React中useState使用
Ljwen_ 人气:0一、基本使用
useState是 react 提供的一个定义响应式变量的 hook 函数,基本语法如下:
const [count, setCount] = useState(initialCount)
- 它返回一个状态和一个修改状态的方法,状态需要通过这个方法来进行修改;
- initialCount 是我们传入的一个初始状态,它是惰性的,我们可以通过传一个函数来返回一个值当作初始状态,并且这个函数只会在初始渲染时执行一次;
const [count, setCount] = useState(() => {
const initialCount = someExpensiveComputation();
return initialCount
})
接下来把定义好的状态运用到页面:
import { useState } from 'react'
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
const handleClick = () => {
setCount(count + 1)
// 传入一个函数,更新的值是基于之前的值来执行
// setCount(count => count + 1)
}
return (
<div>
<h4>count: {count}</h4>
<button onClick={ handleClick }>点击更新状态</button>
</div>
)
}
页面渲染完成后,我们可以看到 count的值是 0,当我们点击按钮时,会将 count的值加 1,页面也同时更新;
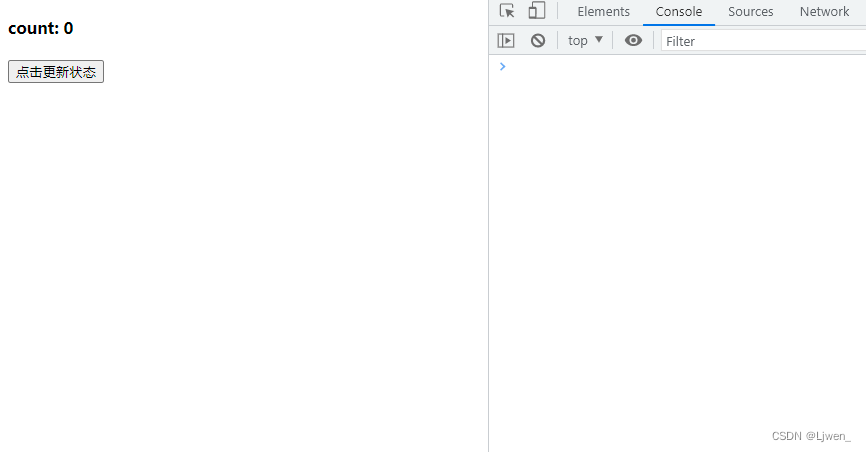
了解完基础用法后,我们可以思考几个问题;
setCount修改值时它是同步还是异步?- 连续调用
setCount会发生什么?
第一个问题:setCount修改值时它是同步还是异步?
const handleClick = () => {
console.log("value1: ", count)
setCount(count => count + 1)
console.log("value2: ", count)
}
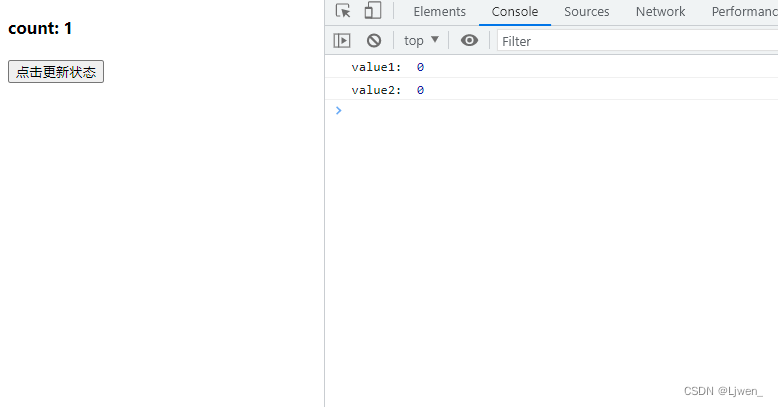
从图中我们可以看出,页面的值是更新了,但是控制台打印的是之前的值,这是不是也表示 setCount是异步的呢?我们换一种方法,用异步来修改状态;
const handleClick = () => {
console.log("value1: ", count)
setTimeout(() => {
setCount(count => count + 1)
console.log("value2: ", count)
}, 0)
}
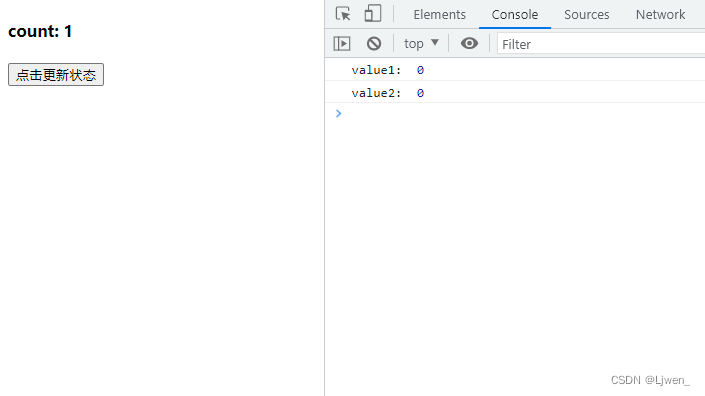
显然,异步修改状态跟同步修改状态的结果是一致的,这也表明了 setCount 是异步更新的;那我们要怎么拿到更新后的值呢,我们可以用另外一个 hook 函数 useRef,代码如下:
