streaming 方式
客户端流调用不需要在客户端发送请求之后开始,客户端可以选择发送带有RequestStream.WriteAsync的发送消息,当客户端完成发送消息请求流时。调用CompleteAsync来通知服务,当服务返回响应消息时,调用结束。
var client = new Counter.CounterClient(channel);
using (var call = client.AccumulateCount())
{
//调用三次
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
await call.RequestStream.WriteAsync(new CounterRequest { Count = 1 });
}
//通知服务写好了
await call.RequestStream.CompleteAsync();
//获取返回结果
var response = await call;
Console.WriteLine($"Count: {response.Count}");
// Count: 3
}④Bi-directional streaming call 方式
相当于②和③的结合,也不需要等待客户端发送完请求,使用RequestStream.WriteAsync写入消息,通过ResponseStream.MoveNext()或者ResponseStream.ReadAllAsync()读取服务端返回的数据。当服务端不在返回的时候,结束请求。
using (var call = client.Echo())
{
Console.WriteLine("Starting background task to receive messages");
var readTask = Task.Run(async () =>
{
await foreach (var response in call.ResponseStream.ReadAllAsync())
{
Console.WriteLine(response.Message);
// Echo messages sent to the service
}
});
Console.WriteLine("Starting to send messages");
Console.WriteLine("Type a message to echo then press enter.");
while (true)
{
var result = Console.ReadLine();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(result))
{
break;
}
await call.RequestStream.WriteAsync(new EchoMessage { Message = result });
}
Console.WriteLine("Disconnecting");
await call.RequestStream.CompleteAsync();
await readTask;
}此外这里补充一下几种方式适用的场景
- (1) 简单模式(Simple RPC)
这种模式最为传统,即客户端发起一次请求,服务端响应一个数据,这和大家平时熟悉的RPC没有什么大的区别,所以不再详细介绍。
- (2) 服务端数据流模式(Server-side streaming RPC)
这种模式是客户端发起一次请求,服务端返回一段连续的数据流。典型的例子是客户端向服务端发送一个股票代码,服务端就把该股票的实时数据源源不断的返回给客户端。
- (3) 客户端数据流模式(Client-side streaming RPC)
与服务端数据流模式相反,这次是客户端源源不断的向服务端发送数据流,而在发送结束后,由服务端返回一个响应。典型的例子是物联网终端向服务器报送数据。
- (4) 双向数据流模式(Bidirectional streaming RPC)
顾名思义,这是客户端和服务端都可以向对方发送数据流,这个时候双方的数据可以同时互相发送,也就是可以实现实时交互。典型的例子是聊天机器人。
四、举例使用Grpc创建一个服务
1.创建两个控制台程序,分别为服务端和客户端
2.在服务端创建服务
①在GrpcService中引入Grpc.AspNetCore包,此包会在编译的时候,将.proto文件生成对应的服务端grpc服务代码。
.net core需要自己去生成,3.0以后已经在上面的包中集成的生成的功能,只要生成代码就会调用Grpc.Tools和Google.Protobuf去产生对应的cs文件
②创建一个proto文件
syntax = "proto3";
option csharp_namespace = "GrpcService";
package Hello;
service Hello {
//通过一元方式传输
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply);
//通过客户端流的方式传输
rpc SayHelloClientStream (stream HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply);
//通过服务端流的方式传输
rpc SayHelloServerStream (HelloRequest) returns (stream HelloReply);
//通过双向流的方式传输
rpc SayHelloStream (stream HelloRequest) returns (stream HelloReply);
}
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
message HelloReply {
string message = 1;
}并修改对应的服务端csproj文件,将该proto文件加入到项目中,否则不会生成服务端代码。
<ItemGroup>
<Protobuf Include="Hello.proto" GrpcServices="Server" />
</ItemGroup>③创建一个HelloService类,继承自生成出来的抽象类XXXBase,然后可以重写对应我们声明的方法,以便于提供客户端访问。
注:xxx.xxxBase 可能在继承的时候显示不存在,那是因为没有②之后没有进行编译,编译之后就能生成了。
public class HelloService : Hello.HelloBase
{
public override Task<HelloReply> SayHello(HelloRequest request, ServerCallContext context)
{
return Task.FromResult(new HelloReply
{
Message = "Response:" + request.Name
});
}
public override async Task<HelloReply> SayHelloClientStream(IAsyncStreamReader<HelloRequest> requestStream, ServerCallContext context)
{
var current = new HelloRequest();
while (await requestStream.MoveNext())
{
current = requestStream.Current;
}
var task = new Task<HelloReply>(() =>
{
var reply = new HelloReply()
{
Message = "Response:" + current.Name
};
return reply;
});
task.Start();
var result = await task;
return result;
}
public override async Task SayHelloServerStream(HelloRequest request, IServerStreamWriter<HelloReply> responseStream, ServerCallContext context)
{
await responseStream.WriteAsync(new HelloReply() { Message = "Response:" + request.Name });
}
public override async Task SayHelloStream(IAsyncStreamReader<HelloRequest> requestStream,
IServerStreamWriter<HelloReply> responseStream,
