Java中国象棋游戏
Seven、琪 人气:0实现一个小游戏需要知道从哪里下手,一步步实现和完善,对于一个中国象棋的小游戏,我们可以按这样的顺序展开:
一、界面
下棋的棋盘首先要准备好,这就是一个合适大小合适比例合适位置的界面,然后在窗体上画上(没错drawLine的那种画上)n条直线和斜线,具体数值根据你的界面大小设置。这样画出的界面整齐好看~
public void paint(Graphics g){
super.paint(g);//重写画图函数
Font f=new Font("微软雅黑",Font.BOLD,30);
g.setFont(f);
g.drawRect(60, 50, 500, 560);//外圈
g.drawRect(70, 60, 480, 540);//内圈
//横线部分
int length=60;
for(int i=0;i<9;i++){
g.drawLine(70, length, 550, length);
length+=60;
}
//中间汉字
g.drawString("楚河", 160, 340);
g.drawString("汉界", 400, 340);
//竖线部分
length=130;
for(int i=0;i<7;i++){
//上半部分竖线
g.drawLine( length,60, length,300);
//下半部分竖线
g.drawLine( length,360, length,600);
length+=60;
}
//上半部分九宫格斜线
g.drawLine(250, 60, 370, 180);
g.drawLine(370, 60, 250, 180);
//下半部分九宫格斜线
g.drawLine(250, 480, 370, 600);
g.drawLine(250, 600, 370, 480);
}二、按钮
画好棋盘之后加上功能按钮,这个时候的功能暂时不考虑实现,可以根据喜好随意添加。这里推荐将按钮类型设置成数组,便于及时增删。
//添加到面板上
String[] type = {"开始游戏","重新开始","认 输","悔 棋"};
for(int i=0;i<type.length;i++){
Button btn = new Button(type[i]);
btn.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(150,50));
anniu.add(btn);
}
这个时候你会发现在加按钮的地方贴的十分紧凑,我的解决办法是在这一块面板上再加一个面板设置为白色覆盖在上面,这样根据面板的流式布局按钮就会下移,调整空白面板的宽度可以改变按钮的位置。
三、加棋子
将找到的棋子图片加到棋盘交叉的位置上才是给棋盘注入灵魂,将所有的十四类图片加到package中以便程序之后可以在其他电脑上运行(这里推荐png格式,jpg格式会有方形边框)。
接下来分三步走
1.创建一个10行9列的整数数组,用来存储每个位置的数据;
2.创建一个长度为14的Image数组,用来与棋子类型对应;
3.遍历整数数组画出对应的棋子;
这是棋盘的直观图,也就是我们的整数数组的初始值:
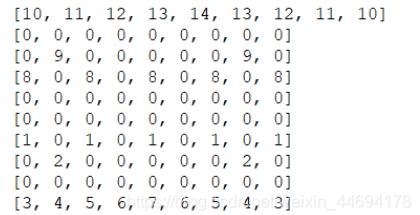
将Image与棋子图片对应:
//初始化给每个chess定义
for(int k=0; k<14; k++){
chess[k] = new ImageIcon(this.getClass().getResource((k+1)+".png")).getImage();
}遍历画图:
//根据棋盘布局
for(int i=0;i<place.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<place[0].length;j++){
if(place[i][j] >0){
bg.drawImage(chess[place[i][j]-1], chessX+60*j, chessY+60*i, 50, 50, null);
}
}
}四、实现棋子的移动
通过函数获得鼠标拖动前后两个点所代表的棋盘上的位置,并将这两个位置的二维数组的值交换,然后重新绘图实现棋子的移动。
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
x1 = e.getX();
y1 = e.getY();
x1 = getj(x1);
y1 = geti(y1);
}
public void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e) {
x2 = e.getX();
y2 = e.getY();
x2 = getj(x2);
y2 = geti(y2);
}
//根据点的坐标得到其代表的位置,具体参数可以微调,我的格子是60x60大小
public int getj(int x){
return (x-50)/60;
}
public int geti(int y){
return (y-40)/60;
}这个时候遇到的状况就是你每次移动一次之后,整个界面都要重绘一次,而画面是直接画在窗体上的,数据会直接传到电脑硬件,这样一来画图速度就慢了,所以会出现每走一步界面就闪烁一次的情况,这种情况下,我们可以将画面先存在缓存中,就不经过硬件直接画出来,这样效率就可以明显提高。
BufferedImage buffer = new BufferedImage(this.getWidth(), this.getHeight(), BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB); Graphics bg = buffer.getGraphics(); //这个中间写的是你画界面的方法,也就是上面提到的paint方法内部 //...... //绘制缓存到窗体上 g.drawImage(buffer, 0, 0, null);
五、判断胜负
率先吃掉对方帥或将的队伍获胜,写一个函数判断谁胜谁负显示胜局,同时将数据初始化为0,准备再来一局:
(showMessageDialog方法可以直接跳出一个框)
//判断游戏结束并显示胜局
public void isWine() {
System.out.println(place[y1][x1]+" "+place[y2][x2]);
if (place[y2][x2]==7&&place[y1][x1]!=0) {
place[y2][x2] = place[y1][x1];
place[y1][x1] = 0;
UI.repaint();
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "黑方 胜利!");
again();
