MyBatis后端对数据库操作
Fly upward 人气:01.MyBatis 是什么?
MyBatis 是⼀款优秀的持久层框架,它⽀持⾃定义 SQL、存储过程以及⾼级映射。MyBatis 去除了很多JDBC 代码以及设置的参数和获取结果集的工作。MyBatis 可以通过简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原始类型、接⼝和 Java POJO (Plain Old Java Object。普通老式 Java对象)为数据库中的记录。
2. MyBatis 的重要性
对于后端开发来说,程序是由两个重要部分组成的:
1.后端程序
2.数据库
⽽这两个重要的组成部分要通讯,就要依靠数据库连接⼯具
1.JDBC
2. MyBatis
JDBC 的操作流程:
1. 创建数据库连接池 DataSource
2. 通过 DataSource 获取数据库连接 Connection
3. 编写要执⾏带 ? 占位符的 SQL 语句
4. 通过 Connection 及 SQL 创建操作命令对象 Statement
5. 替换占位符:指定要替换的数据库字段类型,占位符索引及要替换的值
6. 使⽤ Statement 执⾏ SQL 语句
7. 查询操作:返回结果集 ResultSet,更新操作:返回更新的数量
8. 处理结果集
9. 释放资源
对于 JDBC 来说,整个操作⾮常的繁琐,我们不但要拼接每⼀个参数,⽽且还要按照模板代码的⽅式,⼀步步的操作数据库,并且在每次操作完,还要⼿动关闭连接等,⽽所有的这些操作步骤都需要在每个⽅法中重复书写。 对于 MyBatis ,它可以帮助我们更⽅便、更快速的操作数据库。
3. MyBatis 查询
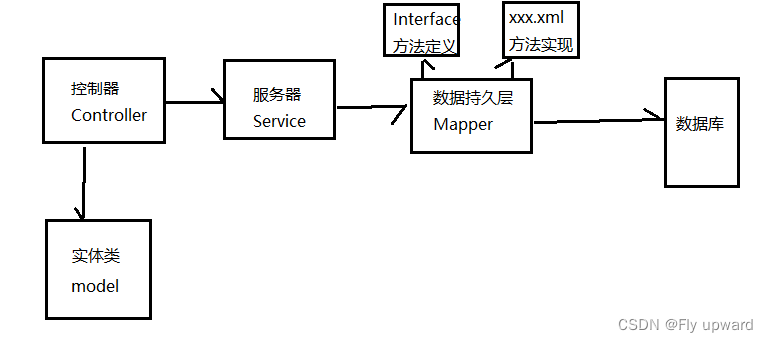
框架交互流程
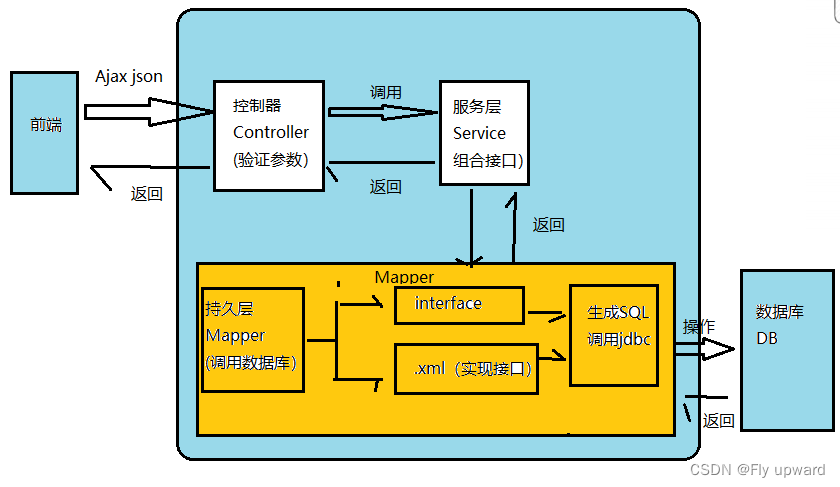
MyBatis 也是⼀个 ORM 框架, ORM(Object Relational Mapping),即对象关系映射。在⾯向对 象编程语⾔中,将关系型数据库中的数据与对象建⽴起映射关系,进⽽⾃动的完成数据与对象的互相转换:
1. 将输⼊数据(即传⼊对象)+SQL 映射成原⽣ SQL
2. 将结果集映射为返回对象,即输出对象ORM 把数据库映射为对象:
数据库表(table)--> 类(class)
记录(record,⾏数据)--> 对象(object)
字段(field) --> 对象的属性(attribute)
⼀般的 ORM 框架,会将数据库模型的每张表都映射为⼀个 Java 类。 也就是说使⽤ MyBatis 可以像操作对象⼀样来操作数据库中的表,可以实现对象和数据库表之间的转换。
3.1 创建数据库和表
使⽤ MyBatis 的⽅式来读取⽤户表中的所有⽤户
创建用户表
drop table if exists userinfo;
create table userinfo(
id int primary key auto_increment,
username varchar(100) not null,
password varchar(32) not null,
photo varchar(500) default '',
createtime datetime default now(),
updatetime datetime default now(),
`state` int default 1
) default charset 'utf8mb4';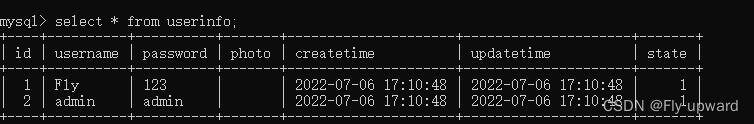
3.2 添加MyBatis框架⽀持
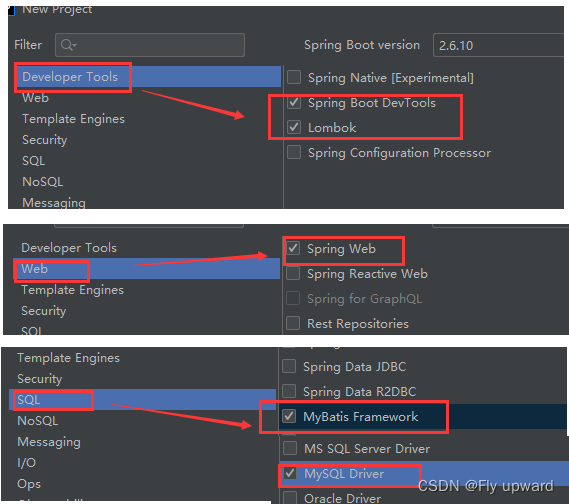
3.2.1 新项目添加MyBatis
在创建新项目时,来到这一步,只需将下面的勾选即可
3.2.1 老项⽬添加 MyBatis
在 pom.xml 文件页面 鼠标右键进行下面操作