ServerCallContext context)
{
while (await requestStream.MoveNext())
{
await responseStream.WriteAsync(new HelloReply() { Message = "Response:" + requestStream.Current.Name });
}
}
}④因为是服务端,一旦实现了所有的方法,还需要启动一个gRPC服务器,这样客户端才可以使用服务。
可以采用两种方式来持久化服务,监听端口,处理请求:
a.使用Grpc.Core里面的Server (适用于.net core 3.0以下版本)
b.配置startup.cs中的ConfigureServices添加服务,Configure方法中配置终结点,并且配置对应的Kestrel服务器
第一种方式:
class Program
{
private static Server _server;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
_server = new Server
{
Services = { Hello.BindService(new HelloService()) },
//这里使用的是不安全的方式
Ports = { new ServerPort("localhost", 50001, ServerCredentials.Insecure) }
};
_server.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Listen Port 50001");
Console.ReadKey();
_server?.ShutdownAsync().Wait();
}
}第二种方式:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 使用Kestrel服务器
CreateHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
#endregion
}
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.ConfigureKestrel(options =>
{
// Setup a HTTP/2 endpoint without TLS.
options.ListenLocalhost(50001, o => o.Protocols =
HttpProtocols.Http2);
});
webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>();
});
}Startup.cs
public class Startup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddGrpc();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapGrpcService<HelloService>();
endpoints.MapGet("/", async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Communication with gRPC endpoints must be made through a gRPC client." +
" To learn how to create a client, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2086909");
});
});
}
}3.在GrpcClient中引入如下包
①添加相关的依赖包
Install-Package Grpc.Net.Client
Install-Package Google.Protobuf
Install-Package Grpc.Tools
②添加之后,把服务端的proto文件一样复制一份到客户端,并在csproj下面追加如下的代码,并编译一次:
<ItemGroup>
<Protobuf Include="Hello.proto" GrpcServices="Client" />
</ItemGroup>③编写客户端调用的具体内容
class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
// This switch must be set before creating the GrpcChannel/HttpClient.
AppContext.SetSwitch("System.Net.Http.SocketsHttpHandler.Http2UnencryptedSupport", true);
var channel = GrpcChannel.ForAddress("http://localhost:50001");
var helloClient = new Hello.HelloClient(channel);
//一元调用(同步方法)
var reply = helloClient.SayHello(new HelloRequest { Name = "一元同步调用" });
Console.WriteLine($"{reply.Message}");
//一元调用(异步方法)
var reply2 = helloClient.SayHelloAsync(new HelloRequest { Name = "一元异步调用" }).GetAwaiter().GetResult();
Console.WriteLine($"{reply2.Message}");
//服务端流
var reply3 = helloClient.SayHelloServerStream(new HelloRequest { Name = "服务端流" });
while (await reply3.ResponseStream.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(reply3.ResponseStream.Current.Message);
}
//客户端流
using (var call = helloClient.SayHelloClientStream())
{
await call.RequestStream.WriteAsync(new HelloRequest { Name = "客户端流" + i.ToString() });
await call.RequestStream.CompleteAsync();
var reply4 = await call;
Console.WriteLine($"{reply4.Message}");
}
//双向流
using (var call = helloClient.SayHelloStream())
{
Console.WriteLine("Starting background task to receive messages");
var readTask = Task.Run(async () =>
{
await foreach (var response in call.ResponseStream.ReadAllAsync())
{
Console.WriteLine(response.Message);
}
});
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
await call.RequestStream.WriteAsync(new HelloRequest { Name = "双向流" + i.ToString()});
}
await call.RequestStream.CompleteAsync();
await readTask;
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}执行:

这里要注意一段代码AppContext.SetSwitch("System.Net.Http.SocketsHttpHandler.Http2UnencryptedSupport", true),如果不使用这段代码,并且channel当中还是http的话,那么就会出现下面的异常:
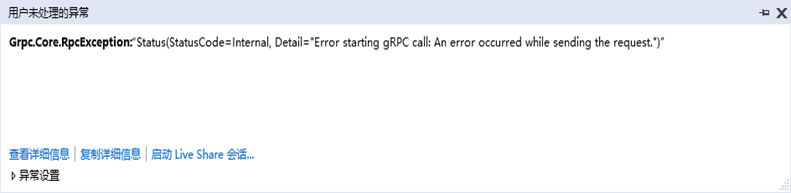
到此这篇关于ASP.NET Core中Grpc通信基础的文章就介绍到这了。希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持。
加载全部内容