python魔术方法
henry_rhy 人气:0什么是魔术方法(魔法方法/特殊方法)
- 魔术方法都不需要手动去调用
- 是在特定的情况下触发的
- 魔术方法都是在python事先定义好的,在定义方法的时候,不要使用魔术方法的命名规范
- 魔术方法是双划线开头,双划线结尾的
一、python内置的基本魔术方法
init方法
init 是类在实例化时的方法
# 例如
class Mytest():
def __init__(self):
print("----这是魔术方法__init__")
Mytest()
call方法
__call__方法的作用 :实现对象可调用
1.没有实现 __call__方法时,对象是不可以被调用的
# 类
class Demo:
pass
# 判断对象是否可被调用,有个函数可以使用——callable
print(callable(Demo)) ======》 返回True,可被调用
# demo类创建出来的对象是否可被调用,是不能的被调用的
obj = Demo()
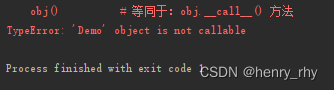
obj()执行结果:提示:‘Demo’ object is not callable ----- 没有__call__方法
2.如果要类创建对象出来的对象可别调用,就要用到__call__方法
class Demo:
def __call__(self, *args,**kwds):
print("这是__call__方法执行了")
print(callable(Demo))
# demo类创建出来的对象是否可被调用(不能被调用)
obj = Demo()
obj() # 等同于:obj.__call__() 方法
obj()
obj()
new 方法
__new__方法的作用 : 是创建对象的方法
__init__方法的作用 : 是用来初始化对象的方法
类的对象要能被调用:
首要new方法创建对象,然后通过init方法初始化
什么时候会需要用到New方法:
干预类实例化对象的过程
注意点:
- 一般情况不要重写new方法,除非有特定的需求需要使用new方法来实现
- 定义了new方法之后,需要调用父类的new来创建对象 并返回
class MyTest(object):
# 初始化对象
def __init__(self):
print('-------init------方法')
# 创建对象
def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
print('------new方法-------')
obj = super().__new__(cls) # 调用父类的new来创建对象
return obj # 并返回新的对象
obj = MyTest()bool(self)方法
定义当被 bool() 调用时的行为,应该返回 True 或 False
class Demo:
def __bool__(self):
"""内置函数bool(),获取对象的布尔值是会执行这个方法"""
return True
b = Demo()
# 获取对象的布尔值,返回True 或 False
print(bool(b)) =====》 返回 Truestr(self)方法
使用print去输出对象时,输出到控制台的内容是由__str__来决定的
class Demo:
def __str__(self):
"""
使用print去输出对象时,输出到控制台的内容是由__str__来决定的
"""
return 'zifuc'
b = Demo()
# str方法
s = str('123')
print(s) =======》 返回 123repr(self)方法
这个方法也是控制对象显示的,一般会显示对象的原始信息
class Demo:
def __repr__(self):
"""
这个方法也是控制对象显示的,一般会显示对象的原始信息
"""
return 'repr-number'
b = Demo()
# repr方法
s = repr('123')
print(s) =======》 返回 '123'len(self)方法
获取对象的长度
class Demo:
def __len__(self):
"""
这个方法是获取对象的长度
:return:
"""
return 3
b = Demo()
# 获取对象的长度
print(len(b)) =====》 返回 3hash(self)方法
返回对象的hash值
class Demo:
def __hash__(self):
"""
这个方法是获取hash值
:return:
"""
return 999
b = Demo()
# 获取hash值
print(hash(b)) =====》 返回 999二、python中容器类型的的魔术方法
setitem(self, key, value)方法
定义设置容器中指定元素的行为,语法:self[key] = value
class Mytest:
def __setitem__(self, key, value):
return setattr(self, key, value)
m = Mytest()
print(m.__dict__) 没有数据,为空字典
m.name = 'gddg' ==== 》 设置name属性,值为gddg
m['age'] = 18 ==== 》 设置age属性,值为18getitem(self, item)方法
定义获取容器中指定元素的行为,语法: self[key]
class Mytest:
def __getitem__(self,item):
return getattr(self,item)
m = Mytest()
print(m['name']) ==== 》 name属性,值为gddgdelitem(self, item)方法
定义删除容器中指定元素的行为,相当于 del self[key]
class Mytest:
def __delitem__(self,item):
delattr(self,item)
m = Mytest()
del m['name'] ==== 》 删除name属性contains(self, item)方法
定义当使用成员测试运算符(in 或 not in)时的行为, 返回 True 或 False
class MyTest:
def __contains__(self, item):
"""成员运算符触发的魔术方法"""
return True
a = MyTest()
b = MyTest()
print(a in b) =======》 返回 True迭代协议:__iter__方法
定义当迭代容器中的元素的行为
class IterClass:
def __iter__(self):
"""
__iter__方法的返回值必须是一个迭代器
"""
return iter([11, 22, 33, 44]) ===== 》返回一个迭代器
li = IterClass()
for i in li :
print(i )
for遍历对象:
1、执行对象的__iter__方法(返回迭代器)
2、在循环使用next对迭代器进行迭代三、python中算数运算符的魔术方法
add(a,b)方法 和 sub(a,b)方法
a = 1 b = 2 print(a + b) ======》 实际执行的是:a.__add__(a,b) print(a - b) ======》 实际执行的是:a.__sub__(a,b)
字符串类型的是否支持加减的操作
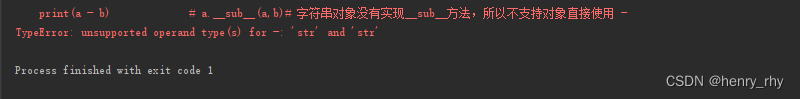
a = '123' b = '12' print(a + b) ======》 实际执行的是:a.__add__(a,b) print(a - b) ======》 实际执行的是:a.__sub__(a,b)
对字符串对象没有实现__sub__方法,所以不支持对象直接使用 -
自己在重新定义__sub__方法,实现对字符串对象的减法
class MyStr(str):
def __sub__(self, other):
return self.replace(other, '')
a = MyStr('1234')
b = MyStr('123')
print(a + b) ======= 》 返回 1234123
print(a - b) ======= 》 返回 4加载全部内容