3.3 配置连接字符串和MyBatis
3.3.1 配置连接字符串

将当前运行环境选择开发环境的配置
application-dev.yml
#开发环境
#配置数据库连接
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/myblog?characterEncoding=utf8
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# 开启 MyBatis SQL 打印
logging:
level:
com:
example:
demo: debug
mybatis:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImplapplication.yml
选择开发环境
spring:
profiles:
active: dev3.3.2 配置mybatis 中的 xml 保存路径
MyBatis 的 XML 中保存是查询数据库的具体操作 SQL,配置在 application.yml 中
#配置mybatis xml 保存路径 mybatis: mapper-locations: classpsth:mybatis/**Mapper.xml
3.4 添加后端代码
下⾯按照后端开发的⼯程思路,也就是下⾯的流程来实现 MyBatis 查询所有⽤户的功能
目录结构:
3.4.1 添加实体类
先添加用户实体类
/**
* 普通用户实体类
*/
@Data
public class UserInfo {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String password;
private String photo;
private String createtime;
private String updatetime;
private int state;
}3.4.2 添加 mapper 接口
数据持久层的接口定义:
/**
* 实现数据库映射
*/
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
//查询用户 ID
public UserInfo getUserById(@Param("id") Integer id);
}3.4.3 添加UserMapper.xml
数据持久层的实现,mybatis 的固定 xml 格式
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- namespace 要设置是实现接口的具体包名加类名 --> <mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper"> </mapper>
UserMapper.xml 查询所有⽤户的具体实现 SQL:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- namespace 要设置是实现接口的具体包名加类名 -->
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseMap" type="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
<!-- 主键映射 -->
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<!-- 普通属性映射 -->
<result column="username" property="name"></result>
</resultMap>
<!-- 根据 id 查询用户 -->
<select id="getUserById" resultMap="BaseMap">
select * from userinfo where id=${id}
</select>
</mapper>标签说明:
<mapper>标签:需要指定 namespace 属性,表示命名空间,值为 mapper 接⼝的全限定名,包括全包名.类名。
<select>查询标签:是⽤来执⾏数据库的查询操作的:
- id:是和 Interface(接⼝)中定义的⽅法名称⼀样的,表示对接⼝的具体实现⽅法。
- resultType:是返回的数据类型,也就是开头我们定义的实体类

