pytest多进程或多线程测试
网名余先生 人气:1前言:
- 实际项目中的用例数量会非常多,几百上千;如果采用
单进程串行执行的话会非常耗费时间。假设每条用例耗时2s,1000条就需要2000s $\approx$ 33min;还要加上用例加载、测试前/后置套件等耗时;导致测试执行效率会相对低。 - 想象一下如果开发改动一块代码,我们需要回归一下,这时候执行一下自动化用例需要花费大半个小时或者好几个小时的时间,这是我们无法容忍的。
- 为了节省项目测试时间,需要多个测试用例同时
并行执行;这就是一种分布式场景来缩短测试用例的执行时间,提高效率。
分布式执行用例的原则:
- 用例之间是相互独立的,没有依赖关系,完全可以独立运行;
- 用例执行没有顺序要求,随机顺序都能正常执行;
- 每个用例都能重复运行,运行结果不会影响其他用例。
项目结构

测试脚本
# test1/test_1.py import time def test1_test1(): time.sleep(1) assert 1 == 1, "1==1" def test1_test2(): time.sleep(1) assert 1 == 1, "1==1" class TestDemo1: def test_inner_1(self): time.sleep(1) assert 1 == 1, "1==1" class TestDemo2: def test_inner_2(self): time.sleep(1) assert 1 == 1, "1==1" # test1/inner/test_3.py import time def test3_test1(): time.sleep(1) assert 1 == 1, "1==1" def test3_test2(): time.sleep(1) assert 1 == 1, "1==1" # test2/test_2.py import time def test2_test1(): time.sleep(1) assert 1 == 1, "1==1" def test2_test2(): time.sleep(1) assert 1 == 1, "1==1" # test2/inner/test_3.py import time def test4_test1(): time.sleep(1) assert 1 == 1, "1==1" def test4_test2(): time.sleep(1) assert 1 == 1, "1==1"
正常执行:需要8.10s

多进程执行用例之pytest-xdist
多cpu并行执行用例,直接加个-n参数即可,后面num参数就是并行数量,比如num设置为3
pytest -v -n num
参数:
- -n auto : 自动侦测系统里的CPU数目
- -n num : 指定运行测试的处理器进程数
多进程并行执行:耗时2.66s大大的缩短了测试用例的执行时间。
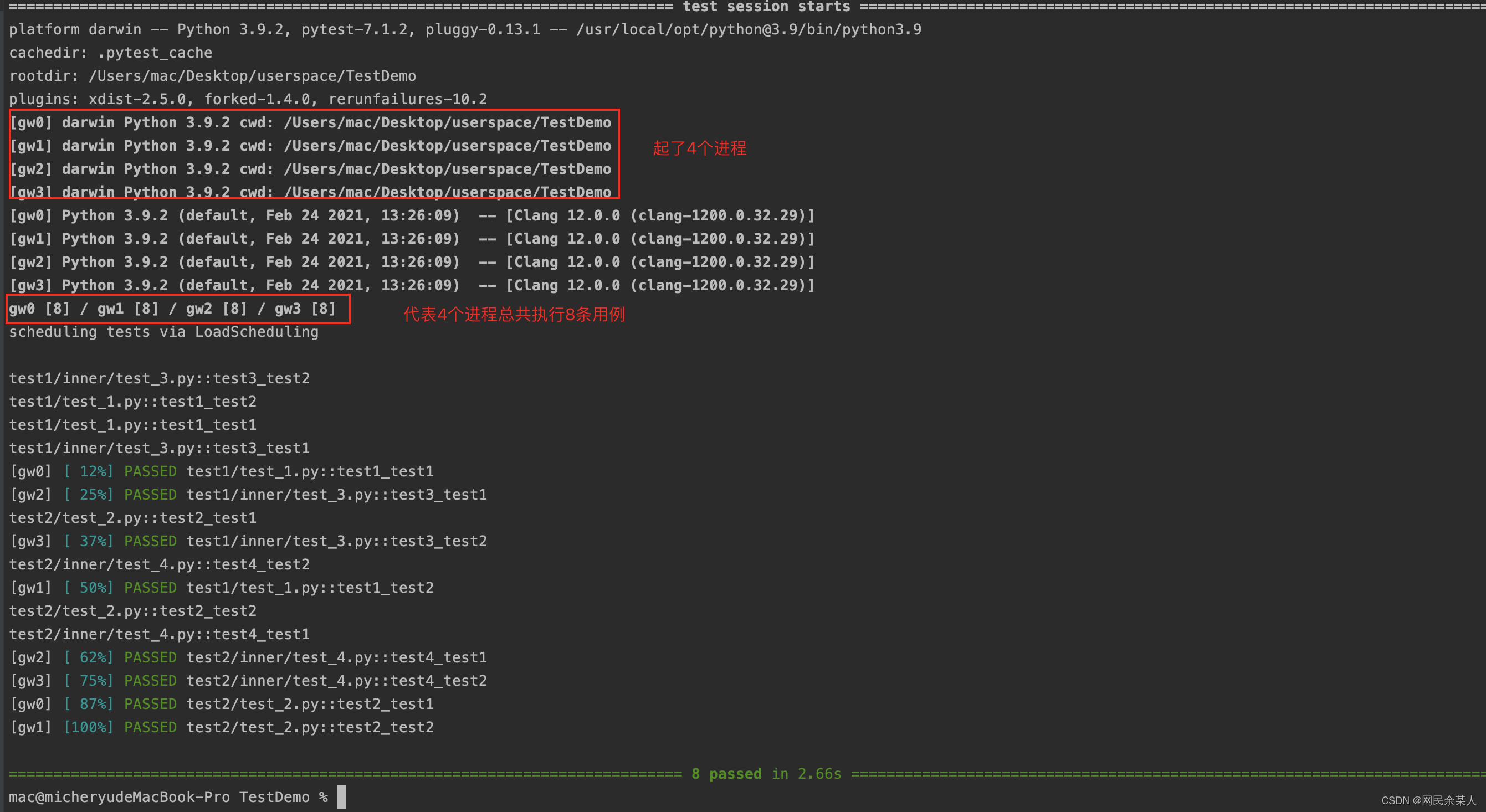
pytest-xdist分布式测试的原理:
xdist的分布式类似于一主多从的结构,master负责下发命令,控制slave;slave根据master的命令执行特定测试任务。
在xdist中,主是master,从是workers;xdist会产生一个或多个workers,workers都通过master来控制,每个worker相当于一个
mini版pytest执行器。master不执行测试任务,只对worker收集到的所有用例进行分发;每个worker负责执行测试用例,然后将执行结果反馈给master;由master统计最终测试结果。