} else if(place[y2][x2]==14&&place[y1][x1]!=0) {
place[y2][x2] = place[y1][x1];
place[y1][x1] = 0;
UI.repaint();
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "红方 胜利!");
again();
}
}
//游戏结束时要重绘
public void again(){
for(int i=0; i<place.length; i++){
for(int j=0; j<place[0].length; j++){
place[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}六、按钮“开始游戏”和“重新开始”的实现
加动作监听器
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
type = e.getActionCommand();
if("开始游戏".equals(type)||"重新开始".equals(type)){
x=0;
count = 1;//这里要把每次的走棋方刷新,认输时也需要刷新
init();
UI.repaint();
}
}
//初始化place坐标
public void init(){
/*红兵 1.png
*红炮 2.png
*红車 3.png
*红马 4.png
*红相 5.png
*红仕 6.png
*红帥 7.png
*黑卒 8.png
*黑炮 9.png
*黑車 10.png
*黑马 11.png
*黑象 12.png
*黑士 13.png
*黑将 14.png
*/
for(int i=0;i<place.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<place[0].length;j++){
place[i][j] = 0;
}
}
place[0][0] = 10; place[9][0] = 3;
place[0][1] = 11; place[9][1] = 4;
place[0][2] = 12; place[9][2] = 5;
place[0][3] = 13; place[9][3] = 6;
place[0][4] = 14; place[9][4] = 7;
place[0][5] = 13; place[9][5] = 6;
place[0][6] = 12; place[9][6] = 5;
place[0][7] = 11; place[9][7] = 4;
place[0][8] = 10; place[9][8] = 3;
place[2][1] = 9; place[7][1] = 2;
place[2][7] = 9; place[7][7] = 2;
place[3][0] = 8; place[6][0] = 1;
place[3][2] = 8; place[6][2] = 1;
place[3][4] = 8; place[6][4] = 1;
place[3][6] = 8; place[6][6] = 1;
place[3][8] = 8; place[6][8] = 1;
} 这里的init函数是给整数二维数组初始化为开局后遍历可以加上棋子的状态。
七、加规则
//规定各个棋子的移动规则
public boolean rule(int gi, int gj,int si, int sj){
int x = place[gi][gj];
int y = place[si][sj];
int start, end;
//判断为何种棋子
//車:只能走直线
if(x == 3||x == 10){
if(gi != si&&gj != sj) return false;
else if(gi == si){
start = Math.min(gj, sj);
end = Math.max(gj, sj);
for(int m = 1; m < end - start; m++){
if(place[gi][start+m] != 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
else if(gj == sj){
start = Math.min(gi, si);
end = Math.max(gi, si);
for(int m = 1; m < end - start; m++){
if(place[start+m][gj] != 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
else return true;
}
//马:走日,且某个位置不可以有棋子
else if(x == 4||x == 11){
//下
if(si - gi == 2&&Math.abs(gj-sj) == 1&&place[gi+1][gj] == 0) return true;
//上
else if(gi - si == 2&&Math.abs(gj-sj) == 1&&place[gi-1][gj] == 0) return true;
//右
else if(sj - gj == 2&&Math.abs(gi-si) == 1&&place[gi][gj+1] == 0) return true;
//左
else if(gj - sj == 2&&Math.abs(gi-si) == 1&&place[gi][gj-1] == 0) return true;
//否则不可以走
else return false;
}
//相:走田,且不能过河
else if(x == 5||x == 12){
//左上
if(gi - si == 2&&gj - sj == 2&&place[gi-1][gj-1] == 0){
if((x == 5&&si >= 5)||(x == 12&&si < 5)) return true;
else return false;
}
//右上
else if(gi - si == 2&&sj - gj == 2&&place[gi-1][gj+1] == 0){
if((x == 5&&si >= 5)||(x == 12&&si < 5)) return true;
else return false;
}
//左下
else if(si - gi == 2&&gj - sj == 2&&place[gi+1][gj-1] == 0){
if((x == 5&&si >= 5)||(x == 12&&si < 5)) return true;
else return false;
}
//右下
else if(si - gi == 2&&sj - gj == 2&&place[gi+1][gj+1] == 0){