3.4.4 添加Service
决定调用哪个mapper
@Service
public class UserService {
@Resource
private UserMapper userMapper;
public UserInfo getUserById(Integer id) {
return userMapper.getUserById(id);
}
}3.4.5 添加 Controller
@Controller
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
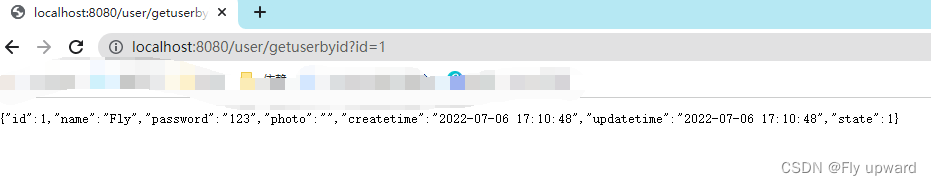
@RequestMapping("/getuserbyid")
public UserInfo getUserById(Integer id) {
if (id == null) return null;
return userService.getUserById(id);
}
}以上代码写完,整个 MyBatis 的查询功能就实现完了
4.增删改操作
4.1 修改用户操作
在 UserMapper 中增加修改的代码
//修改方法根据 ID 修改名称
public int update(@Param("id") Integer id,
@Param("name") String username);UserMapper.xml 中增加接口的实现标签和具体的执行SQL
<update id="update" >
update userinfo set username=#{name} where id=#{id}
</update>
通过单元测试,实现成功
@Test
void update() {
int result = userMapper.update(2,"fei");
Assertions.assertEquals(1,result);
}
查询SQL语句可知,已经修改了