pytest-xdist分布式测试的流程:
第一步:master创建worker
master在
测试会话(test session)开始前产生一个或多个worker。实际编译执行测试代码的worker可能是本地机器也可能是远程机器。
第二步:workers收集测试项用例
每个worker类似一个迷你型的
pytest执行器。worker会执行一个完整的
test collection过程。【收集所有测试用例的过程】然后把测试用例的
ids返回给master。【ids表示收集到的测试用例路径】master不执行任何测试用例。
注意:分布式测试(pytest-xdist)方式执行测试时不会输出测试用例中的print内容,因为master并不执行测试用例。
第三步:master检测workers收集到的测试用例集
master接收到所有worker收集的测试用例集之后,master会进行一些完整性检查,以确保所有worker都收集到一样的测试用例集(包括顺序)。
如果检查通过,会将测试用例的ids列表转换成简单的索引列表,每个索引对应一个测试用例的在原来测试集中的位置。
这个方案可行的原因是:所有的节点都保存着相同的测试用例集。
并且使用这种方式可以节省带宽,因为master只需要告知workers需要执行的测试用例对应的索引,而不用告知完整的测试用例信息。
第四步:master分发测试用例
有以下四种分发策略:命令行参数 --dist=mode选项(默认load)
each:master将完整的测试索引列表分发到每个worker,即每个worker都会执行一遍所有的用例。

load:master将大约$\frac{1}{n}$的测试用例以轮询的方式分发到各个worker,剩余的测试用例则会等待worker执行完测试用例以后再分发;每个用例只会被其中一个worker执行一次。
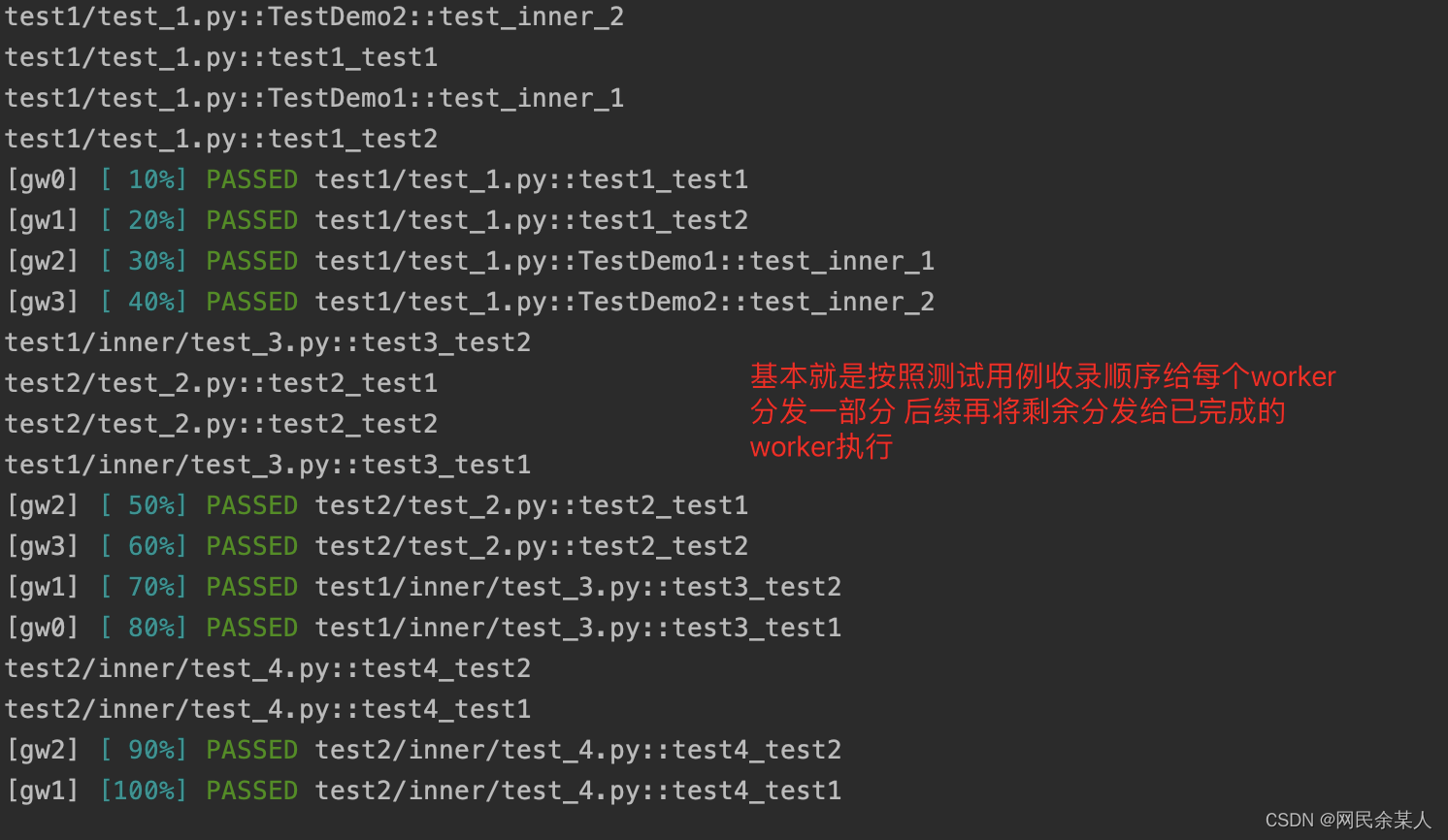
loadfile:master分发用例的策略为按ids中的文件名(test_xx.py/xx_test.py)进行分发,即同一个测试文件中的测试用例只会分发给其中一个worker;具有一定的隔离性。

loadscope:master分发用例对策略为按作用域进行分发,同一个模块下的测试函数或某个测试类中的测试函数会分发给同一个worker来执行;即py文件中无测试类的话(只有测试function)将该模块分发给同一个worker执行,如果有测试类则会将该文件中的测试类只会分发给同一个worker执行,多个类可能分发给多个worker;目前无法自定义分组,按类 class 分组优先于按模块 module 分组。

注意:可以使用pytest_xdist_make_scheduler这个hook来实现自定义测试分发逻辑。
如:想按目录级别来分发测试用例:
from xdist.scheduler import LoadScopeScheduling
class CustomizeScheduler(LoadScopeScheduling):
def _split_scope(self, nodeid):
return nodeid.split("/", 1)[0]
def pytest_xdist_make_scheduler(config, log):
return CustomizeScheduler(config, log)- 只需在最外层conftest中继承
xdist.scheduler.LoadScopeScheduling并重写_split_scope方法 - 重写钩子函数
pytest_xdist_make_scheduler
pytest -v -n 4 --dist=loadfile

