Spring Bean作用域 生命周期
倔强的牛角 人气:0一、Spring Bean 作用域
常规的 Spring IoC 容器中Bean的作用域有两种:singleton(单例)和prototype(非单例)
注:基于Web的容器还有其他种作用域,在这就不赘述了。
singleton(单例)
singleton是Spring默认的作用域。当 Bean 的作用域为 singleton 时,Spring IoC 容器中只会存在一个共享的 Bean 实例。可以更好地重用对象,节省重复创建对象的开销。- 设置方式:将 <bean> 元素的 scope 属性设置为
singleton(其实也可以不用设置,因为spring默认就是单例模式)
案例1
1.创建Dept类
public class Dept {
//部门编号
private int deptNo;
//部门名称
private String deptName;
}
2.编写Spring配置文件,并将scope 属性设置为singleton
<bean id="dept" class="com.bighorn.pojo.Dept" scope="singleton"> </bean>
3.编写运行程序
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取IoC容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//从容器中获取对象
Dept dept1 = context.getBean("dept", Dept.class);
Dept dept2 = context.getBean("dept", Dept.class);
//打印对象
System.out.println(dept1);
System.out.println(dept2);
}
4.结果如下,可以发现打印出的是同一个对象
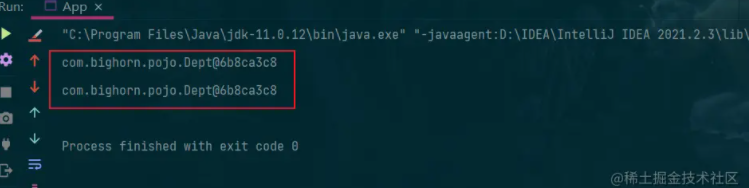
prototype(原型)
prototype表示原型(非单例)模式。当 Bean 的作用域为 prototype时,Spring 容器会在每次请求该 Bean 时,都创建一个新的 Bean 实例。- 设置方式:将 <bean> 元素的 scope 属性设置为
prototype
案例2
1.只需修改scope 属性为prototype,其他代码不变。
<bean id="dept" class="com.bighorn.pojo.Dept" scope="prototype"> </bean>
2.运行结果如下
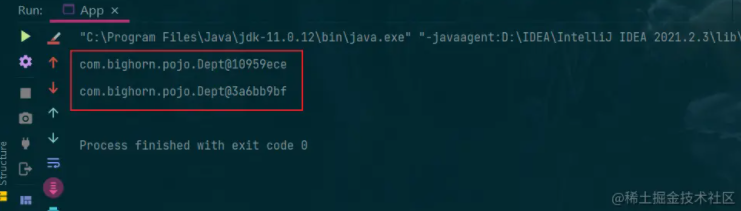
小结
spring bean默认为单例,避免了对象的频繁创建与销毁,达到了bean对象的复用,性能高。
像表现层、业务层、数据层、工具类对象只需要调用方法,比较适合交给Spring IoC容器管理
但是像那种需要封装实例的域对象,因为会引发线程安全问题,不适合交给Spring IoC容器管理。
二、Spring Bean生命周期
Spring Bean生命周期:Spring Bean 对象从创建到销毁的整体过程。
Spring Bean生命周期大致可以分为以下 5 个阶段:1.Bean 的实例化、2.Bean 属性赋值、3.Bean 的初始化、4.Bean 的使用、5.Bean 的销毁
Spring 根据 Bean 的作用域来选择 Bean 的管理方式。
- 对于 singleton 作用域的 Bean ,Spring IoC 容器能够一直追踪bean的生命周期;
- 对于 prototype 作用域的 Bean ,Spring IoC 容器只负责创建,然后就将 Bean 的实例交给客户端代码管理,Spring IoC 容器将不再跟踪其生命周期。
综上所述: 为了更好研究如何控制bean周期,下面案例中创建的bean默认都使用单例模式。
如何关闭容器
由于ApplicationContext类中没有关闭容器的方法,所以想要关闭容器需要用到ApplicationContext的子类——ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类。该类又有两种方法可以关闭容器
1、close关闭容器
close()方法,在调用的时候关闭容器
//获取 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//调用close方法关闭容器
context.close();
2、注册钩子关闭容器
registerShutdownHook()方法,在JVM退出前调用关闭容器
//获取 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//调用注册狗子关闭容器
context.registerShutdownHook();
生命周期回调
Bean 的生命周期回调方法主要有两种:
- 初始化回调方法:在 Spring Bean 被初始化后调用,执行一些自定义的回调操作。
- 销毁回调方法:在 Spring Bean 被销毁前调用,执行一些自定义的回调操作。
我们可以通过以下 2种方式自定义 Bean 的生命周期回调方法:
- 通过接口实现
- 通过 XML 配置实现
通过接口设置生命周期
我们可以在 Spring Bean 的 Java 类中,通过实现 InitializingBean 和 DisposableBean 接口,指定 Bean 的生命周期回调方法。
案例1
1.创建User类,并实现InitializingBean, DisposableBean接口,重写afterPropertiesSet()和destroy()方法。代码如下
/**
* 继承接口,程序初始化回调和销毁回调方法
*/
public class User implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
String name;
int age;
//setter方法
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//初始化回调方法
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("这是初始化回调方法");
}
//销毁回调方法
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("这是销毁回调方法");
}
//toString方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
2.编写spring配置文件
<bean id="user" class="com.bighorn.pojo.User">
<property name="name" value="bighorn"/>
<property name="age" value="18"/>
</bean>
3.编写运行程序
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//从容器中获取对象
User user = context.getBean("user", User.class);
//使用bean
System.out.println(user);
//调用close方法关闭容器
context.close();
}
}
4.运行结果如下
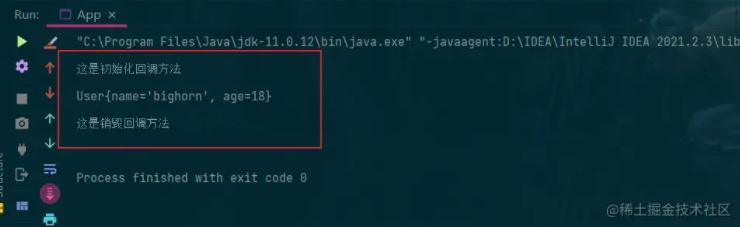
通过xml设置生命周期
注意:由于通过接口设置生命周期的方式会导致代码的耦合性过高,所以通常情况下,我们会通过xml设置生命周期。
通过 <bean> 元素中的 init-method 和 destory-method 属性,指定 Bean 的生命周期回调方法。
案例2
1.创建User类,这次不需要继承那两个接口了,但要在添加两个普通方法(方法名可任意):init()和destory()代表初始化和销毁方法。代码如下
/**
* 通过XML配置指定回调方法
*/
public class User {
String name;
int age;
//setter方法
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//初始化回调方法
public void init() throws Exception {
System.out.println("这是初始化回调方法");
}
//销毁回调方法
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("这是销毁回调方法");
}
//toString方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
2.编写spring配置文件,在<bean>元素里添加init-method和destroy-method属性,并指定User类中自定义的init和destory方法(关键)
<!--通过XML配置指定回调方法-->
<bean id="user" class="com.bighorn.pojo.User" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="name" value="bighorn"/>
<property name="age" value="18"/>
</bean>
3.运行程序和运行结果都与案例1相同,这里就少些笔墨介绍了
加载全部内容