如果仅仅是为了测试功能是否实现,而不修改数据库中的内容,可以加入注解 @Transactional
@Test
@Transactional // 添加此注解后,执行完单元测试,不会修改数据库中的内容,即事务回滚
void update() {
int result = userMapper.update(2,"fei");
Assertions.assertEquals(1,result);
}4.2 删除用户操作
在 UserMapper 中增加删除的代码
//删除方法
public int del(@Param("id") Integer id);UserMapper.xml 中增加接口的实现标签和具体的执行SQL
<!--删除操作-->
<delete id="del">
delete from userinfo where id=#{id};
</delete>单元测试
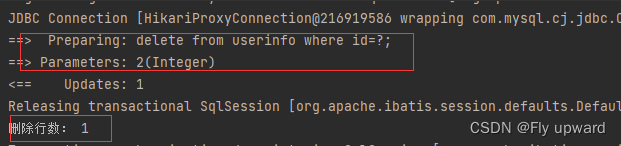
@Test
@Transactional
void del() {
int result = userMapper.del(2);
System.out.println("删除行数: " + result);
Assertions.assertEquals(1,result);
}
4.3 增加用户操作
在 UserMapper 中添加增加的代码
//增加用户方法
// 传过来的是对象而不是某个成员变量
public int add(UserInfo userInfo);UserMapper.xml 中增加接口的实现标签和具体的执行SQL
<!--增加操作,返回受影响的行数-->
<insert id="add">
insert into userinfo(username,password,photo)
values(#{username}, #{password}, #{photo}); <!--和对象里面的属性一一对应-->
</insert>单元测试
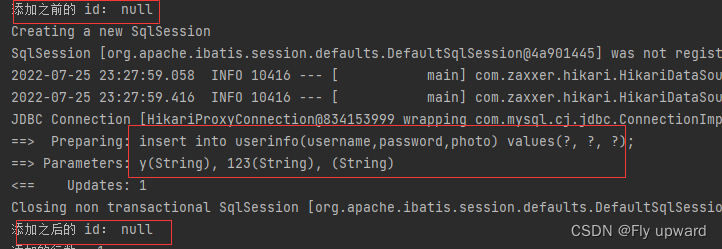
@Test
//@Transactional
void add() {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setName("y");
userInfo.setPassword("123");
userInfo.setPhoto("");
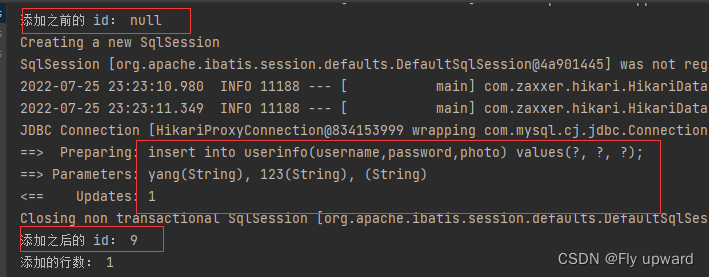
System.out.println("添加之前的 id: " + userInfo.getId());
int result = userMapper.add(userInfo);
System.out.println("添加之后的 id: " + userInfo.getId());
System.out.println("添加的行数: " + result);
Assertions.assertEquals(1,result);
}
4.4 增加用户并有自增ID
在 UserMapper 中添加增加的代码
//添加用户,返回自增ID
public int addGetId(UserInfo userInfo);UserMapper.xml 中增加接口的实现标签和具体的执行SQL
<!--增加操作,返回受影响的行数和自增ID-->
<insert id="addGetId" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id" keyColumn="id">
insert into userinfo(username,password,photo)
values(#{name}, #{password}, #{photo}); <!--和对象里面的属性一一对应-->
</insert>单元测试
@Test
//@Transactional
void addGetId() {
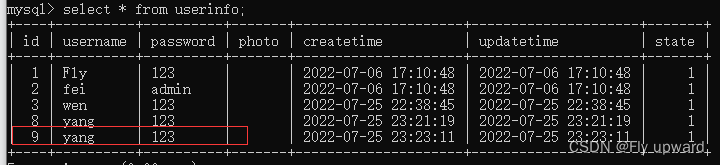
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setName("yang");
userInfo.setPassword("123");
userInfo.setPhoto("");
System.out.println("添加之前的 id: " + userInfo.getId());
int result = userMapper.addGetId(userInfo);
System.out.println("添加之后的 id: " + userInfo.getId());
System.out.println("添加的行数: " + result);
Assertions.assertEquals(1,result);
}
5. 参数占位符 #{} 和 ${}
#{}:预编译处理 。处理时,成一个 问号? ,赋值时会加上 单引号 ‘ ’
${}:字符直接替换
区别:
1.定义不同
预编译处理是指:MyBatis 在处理#{}时,会将 SQL 中的 #{} 替换为?号,使⽤ PreparedStatement 的set ⽅法来赋值。
直接替换:是MyBatis 在处理 ${} 时,就是把 ${} 替换成变量的值。
2.使用不同:#{} 适用于所有类型的参数匹配,但${} 只适用于数值类型
3.安全性不同:#{} 性能高,并且没有安全问题;但 ${} 存在SQL注入的安全问题
#{}:预编译处理 占位符,当成 value 值来使用, 即加上 ‘ ’
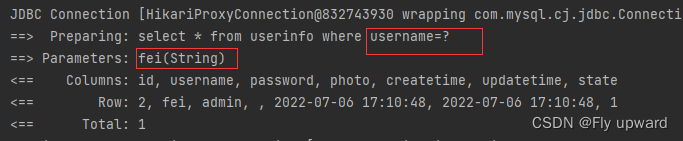
<select id="gerUserFullById" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
select * from userinfo where username=#{name}
</select> @Test
void gerUserFullById() {
UserInfo userInfo = userMapper.gerUserFullById("fei");
System.out.println("userInfo: " + userInfo);
}
${}:字符直接替换
不加任何符合,直接替换上去,连成一个SQL 命令
<select id="gerUserFullById" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
select * from userinfo where username=${name}
</select>单元测试结果

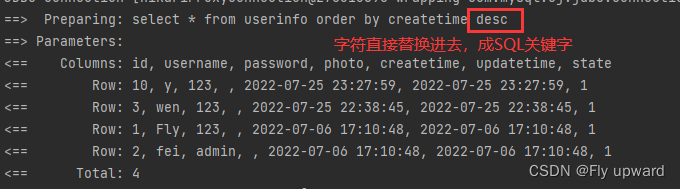
5.1 desc 降序排序
//对用户进行排序
public List<UserInfo> getOrderList(@Param("order") String order);此处使用的是 ${}, 如果使用 #{} 的话,会编译出错,因为它会把 desc 当成 ‘desc’ 一个value 值来使用,不构成一个 SQL命令语句
<select id="getOrderList" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
select * from userinfo order by createtime ${order}
</select>单元测试
@Test
void getOrderList() {
List<UserInfo> list = userMapper.getOrderList("desc");
log.info("列表: " + list);
}