if((x == 5&&si >= 5)||(x == 12&&si < 5)) return true;
else return false;
}
else return false;
}
//士:斜着走不能出田字格
else if(x == 6||x == 13){
if(Math.abs(gj-sj)==1&&Math.abs(gi-si)==1){
if(x == 6&&si >= 7&&sj >= 3&&sj <= 5) return true;
else if(x == 13&&si <= 2&&sj >= 3&&sj <= 5) return true;
else return false;
}
else return false;
}
//将:不能出田字格且不能会面
else if(x == 7||x == 14){
if((Math.abs(gj-sj)==1&&gi - si ==0)||(gj - sj ==0&&Math.abs(gi-si)==1)){
if(x == 7&&si >= 7&&sj >= 3&&sj <= 5) return true;
else if(x == 14&&si <= 2&&sj >= 3&&sj <= 5) return true;
else return false;
}
else return false;
}
//炮:隔一个
else if(x == 2||x == 9){
//若要吃棋子,必须中间有且只有一枚棋子
if(x*y!=0){
int t = 0;
if(gi == si){
for(int m = Math.min(gj, sj); m <= Math.max(gj, sj); m++){
if(place[gi][m] != 0) t++;
}
}
else if(gj == sj){
for(int m = Math.min(gi, si); m <= Math.max(gi, si); m++){
if(place[m][gj] != 0) t++;
}
}
if(t == 3) return true;
}
//若为不吃棋子的情况,中间不可以有其他棋子,且只能走直线
else {
int t = 0;
if(gi == si){
for(int m = Math.min(gj, sj); m <= Math.max(gj, sj); m++){
if(place[gi][m] != 0) t++;
}
}
else if(gj == sj){
for(int m = Math.min(gi, si); m <= Math.max(gi, si); m++){
if(place[m][gj] != 0) t++;
}
}
if(t == 1) return true;
else return false;
}
}
//兵:不能后退,且过了河才可以左右移动
else if(x == 1||x == 8){
//判断是否过河
if(x == 1){
if(gi >=5){
if(gi - si == 1&&gj == sj) return true;
else return false;
}
else if((gi - si == 1&&sj - gj == 0)||(gi - si == 0&&Math.abs(sj-gj) == 1)) return true;
else return false;
}
else if(x == 8){
if(gi <5){
if(si - gi == 1&&gj == sj) return true;
else return false;
}
else if(((si - gi == 1&&sj - gj == 0))||(gi - si == 0&&Math.abs(sj-gj) == 1)) return true;
else return false;
}
else return false;
}
return false;
}长长的一大串,这里对于炮和将需单独考虑,炮有直行和隔一个两种走法,需分开考虑,而将就更是麻烦
//判断将是否会面
public boolean meet(){
int jiangi=0, jiangj=0, shuaii=0, shuaij=0, temp=0;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
for(int j=0; j<9; j++){
if(place[i][j]==7){
shuaii = i;
shuaij = j;
}
else if(place[i][j]==14){
jiangi = i;
jiangj = j;
}
}
}
if(shuaij == jiangj){
for(int i=jiangi+1; i<shuaii; i++){
if(place[i][shuaij] != 0) temp++;
}
}
else return false;//没会面
if(temp != 0) return false;//没会面
else return true;//会面了
}八、轮次
红黑轮流下棋
我单独写了一个方法判断将是否会面,因为导致将会面的不仅是将自身的移动导致,还可能是其他棋子的移动,所以也是一个boolean函数,只有同时满足前一个函数以及这个函数返回的是不会面,才可以移动,移动时我定义了一个参数x记录局数,根据他的奇偶判断轮到哪一方走。这样就实现了象棋的规则。
九、悔棋
难免会有失误,加上悔棋功能更合适。
我们在交换两个点的值时(或者吃子的情况)需记录下之前的值,然后当动作监听器监听到点击悔棋时又交换回来。
一次只能悔棋一次,且刚开始时棋子没有移动不能悔棋。
十、背景 及 提示
加上自己挑的背景,并为了方便下棋,标注轮到哪一方。
加背景可以用到画棋子同样的方法,所以要画在棋盘前面,防止被覆盖住。
这样加上去又有一个很明显的问题,就是你每操作一次右边的按钮都会消失,被你的背景图覆盖了,这怎么办呢?
于是乎,又总结出了三种方法:
1.重写按钮的paint方法;
2.将按钮以菜单的形式加在左上角;
3.将按钮直接p在背景图上(截图),再画就可以了;
此外你还可以在背景图上加上“当前下棋方”的字样,在边上显示当前下棋方将领的图片。
这里借用了count参数并将其传到了监听器中,重写了构造函数。
int count=1;
if(listener.count==1){
//画帥
bg.drawImage(chess[6], 708, 322, 50, 50, null);
}else if(listener.count==-1){
//画将
bg.drawImage(chess[13], 708, 322, 50, 50, null);
}每下一子,count×(-1),以此标记是哪一方并画图。
附一张成果图:

最后导出到电脑上,这样就完成了一个中国象棋的小游戏。
加载全部内容