spring aop概念
御狐神 人气:0Spring容器包含两个重要的特性:面向切面编程(AOP)和控制反转(IOC)。面向切面编程是面向对象(OOP)的一种补充,在面向对象编程的过程中编程针对的目标是一个个对象,而面向切面编程中编程针对的目标是一个个切面。切面支持跨类型跨对象(如事务的切面可以加在任何地方)进行模块化。
前言
AOP是Spring的关键特性之一,虽然Spring的IOC特性并不依赖于AOP(意味着你可以只使用Spring的IOC特性而不使用AOP特性),但是二者结合起来可以灵活的实现很多中间件解决方案。比如我们经常使用的事务(@Transaction),就是通过AOP方案实现的。本文重点介绍AOP编程中的一些术语,这些术语不仅仅局限于Spring,它适用于所有的AOP编程。
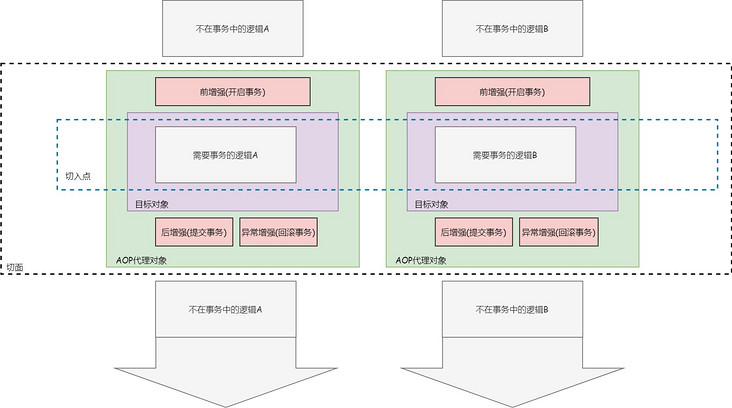
- 切面(Aspect):面向切面编程可以跨类跨对象进行切面编程,一个切面就是对一类横切关注点的模块化。
- 切入点(JoinPoint):程序执行过程中的一个点,如方法调用、字段访问和异常抛出等。
- 增强(Advice):用于对切面增强,包含前增强、后增强和环绕增强。大多数AOP框架会对切入点进行拦截,并在切入点维护一个拦截器链。
- 目标对象(TargetObject):包含一个或者多个切面的对象。
- AOP代理(AOPProxy):通过Java动态代理或者CGLib增强得到的代理对象。
- 织入(Weaving):将切面整合到完整的流执行流程。
Spring的AOP的功能和目标
Spring的AOP使用纯Java语言实现(如AspectJ就不是Java语言),不需要任何额外的编译流程,不需要修改类加载器,适用于任何Servlet容器和应用服务。Spring的AOP只支持方法拦截,不支持字段拦截,如果用户需要使用字段拦截,可以考虑引入AspectJ等类似的框架。
Spring的AOP框架和其它的框架有些不同,Spring的Aop框架不仅仅是为了提供一个AOP功能,它更重要的功能是和Spring的IOC容器结合,提供一些企业应用服务的解决方案(如事务等),我们可以和定义一个普通Bean一样的方式去定以一个切面。Spring的AOP不支持非常细粒度的AOP,只支持对容器中的Bean进行AOP,如果需要更细粒度的AOP,可以考虑使用AspectJ。Spring容器的一个优秀的特性就是非侵入性,所以你可以灵活的选择自己的AOP方案,不一定非要使用Spring的方案。
代理方式
Spring对实现接口的方法默认使用Java动态代理实现AOP拦截,对于非接口方法则会使用CGLIB字节码工具实现代理。
@AspectJ的支持
@AspectJ注解可以把一个普通的Java类声明为切面。@AspectJ注解是AspectJ5引入的注解,Spring虽然可以读取AspectJ5的注解用于切面元数据的配置,但是在运行的时候使用的仍然是Spring AOP进行代理,而没有使用AspectJ的编译器或者织入逻辑。我们会在后续讨论如何在Spring中使用AspectJ的编译器和织入逻辑。
启用@AspectJ
Spring默认没有启用AspectJ,如果你需要Spring支持@AspectJ注解对应的切面,可以通过在配置类上添加注解或者使用XML启用配置(AspectJ所在的包是:aspectjweaver.jar)。
通过Java注解启用AspectJ注解支持:
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppConfig {
}通过XML配置启用AspectJ注解
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
定义一个切面
当启用AspectJ支持之后,开发者定义的任何Aspect切面会自动地被检测到,然后Spring AOP会对切面进行拦截。下面两个例子展示了如何配置AspectJ切面,你可以通过添加@Component注解把切面Bean注册到Spring容器中。
<bean id="myAspect" class="org.xyz.NotVeryUsefulAspect">
<!-- configure properties of the aspect here -->
</bean>package org.xyz;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
@Aspect
public class NotVeryUsefulAspect {
}声明一个切入点
切入点程序运行过程中我们感兴趣的一个点,Spring的AOP框架只支持发现对Spring Bean方法上的切入点,因此你可以简单的把切入点理解为SpringBean的方法。
切入点确定感兴趣的连接点,从而使我们能够控制何时运行通知。springaop只支持springbean的方法执行连接点,因此可以将切入点看作与springbean上方法的执行相匹配。切入点声明由两部分组成:一部分是由名称和任何参数组成的签名,另一部分是确定我们感兴趣的方法执行的切入点表达式。在AOP的@AspectJ注释样式中,切入点签名由常规方法定义提供,切入点表达式由@pointcut注释指示(用作切入点签名的方法必须具有void返回类型)。切入点由两部分组成,一部分是用于区别不同切入点的标识(下面例子中的 private void anyOldTransfer() {} )),另外一部分是确定我们感兴趣的Bean方法的表达式(下面例子中的 @Pointcut("execution(* transfer(..))") ), 下面的例子展示了一个切入点的定义:
@Pointcut("execution(* transfer(..))") // the pointcut expression
private void anyOldTransfer() {} // the pointcut signatureSpring匹配切入点的语法使用了AspectJ5中的表达式语法,我们可以参考AspectJ文档相关的语法.