5.2 登录(SQL注入)
//登录功能
public UserInfo login(@Param("name") String username,
@Param("password") String password);1) 在使用${} 时,需要加单引号,因为是直接替换
<select id="login" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
select * from userinfo where username='${name}' and password='${password}';
</select>单元测试
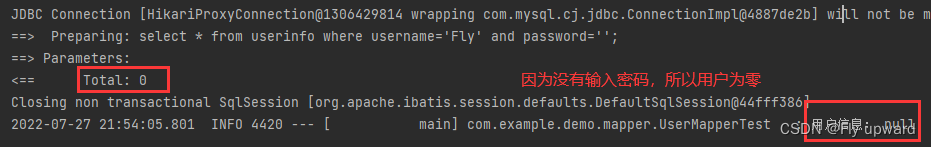
@Test
void login() {
String username = "Fly";
String password = "";
UserInfo userInfo = userMapper.login(username,password);
log.info("用户信息: " + userInfo);
}
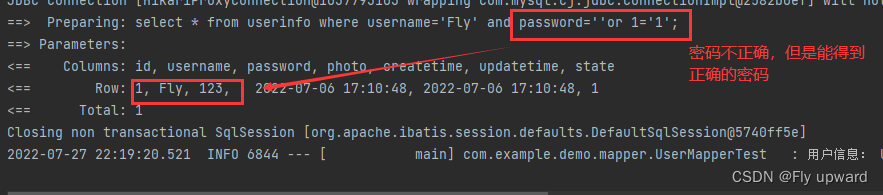
使用 " 'or 1=' 1" 时,SQL注入,密码会泄露,如下,因此在登录时应使用#{}
@Test
void login() {
String username = "Fly";
//String password = "";
String password = "'or 1='1";
UserInfo userInfo = userMapper.login(username,password);
log.info("用户信息: " + userInfo);
}
2)#{} 预编译处理,不会出现密码泄露
<!--登录功能-->
<select id="login" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
<!--select * from userinfo where username='${name}' and password='${password}'; -->
select * from userinfo where username=#{name} and password=#{password};
</select>
5.3 like 查询
//like 模糊查询
public List<UserInfo> getUserByName(@Param("name") String username);1)直接使用 #{} 会报错
因为赋值时会加上单引号 ‘’
select * from userinfo where username like '%#{name}%'就相当于下面的语句,不符合查询条件
select * from userinfo where username like '%'name'%'
2)使用${} 是不会报错,但在业务层的值不能穷举
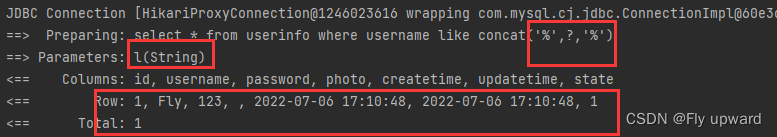
3)#{} 在like中的正确用法,加上contat 拼接,演示如下

正确用法
因为#{} 在赋值的时候,会带上单引号‘’ ,所以下面的#{}不需要带单引号
<!--like 模糊查询-->
<select id="getUserByName" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
<!-- select * from userinfo where username like '%#{name}%'-->
select * from userinfo where username like concat('%',#{name},'%')
</select>单元测试
@Test
void getUserByName() {
String username = "l";
List<UserInfo> list= userMapper.getUserByName(username);
log.info("用户列表: " + list);
}
6.多表查询
6.1 返回类型:resultType
绝大数查询场景可以使用 resultType 进行返回,如下
<!-- 根据 id 查询用户 -->
<select id="getUserById" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
select * from userinfo where id=${id}
</select>它的优点是使⽤⽅便,直接定义到某个实体类即可 6.2 返回字典映射:resultMap 使用场景:
字段名称和程序中的属性名不同的情况, 可使⽤ resultMap 配置映射; 一对一和一对多关系可以使用 resultMap 映射并查询数据
1)字段名程序中的属性名不一致

userMapper.xml 代码如下
<!-- 根据 id 查询用户 -->
<select id="getUserById" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
select * from userinfo where id=${id}
</select>查询结果

