C++类与封装
清风自在 流水潺潺 人气:0一、类的组合
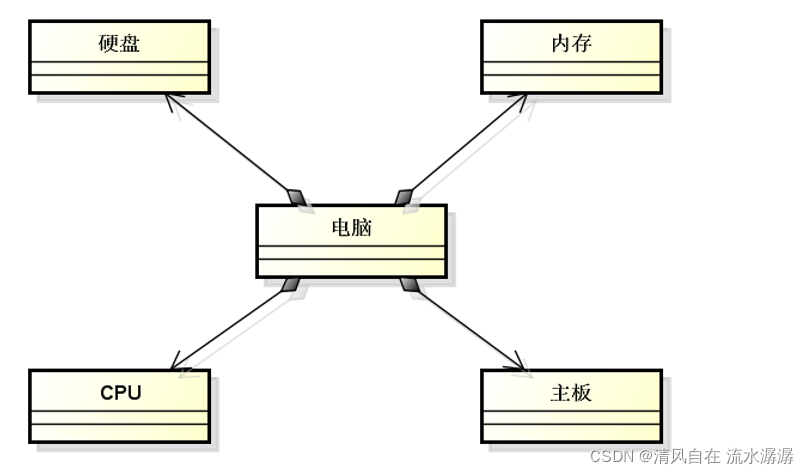
电脑一般而言是由 CPU,内存,主板,键盘和硬盘等部件组合而成。
二、类的封装
类通常分为以下两个部分
- 类的实现细节
- 类的使用方式
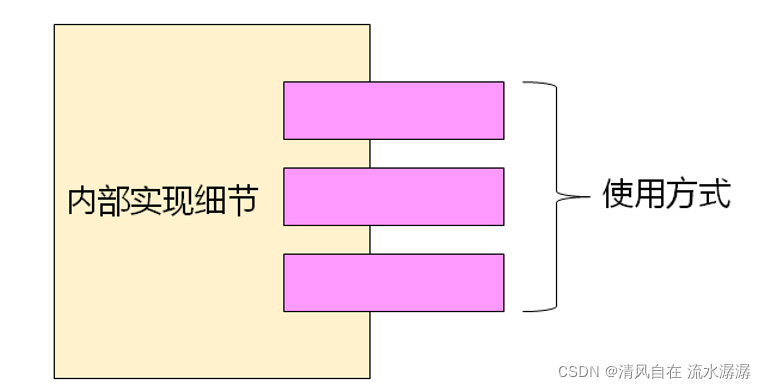
- 当使用类时,不需要关心其实现细节
- 当创建类时,才需要考虑其内部实现细节
例:
普通用户使用手机
- 只需要学习如何发短信,打电话,拍照,等等
手机开发工程师
- 需要考虑手机内部的实现细节
封装的基本概念
根据经验:并不是类的每个属性都是对外公开的
- 如:女孩子不希望外人知道自己的体重和年龄
- 如:男孩子不希望别人知道自己的身高和收入
而一些类的属性是对外公开的
- 如:人的姓名,学历,国籍,等
必须在类的表示法中定义属性和行为的公开级别
- 类似文件系统中文件的权限
C++中类的封装
- 成员变量:C++中用于表示类属性的变量
- 成员函数:C++中用于表示类行为的函数
- C++中可以给成员变量和成员函数定义访问级别
public
- 成员变量和成员函数可以在类的内部和外界访问和调用
private
- 成员变量和成员函数只能在类的内部被访问和调用
下面看一段类成员的访问属性的代码:
#include <stdio.h>
struct Biology
{
bool living;
};
struct Animal : Biology
{
bool movable;
void findFood()
{
}
};
struct Human : Animal
{
void sleep()
{
printf("I'm sleeping...\n");
}
void work()
{
printf("I'm working...\n");
}
};
struct Girl : Human
{
private:
int age;
int weight;
public:
void print()
{
age = 22;
weight = 48;
printf("I'm a girl, I'm %d years old.\n", age);
printf("My weight is %d kg.\n", weight);
}
};
struct Boy : Human
{
private:
int height;
int salary;
public:
int age;
int weight;
void print()
{
height = 175;
salary = 9000;
printf("I'm a boy, my height is %d cm.\n", height);
printf("My salary is %d RMB.\n", salary);
}
};
int main()
{
Girl g;
Boy b;
g.print();
b.age = 19;
b.weight = 120;
//b.height = 180;
b.print();
return 0;
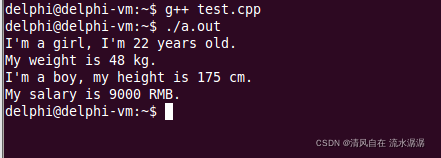
}下面为输出结果:
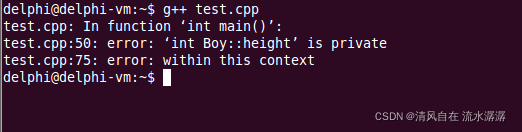
注意:如果我们访问 boy 里面的 height,因为是 private,所以编译时就会报如下错误:
三、类成员的作用域
类成员的作用域
- 类成员的作用域都只在类的内部,外部无法直接访问
- 成员函数可以直接访问成员变量和调用成员函数
- 类的外部可以通过类变量访问 public 成员
- 类成员的作用域与访问级别没有关系
注:C++ 中用 struct 定义的类中所有成员默认为 public
下面看一段类成员的作用域的代码:
#include <stdio.h>
int i = 1;
struct Test
{
private:
int i;
public:
int j;
int getI()
{
i = 3;
return i;
}
};
int main()
{
int i = 2;
Test test;
test.j = 4;
printf("i = %d\n", i); // i = 2;
printf("::i = %d\n", ::i); // ::i = 1;
// printf("test.i = %d\n", test.i); // Error
printf("test.j = %d\n", test.j); // test.j = 4
printf("test.getI() = %d\n", test.getI()); // test.getI() = 3
return 0;
}下面为输出结果:
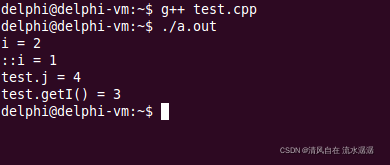
::i 意味着访问默认命名空间中的 i 变量,默认的命名空间就是全局作用域。
四、小结
- 类通常可以分为使用方式和内部细节两部分
- 类的封装机制使得使用方式和内部细节相分离
- C++ 中通过定义类成员的访问级别实现封装机制
- public 成员可以在类的内部和外界访问和调用
- private 成员只能在类的内部被访问和调用
加载全部内容