第五步:worker执行测试用例
- workers 重写了
pytest_runtestloop:pytest的默认实现是循环执行所有在test_session这个对象里面收集到的测试用例。 - 但是在xdist里, workers实际上是等待master为其发送需要执行的测试用例。
- 当worker收到测试任务, 就顺序执行
pytest_runtest_protocol。 - 值得注意的一个细节是:workers 必须始终保持至少一个测试用例在的任务队列里, 以兼容
pytest_runtest_protocol(item, nextitem)hook的参数要求,为了将nextitem传给hook。 - master在worker执行完分配的一组测试后,基于测试执行时长以及每个worker剩余测试用例综合决定是否向这个worker发送更多的测试用例。
- worker会在执行最后一个测试项前等待master的更多指令。
- 如果它收到了更多测试项, 那么就可以安全的执行
pytest_runtest_protocol,因为这时nextitem参数已经可以确定。 - 如果它收到一个
shutdown信号, 那么就将nextitem参数设为None, 然后执行pytest_runtest_protocol
第六步:测试结束
- 当master没有更多执行测试任务时,它会发送一个
shutdown信号给所有worker。 - 当worker将剩余测试用例执行完后退出进程。
- 当workers在测试执行结束时,会将结果被发送回master,然后master将结果转发到其他
pytest hooks比如:pytest_runtest_logstart、pytest_runtest_logreport确保整个测试活动进行正常运作。 - master等待所有worker全部退出并关闭测试会话。
注意:pytest-xdist 是让每个 worker 进程执行属于自己的测试用例集下的所有测试用例。这意味着在不同进程中,不同的测试用例可能会调用同一个 scope 范围级别较高(例如session)的 fixture,该 fixture 则会被执行多次,这不符合 scope=session 的预期。
pytest-xdist 没有内置的支持来确保会话范围的 fixture 仅执行一次,但是可以通过使用锁定文件进行进程间通信来实现;让scope=session 的 fixture 在 test session 中仅执行一次。
示例:需要安装 filelock 包,安装命令pip install filelock
- 比如只需要执行一次login(或定义配置选项、初始化数据库连接等)。
- 当第一次请求这个fixture时,则会利用
FileLock仅产生一次fixture数据。 - 当其他进程再次请求这个fixture时,则不会重复执行fixture。
import pytest
from filelock import FileLock
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def login(tmp_path_factory, worker_id):
# 代表是单机运行
if worker_id == "master":
token = str(random())
print("fixture:请求登录接口,获取token", token)
os.environ['token'] = token
return token
# 分布式运行
# 获取所有子节点共享的临时目录,无需修改【不可删除、修改】
root_tmp_dir = tmp_path_factory.getbasetemp().parent