这个时候就可以使⽤ resultMap 了,resultMap 的使⽤如下
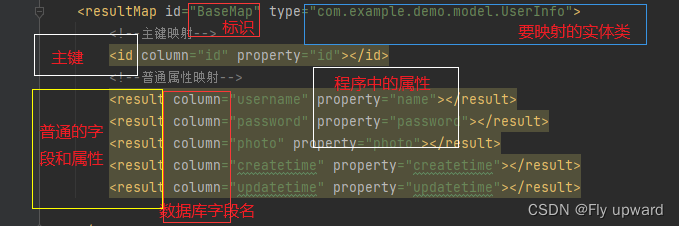
userMapper.xml 代码如下
<resultMap id="BaseMap" type="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
<!--主键映射-->
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<!--普通属性映射-->
<result column="username" property="name"></result>
<result column="password" property="password"></result>
<result column="photo" property="photo"></result>
<result column="createtime" property="createtime"></result>
<result column="updatetime" property="updatetime"></result>
</resultMap>
<!-- 根据 id 查询用户 -->
<select id="getUserById" resultMap="BaseMap">
select * from userinfo where id=${id}
</select>单元测试
@Test
void getUserById() {
UserInfo userInfo = userMapper.getUserById(1);
//Assertions.assertNotNull(userInfo);
log.info("查询行数:" + userInfo);
}查询结果

6.3 一对一表查询
创建文章实体类 ArticleInfo
@Data
public class ArticleInfo {
private int id;
private String title;
private String content;
private String createtime;
private String updatetime;
private int uid;
private int rcount;
private int state;
private UserInfo userInfo;
}mapper 实现数据库映射 ArticleMapper
@Mapper
public interface ArticleMapper {
//根据文章 id 获取文章
public ArticleInfo getArticleById(@Param("id") Integer id); //文章id
}数据库命令,数据持久层的实现, ArticleMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.ArticleMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseMap" type="com.example.demo.model.ArticleInfo">
<!--主键映射-->
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<!--普通属性映射-->
<result column="title" property="title"></result>
<result column="content" property="content"></result>
<result column="createtime" property="createtime"></result>
<result column="uid" property="uid"></result>
<result column="rcount" property="rcount"></result>
<result column="state" property="state"></result>
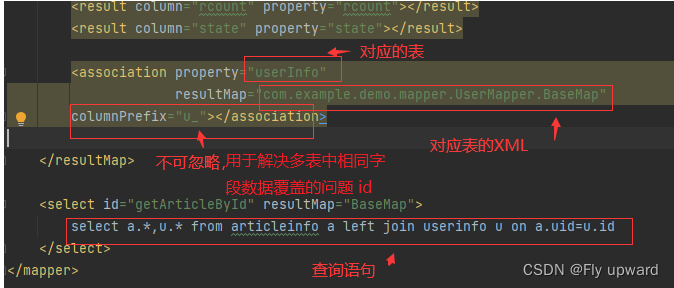
<association property="userInfo"
resultMap="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper.BaseMap"
columnPrefix="u_"></association>
</resultMap>
<select id="getArticleById" resultMap="BaseMap">
select a.*,u.* from articleinfo a left join userinfo u on a.uid=u.id
</select>
</mapper>以上使⽤ <association>标签,表示⼀对⼀的结果映射:
property 属性:指定 Article 中对应的属性,即⽤户。
resultMap 属性:指定关联的结果集映射,将基于该映射配置来组织⽤户数据。
columnPrefix 属性:绑定⼀对⼀对象时,因为对应的是用户表 ,所以是“u-”是通过 columnPrefix+association.resultMap.column 来映射结果集字段。 association.resultMap.column是指 <association>标签中 resultMap属性,对应的结果集映射中,column字段
单元测试
//将类属性注入
@Resource
private ArticleMapper articleMapper;
@Test
void getArticleById() {
ArticleInfo articleInfo = articleMapper.getArticleById(1);
log.info("查询结果:" + articleInfo );
}查询结果