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
const countRef = useRef(count)
countRef.current = count
const handleClick = () => {
setCount(count => count + 1)
console.log("value3: ", count)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(countRef.current)
}, 0)
}
return (
<div>
<h4>count: {count}</h4>
<button onClick={handleClick}>点击更新状态</button>
</div>
)
}
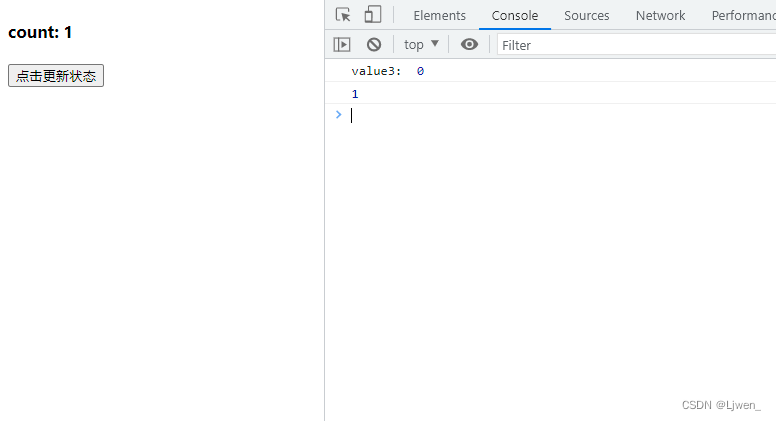
从图中我们可以看出,我们已经拿到了更新之后的值,useRef不仅可以用于访问 DOM 节点,也可以用来表示一个容器,current属性可以保存任何值,而且useRef返回的对象会在整个生命周期内保持;
第二个问题:连续调用 setCount会发生什么?
(1)传入一个基于状态的值
const handleClick = () => {
console.log("value1: ", count)
setCount(count + 1)
console.log("value2: ", count)
setCount(count + 1)
console.log("value3: ", count)
}
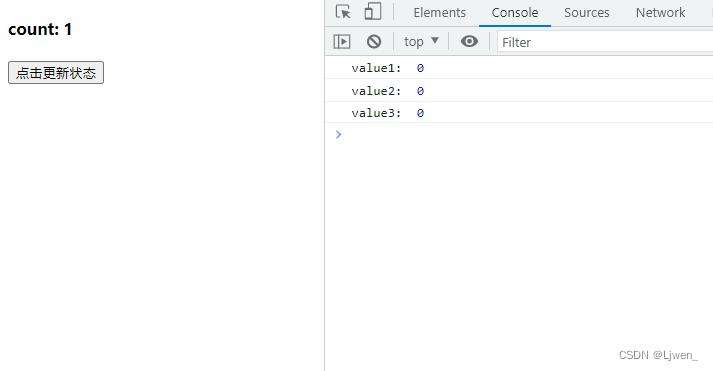
从图片可以看出,如果我们传入的是一个普通值,他只会进行最后一次更新;
(2)传入一个函数
const handleClick = () => {
console.log("value1: ", count)
setCount(count => count + 1)
console.log("value2: ", count)
setCount(count => count + 1)
console.log("value3: ", count)
}
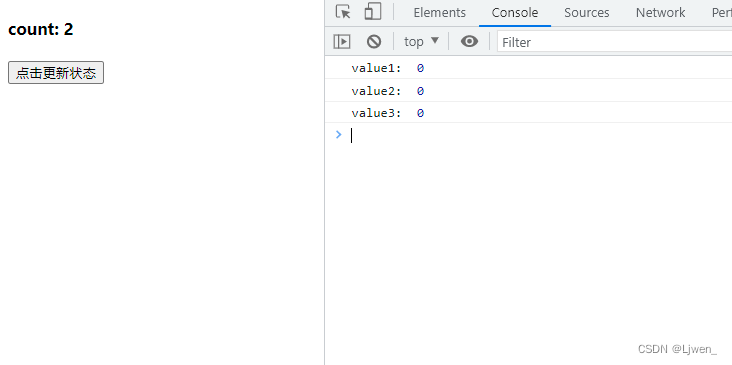
可以看出,传入一个函数的话,它会进行两次赋值,因为它更新的值是基于之前的值来执行,所以在开发中推荐使用函数传入的形式进行修改;
二、注意事项
1、复杂变量的修改
对于复杂类型的变量我们修改时需要重新定义,在原来数据的基础上修改不会引起组件的重新渲染,因为 React 组件的更新机制只进行浅对比,也就是更新某个复杂类型数据时只要它的引用地址没变,就不会重新渲染组件;举个例子
function App() {
const [arr, setArr] = useState([1])
const pushData = () => {
arr.push(4)
setArr(arr)
}
return (
<div>
<h4>{arr.join("-")}</h4>