常见的切入点匹配表达
Spring支持下面常见的AspectJ切面定义语法:
- execution:用于匹配方法的连接点。
@Pointcut("execution(public * *(..))")
private void anyPublicOperation() {}- within:用于匹配类型内的方法。
@Pointcut("within(com.xyz.myapp.trading..*)")
private void inTrading() {}- this:匹配当前AOP代理对象的执行方法
@target(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional)
- target:target匹配目标对象的类型,即被代理对象的类型,例如A继承了B接口,则使用target("B"),target("A")均可以匹配到A
// 当前AOP对象实现了 IPointcutService接口的任何方法
@Pointcut("target(cn.javass.spring.chapter6.service.IPointcutService)")
private void anyPublicOperation() {}- args:用于限定切点方法的参数类型。
args(java.io.Serializable)
- @target:被代理对象应该包含指定的注解。
@target(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional)
- @args: 被代理对象的参数包含指定的注解。
@args(com.xyz.security.Classified)
- @within: 被代理的对象应包含指定注解
@within(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional)
- @annotation:切入点包含指定的注解。
@annotation(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional)
我们可以通过“&&”和“||”对多个条件进行组合,AspectJ还有很多其它的表达式,但是Spring不支持除上述表达式以外的其它表达式。AspectJ其它表达式包含: call, get, set, preinitialization, staticinitialization, initialization, handler, adviceexecution, withincode, cflow, cflowbelow, if, @this, @withincode等。
我们在使用Spring的代理方法之前,应该知道其代理原理。Java动态代理只能拦截public接口方法上的调用,CGLib只能拦截public、protected和defult方法。如果你需要更深层次的拦截,可以考虑使用底层的Aspectj。
切面的增强
我们在上面的步骤定义好了一个切入点,我们现在就可以对这个切入点进行额外操作,这些额外操作被称为增强,Spring支持四种增强方式:前增强、后增强、异常增强和环绕增强。Spring支持在增强方法的定义上直接定义切入点。
前增强BeforeAdvice
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
@Aspect
public class BeforeExample {
@Before("com.xyz.myapp.CommonPointcuts.dataAccessOperation()")
public void doAccessCheck() {
// ...
}
}import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
@Aspect
public class BeforeExample {
@Before("execution(* com.xyz.myapp.dao.*.*(..))")
public void doAccessCheck() {
// ...
}
}后增强
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
@Aspect
public class AfterReturningExample {
@AfterReturning(
pointcut="com.xyz.myapp.CommonPointcuts.dataAccessOperation()",
returning="retVal")
public void doAccessCheck(Object retVal) {
// ...
}
}异常增强
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
@Aspect
public class AfterThrowingExample {
@AfterThrowing(
pointcut="com.xyz.myapp.CommonPointcuts.dataAccessOperation()",
throwing="ex")
public void doRecoveryActions(DataAccessException ex) {
// ...
}
}环绕增强
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
@Aspect
public class AroundExample {
@Around("com.xyz.myapp.CommonPointcuts.businessService()")
public Object doBasicProfiling(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
// start stopwatch
Object retVal = pjp.proceed();
// stop stopwatch
return retVal;
}
}代理机制
我们前面说过,Spring AOP通过动态代理和CGLIB实现AOP对象的代理。我们可以通过如下配置设置动态代理全部走CGLIB。
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<!-- other beans defined here... -->
</aop:config>代理工厂的使用
Spring AOP实现代理的核心类是 AspectJProxyFactory ,我们可以使用这个类编程式生成代理对象:
// create a factory that can generate a proxy for the given target object AspectJProxyFactory factory = new AspectJProxyFactory(targetObject); // add an aspect, the class must be an @AspectJ aspect // you can call this as many times as you need with different aspects factory.addAspect(SecurityManager.class); // you can also add existing aspect instances, the type of the object supplied must be an @AspectJ aspect factory.addAspect(usageTracker); // now get the proxy object... MyInterfaceType proxy = factory.getProxy()
加载全部内容