6.4 一对多
一个用户对应多篇文章
实体类
@Data
public class UserInfo {
private Integer id;
//private String username;//用于resultType
private String name; //用于 resultMap
private String password;
private String photo;
private String createtime;
private String updatetime;
private int state;
//一对多
private List<ArticleInfo> artlist;
}mapper
//一对多,多表查询
//根据用户 id 查询用户及用户发表的所有文章
public UserInfo getUserAndArticleByUid(@Param("uid") Integer uid);XML
<resultMap id="BaseMap" type="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
<!--主键映射-->
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<!--普通属性映射-->
<result column="username" property="name"></result>
<result column="password" property="password"></result>
<result column="photo" property="photo"></result>
<result column="createtime" property="createtime"></result>
<result column="updatetime" property="updatetime"></result>
<result column="state" property="state"></result>
<!--多表查询-->
<collection property="artlist"
resultMap="com.example.demo.mapper.ArticleMapper.BaseMap"
columnPrefix="a_">
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!--多表查询-->
<select id="getUserAndArticleByUid" resultMap="BaseMap">
select u.*,a.id a_id,a.title a_title,a.content a_content,
a.createtime a_createtime,
a.updatetime a_updatetime from userinfo u left join articleinfo a
on u.id=a.uid where u.id=#{uid}
</select>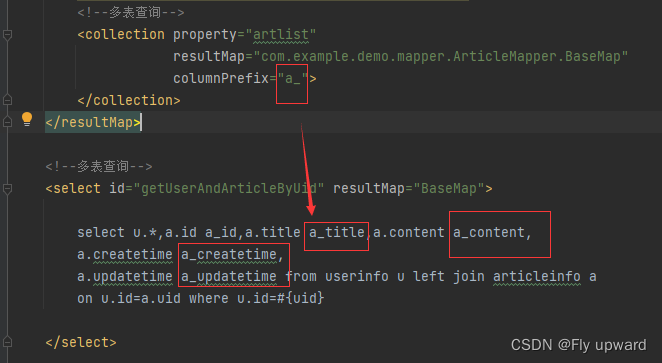
单元测试
@Test
void getUserAndArticleByUid() {
UserInfo userInfo = userMapper.getUserAndArticleByUid(1);
log.info("用户详情:" + userInfo);
}7.动态SQL使用
动态SQL是mybatis 的强大特性之一,能够完成不同条件的SQL拼接
7.1 <if> 标签
在填写个人信息时,会经常遇到一些必填项,一些非必填项,如下
注册分为两种字段:必填字段和⾮必填字段,那如果在添加⽤户的时候有不确定的字段传⼊,程序应该如何实现呢? 这个时候就需要使⽤动态标签 <if> 来判断了:
判断一个参数是否有值,如果没值,就会隐藏 if 中的SQL

现在有一张用户表
在新增用户的时候,将 photo 设为非比传参数

1)传入photo 时
mapper
//动态SQL,添加用户,photo为非必传参数
public int add2(UserInfo userInfo);UserMapper.xml
<!--动态SQL,添加用户-->
<insert id="add2">
insert into userinfo(username,password
<if test="photo !=null">
,photo
</if>
) values(#{name}, #{password}
<if test="photo !=null">
, #{photo}
</if>
)
</insert>注意 test 中的 photo 和 #{},是传⼊对象中的属性,不是数据库字段
单元测试
@Test
void add2() {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setName("杨通");
userInfo.setPassword("123");
userInfo.setPhoto("123.jpg");
int result = userMapper.add2(userInfo);
log.info("添加用户:" + result);
}添加结果


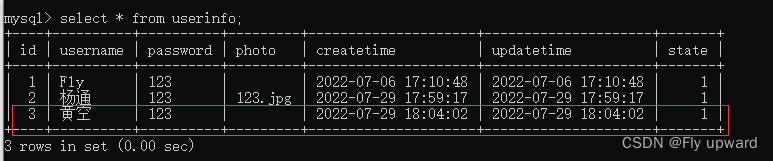
2)不传入 photo 时
不用像没使用动态SQL时,将 userInfo.setPhoto(""); 设为空,直接忽略不写就行了
@Test
void add2() {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setName("黄空");
userInfo.setPassword("123");
//userInfo.setPhoto("123.jpg");
int result = userMapper.add2(userInfo);
log.info("添加用户:" + result);
}动态SQL直接忽略photo,添加成功

7.2 <trim> 标签
最主要的作用:去除SQL语句前后多余的某个字符
语法:

