扁平数据转tree数据扁平化
灵扁扁 人气:0一、写在前面
有时我们拿到的数据的数据结构可能不是理想的,那么此时就要求前端程序员,具有改造数据的能力。例如拿到扁平的数据, 但我们要应用在 tree 树形组件或 Cascader 级联选择器组件中,这样的组件要求数据结构是非扁平的的具有层级递进关系的 tree 结构。
总之就是说,提供数据的接口给到的数据,未必符合要求,而当我们又无法令他人为为我们改变时,需求和要求就来到了前端程序员这里, 所以得具备这样的数据处理能力。
下面是将举两个数据改造的例子:
- 一是扁平化,具有层级递进关系的 tree 数据,转换为扁平结构的的 flat 数据
- 二是反扁平化,扁平结构的 flat 数据,转换为具有层级递进关系的 tree 数据
二、正文部分
2.1 扁平数据转为 tree 数据
扁平化函数
/**
* 扁平化:将具有层级递进关系结构的 tree 数据扁平化
*
* @param treeList 有层级递进关系结构的 tree 数据
* @param flatList 用于接收扁平化结果的变量
* @returns {*} 返回扁平化结果
*/
function treeToFlat (treeList, flatList) {
// flatList.length > 9999 是考虑底线保护原则,出于极限保护的目的设置的,可不设或按需设置。
if (flatList.length > 9999) {
return
}
treeList.map(e => {
flatList.push(e)
// 递归:有条件的自己调用自己,条件是 e.children.length 为真
if (e.children && e.children.length) {
treeToFlat(e.children, flatList)
}
})
// console.log('扁平化后:', flatList)
return flatList
}
2.2 tree 数据转为扁平数据
反扁平化函数
/**
* 反扁平化:将扁平结构的 flat 数据转换为具有层级递进关系结构的 tree 数据
*
* @param flatList 扁平结构的数据
* @param treeList 用于接收反扁平化结果的变量
* @returns {*} 返回反扁平化结果
*/
function flatToTree (flatList, treeList) {
flatList.map(e => {
// 以 e.pid===null,作为判断是不是根节点的依据,或者直接写死根节点(如果确定的话),
// 具体以什么作为判断根节点的依据,得看数据的设计规则,通常是判断层级或是否代表根节点的标记
if (e.pid === null) {
// 避免出现重复数据
const index = treeList.findIndex(sub => sub.id === e.id)
if (index === -1) {
treeList.push(e)
}
}
flatList.map(e2 => {
if (e2.pid === e.id) {
// 避免出现重复数据
const index = e.children.findIndex(sub => sub.id === e2.id)
if (index === -1) {
e.children.push(e2)
}
}
})
})
2.3 完整测试 demo
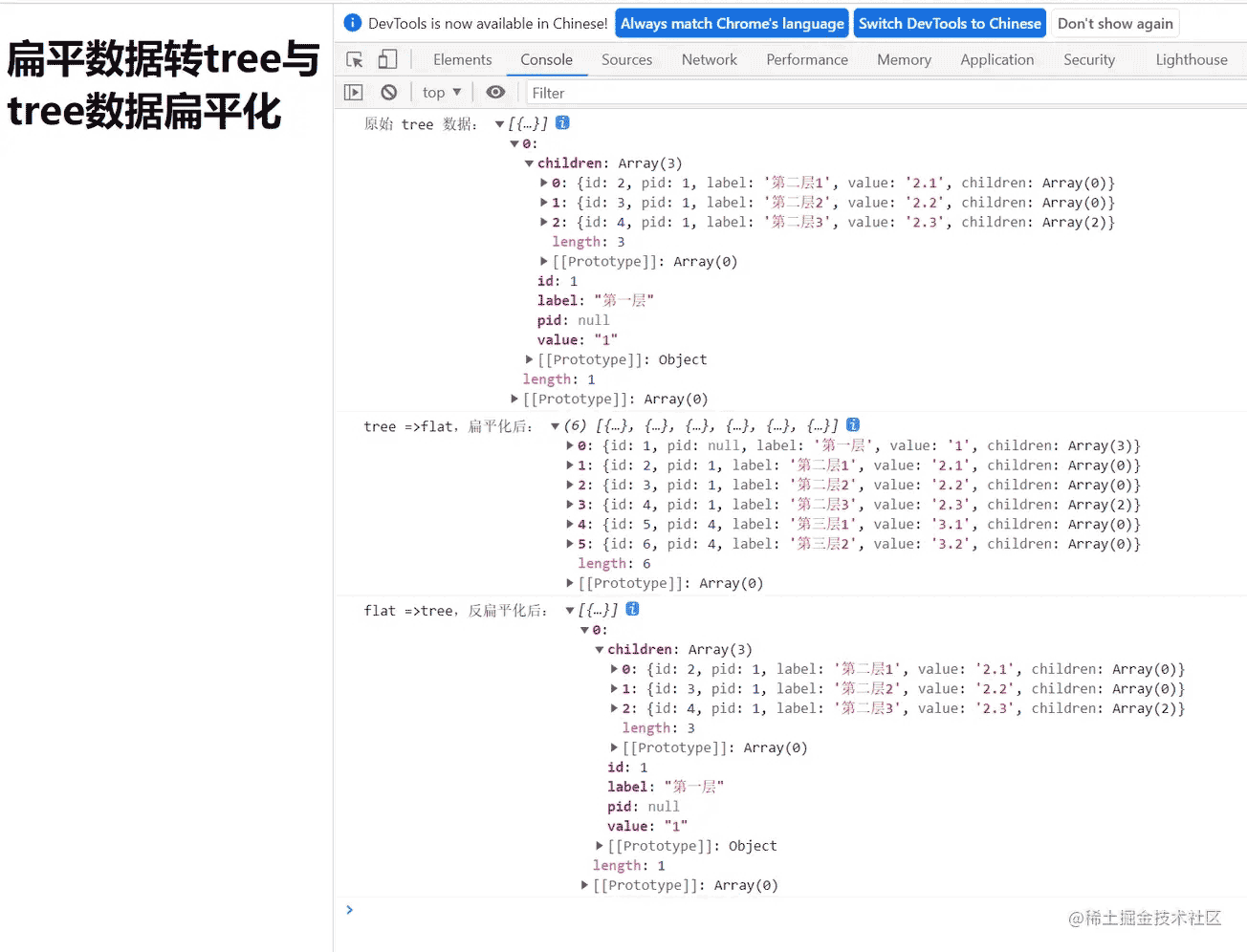
demo 测试结果截图如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<title>扁平数据转tree与tree数据扁平化 Demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>扁平数据转tree与tree数据扁平化</h1>
<script>
window.onload = function () {
test()
}
function test () {
let flatList = [],
treeList = [
{
id: 1,
pid: null,
label: '第一层',
value: '1',
children: [
{
id: 2,
pid: 1,
label: '第二层1',
value: '2.1',
children: []