fn = root_tmp_dir / "data.json"
with FileLock(str(fn) + ".lock"):
if fn.is_file(): # 代表已经有进程执行过该fixture
token = json.loads(fn.read_text())
else: # 代表该fixture第一次被执行
token = str(random())
fn.write_text(json.dumps(token))
# 最好将后续需要保留的数据存在某个地方,比如这里是os的环境变量
os.environ['token'] = token
return token多线程执行用例之pytest-parallel
用于并行和并发测试的 pytest 插件
pip install pytest-parallel
常用参数配置
--workers=n:多进程运行需要加此参数, n是进程数。默认为1--tests-per-worker=n:多线程需要添加此参数,n是线程数
如果两个参数都配置了,就是进程并行;每个进程最多n个线程,总线程数:进程数*线程数
【注意】
在windows上进程数永远为1。
需要使用
if name == “main” :在命令行窗口运行测试用例会报错
示例:
- pytest test.py --workers 3 :3个进程运行
- pytest test.py --tests-per-worker 4 :4个线程运行
- pytest test.py --workers 2 --tests-per-worker 4 :2个进程并行,且每个进程最多4个线程运行,即总共最多8个线程运行。
import pytest
def test_01():
print('测试用例1操作')
def test_02():
print('测试用例2操作')
def test_03():
print('测试用例3操作')
def test_04():
print('测试用例4操作')
def test_05():
print('测试用例5操作')
def test_06():
print('测试用例6操作')
def test_07():
print('测试用例7操作')
def test_08():
print('测试用例8操作')
if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main(["-s", "test_b.py", '--workers=2', '--tests-per-worker=4'])pytest-parallel与pytest-xdist对比说明:
- pytest-parallel 比 pytst-xdist 相对好用,功能支持多;
- pytst-xdist 不支持多线程;
- pytest-parallel 支持python3.6及以上版本,所以如果想做多进程并发在linux或者mac上做,在Windows上不起作用(Workers=1),如果做多线程linux/mac/windows平台都支持,进程数为workers的值。
- pytest-xdist适用场景为:
- 不是线程安全的
- 多线程时性能不佳的测试
- 需要状态隔离
- pytest-parallel对于某些用例(如 Selenium)更好:
- 可以是线程安全的
- 可以对 http 请求使用非阻塞 IO 来提高性能
简而言之,pytest-xdist并行性pytest-parallel是并行性和并发性。
到此这篇关于pytest多进程或多线程执行测试的文章就介绍到这了。希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持。
加载全部内容