<trim>标签中有如下属性:
prefix: 表示这个语句快,以prefix的值作为前缀
suffix:表示整个语句块,以suffix的值作为后缀
prefixOverrides:表示整个语句块要去除掉的前缀
suffixOverrides:表示整个语句块要去除掉的后缀
UserMapper
//动态SQL, <trim> 标签。添加用户,photo为非必传参数
public int add3(UserInfo userInfo);UserMapper.xml
<!--动态SQL,<trim> 标签。添加用户-->
<insert id="add3">
insert into userinfo
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="name != null">
<!--这里拼接的是数据库中的字段-->
username,
</if>
<if test="password != null">
password,
</if>
<if test="photo != null">
photo
</if>
</trim>
values
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="name != null">
#{name},
</if>
<if test="password != null">
#{password},
</if>
<if test="photo != null">
#{photo}
</if>
</trim>
</insert>单元测试
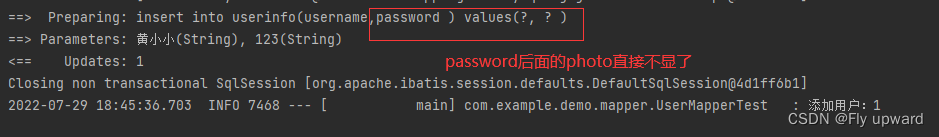
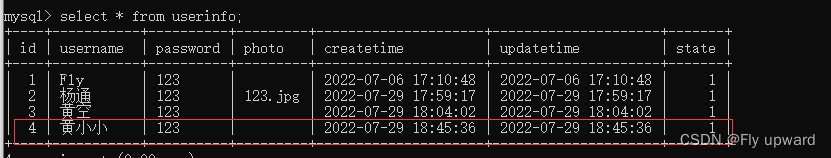
这里不传photo,看拼接的字段前的一个逗号是否还在
@Test
void add3() {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setName("黄小小");
userInfo.setPassword("123");
//userInfo.setPhoto("123.jpg"); 这里不传,看拼接的字段前的一个逗号是否还在
int result = userMapper.add2(userInfo);
log.info("添加用户:" + result);
}
7.3 <where> 标签
主要作用:实现查询中的 where SQL替换,它可以实现如果没有任何的查询条件,那么他可以因此查询中的 where SQL ,但如果存在查询中条件,那么会生成where的 SQL查询,并且使用 where 标签可以自动的去除最后一个 and字符。
1)SQL 替换
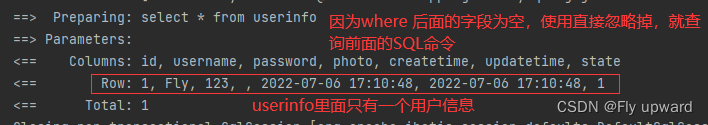
根据 id 查询用户:
<!-- 根据 id 查询用户 -->
<select id="getUserById" resultMap="BaseMap">
select * from userinfo
<where>
<if test="id != null">
id=#{id}
</if>
</where>
</select>
当传入的 id 为 null 时
@Test
void getUserById() {
UserInfo userInfo = userMapper.getUserById(null);
//Assertions.assertNotNull(userInfo);
log.info("查询行数:" + userInfo);
}
2)去除 and

或者通过 id 或者 username 来查询时,如果username 为空就会去掉
7.4 <set> 标签
作用:进行修改操作是,配合 if 来处理非必传字段,他的特点是主动去除最后一个英文逗号
语法:
update table_name
<set>
<if test="xxx">
...
</if>
...
</set>
where ...1)修改用户名
UserMapper
//动态SQL, <set> 标签。修改用户
public int update2(UserInfo userInfo);UserMapper.xml
<update id="update2">
update userinfo
<set>
<if test="name != null">
username=#{name},
</if>
<if test="password != null">
password = #{password},
</if>
<if test="photo != null">
photo = #{photo}
</if>
</set>
</update>单元测试
@Test
void update2() {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setId(1); //查找 id 为 1 的用户
userInfo.setName("fei"); // 将用户名修改为 fei
int result = userMapper.update2(userInfo);
log.info("修改结果: " + result);
}
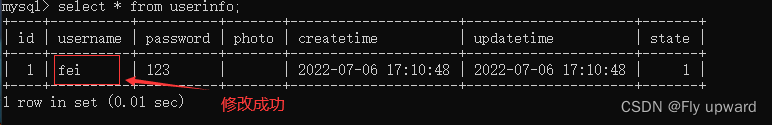
7.5 <foreach> 标签
对集合进⾏遍历时可以使⽤该标签。<foreach>标签有如下属性:
collection: 绑定方法参数中的集合,如List 、Set、Map或数组对象
item: 遍历时的每一个对象
open:语句块开头的字符串
close:语句块结束的字符串
separator:每次遍历之间间隔的字符串
示例:根据用户 id 来对用户进行删除
UserMapper
//动态SQL,<foreach>,删除多个用户
public int delId(List<Integer> ids);UserMapper.xml
<!--动态SQL,删除多个用户-->
<delete id="delId">
delete from userinfo where id in
<foreach collection="ids" open="(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>单元测试
@Test
void delId() {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
int result = userMapper.delId(list);
log.info("删除的行数:" + result);
}结果


总结
加载全部内容