},
{
id: 3,
pid: 1,
label: '第二层2',
value: '2.2',
children: []
},
{
id: 4,
pid: 1,
label: '第二层3',
value: '2.3',
children: [
{
id: 5,
pid: 4,
label: '第三层1',
value: '3.1',
children: []
},
{
id: 6,
pid: 4,
label: '第三层2',
value: '3.2',
children: []
},
]
},
]
}
]
console.log('原始 tree 数据:', JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(treeList)))
// 扁平化
console.log('tree =>flat,扁平化后:', treeToFlat(JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(treeList)), flatList))
// 反扁平化,SON.parse(JSON.stringify()) 为了实现深拷贝
console.log('flat =>tree,反扁平化后:', flatToTree(JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(flatList)), treeList))
}
/**
* 扁平化:将具有层级递进关系结构的 tree 数据扁平化
*
* @param treeList 有层级递进关系结构的 tree 数据
* @param flatList 用于接收扁平化结果的变量
* @returns {*} 返回扁平化结果
*/
function treeToFlat (treeList, flatList) {
// flatList.length > 9999 是考虑底线保护原则,出于极限保护的目的设置的,可不设或按需设置。
if (flatList.length > 9999) {
return
}
treeList.map(e => {
flatList.push(e)
// 递归:有条件的自己调用自己,条件是 e.children.length 为真
if (e.children && e.children.length) {
treeToFlat(e.children, flatList)
}
})
// console.log('扁平化后:', flatList)
return flatList
}
/**
* 反扁平化:将扁平结构的 flat 数据转换为具有层级递进关系结构的 tree 数据
*
* @param flatList 扁平结构的数据
* @param treeList 用于接收反扁平化结果的变量
* @returns {*} 返回反扁平化结果
*/
function flatToTree (flatList, treeList) {
flatList.map(e => {
// 以 e.pid===null,作为判断是不是根节点的依据,或者直接写死根节点(如果确定的话),
// 具体以什么作为判断根节点的依据,得看数据的设计规则,通常是判断层级或是否代表根节点的标记
if (e.pid === null) {
// 避免出现重复数据
const index = treeList.findIndex(sub => sub.id === e.id)
if (index === -1) {
treeList.push(e)
}
}
flatList.map(e2 => {
if (e2.pid === e.id) {
// 避免出现重复数据
const index = e.children.findIndex(sub => sub.id === e2.id)
if (index === -1) {
e.children.push(e2)
}
}
})
})
// console.log('反扁平化后:', treeList)
return treeList
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
三、写在后面
这两个扁平化与反扁平化写法,感觉还有值得优化的方法,但暂时想不到。
此外,递归的应用也是值得注意的地方。
我理解的递归:有条件的自己调用自己
加载全部内容