<button onClick={pushData}>点击添加数组</button>
</div>
)
}
上面的代码在点击按钮时,视图不会发生变化,但是 arr的值是变化了,如果想修改这个数组,需要重新定义一个数组来修改,在原数组上的修改不会引起组件的重新渲染,React 组件的更新机制对只进行浅对比,也就是更新某个复杂类型数据时只要它的引用地址没变,就不会重新渲染组件;
const pushData = () => {
setArr([...arr, 4])
}
2、异步操作获取更新的值
在类组件里面,修改值时异步操作可以拿到更新后的值,但是在函数组件,异步获取是拿不到更新后的值的,举个例子对比一下:
类组件
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
count: 0
}
}
handleClick = () => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1
})
console.log(this.state.count)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(this.state.count)
})
}
render() {
return (
<>
<h4>count: {this.state.count}</h4>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>点击更新状态</button>
</>
);
}
}
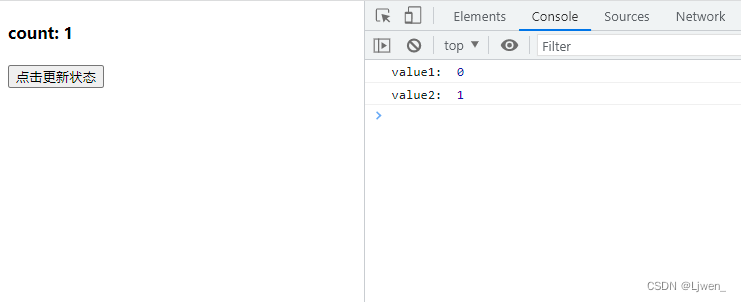
函数组件
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
const handleClick = () => {
setCount(count => count + 1)
console.log("value1: ", count)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("value2: ", count)
})
}
return (
<div>
<h4>count: {count}</h4>
<button onClick={handleClick}>点击更新状态</button>
</div>
)
}
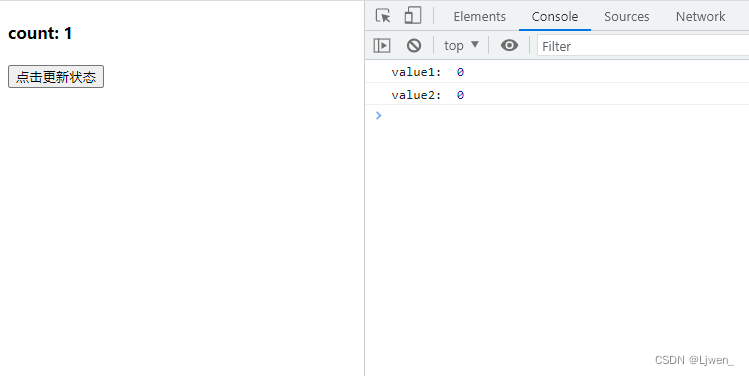
显然,在函数组件中是不能通过异步来获取更新的值,我们可以通过 useRef来获取;
const countRef = useRef(count)
countRef.current = count
const handleClick = () => {
setCount(count => count + 1)
console.log("value1: ", countRef.current)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("value2: ", countRef.current)
})
}
总结
加载全部内容