SpringBoot Redis哨兵模式
wl_Honest 人气:0最近学习到了Redis的哨兵模式,光看视频还不行,需要自己动手实现一遍才能加深映像,特此记录。
由于没有真实的服务器可以供我操作,所以在虚拟机上启动了3个redis服务,分别占用7001、7002、7003端口。
Redis下载安装不多赘述,只在这里记录一下配置。
首先在tmp目录下创建3个文件夹:
cd /tmp mkdir 7001 7002 7003
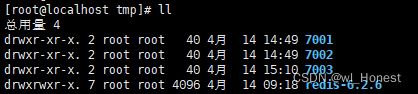
然后将redis的配置文件redis.conf拷贝到刚刚创建的3个文件夹下
cp redis-6.2.6/redis.conf /tmp/7001 cp redis-6.2.6/redis.conf /tmp/7002 cp redis-6.2.6/redis.conf /tmp/7003
接着修改这3个配置文件
vi redise.conf
找到端口,redis默认端口是6379,这里分别将端口改为7001、7002和7003

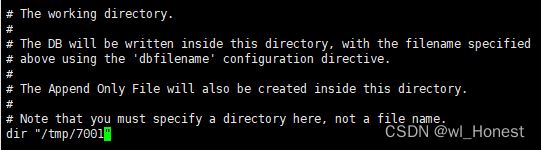
然后修改dir,redis持久化文件保存的路径,分别改为对应的路径
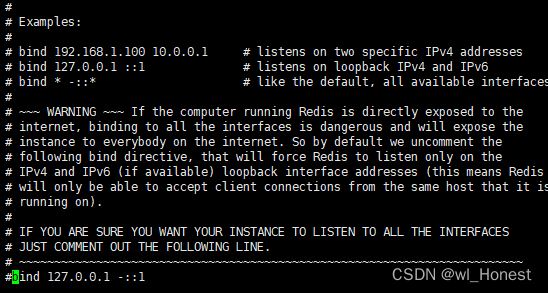
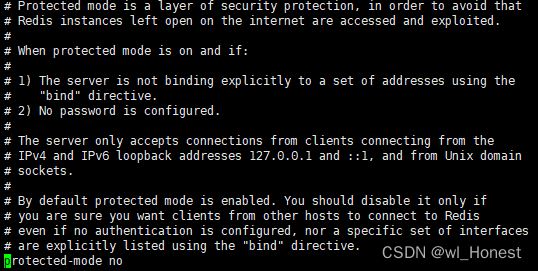
接着注释掉bind并且修改protected-mode为no
redis默认不允许远程连接,修改这2项配置允许我们远程连接
最后在配置文件第一行加上 replica-announce-ip #{ip}
注意:这里#{ip}填自己的ip地址
由于是在虚拟机安装的redis,会有多个ip,这里写明ip防止找不到
3个配置文件都改完后,cd 到对应的目录启动redis

3个服务都启动后,连接7002的redis
redis-cli -p 7002
输入命令,搭建主从集群,让7002成为7001的从节点
REPLICAOF #{ip} 7001注意:这里#{ip}填自己的ip地址
同理,7003也这样操作一遍,这样就搭建好了以7001为主节点,7002和7003位从节点的主从集群模式。
需要注意的是,以命令形式搭建的主从集群,重启后就失效了,想要持久保持可以在配置文件里配置,这里从简就不贴了。
上述操作完成后,接着在tmp目录下创建3个新文件夹
mkdir s1 s2 s3
cd到s1目录,创建文件sentinel.conf,这个文件也可以从redis的目录中拷贝。
编写文件配置
# sentinel端口
port 27001
#工作路径
dir "/tmp/s1"
# 哨兵监控的master,主从配置一样,在进行主从切换时7001会变成当前的master端口,最后的2为客观判断主节# 点下线的节点个数
sentinel monitor mymaster #{ip} 7001 2
# master或slave多长时间不能使用后标记为s_down状态
sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 5000
#若sentinel在该配置值内未能完成failover操作(即故障时master/slave自动切换),
#则认为本次failover失败
sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 60000注意:这里#{ip}填自己的ip地址
然后将sentinel.conf文件cp到s2和s3路径下,只用修改port和dir为各自的配置
然后分别在各自路径下启动3个哨兵
redis-sentinel sentinel.conf
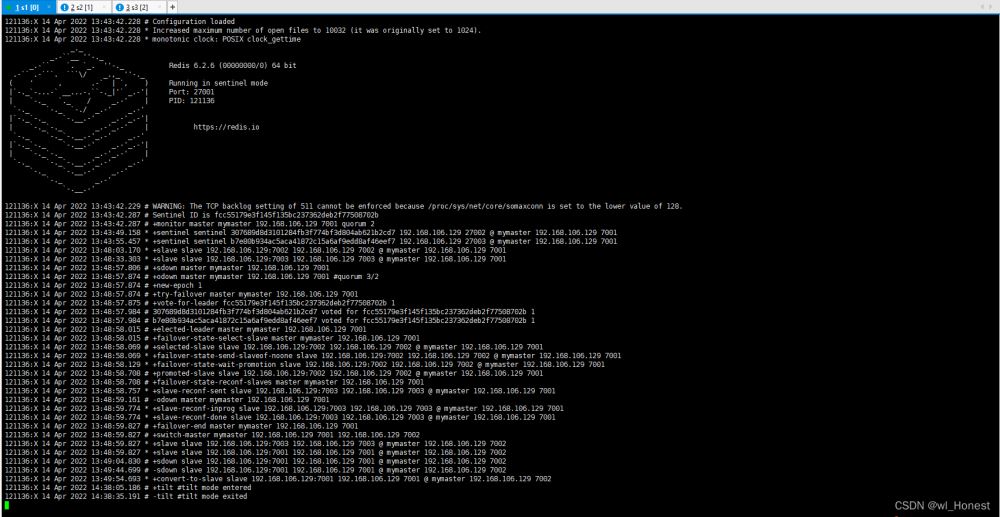
由于之前测试了7001关闭服务,哨兵自动切换主节点为7002了,若为第一次启动,日志和截图中的会稍有不同。
哨兵模式搭建好后,接着在Java端集成此模式
pom.xml引入最基本的依赖即可
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions><!-- 去掉springboot默认配置 -->
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.73</version>
</dependency>application.xml
spring:
redis:
sentinel:
master: mymaster
nodes:
- #{ip}:27001
- #{ip}:27002
- #{ip}:27003注意:这里#{ip}填自己的ip地址
在一个配置类里注入一个bean,实现redis读写分离,配置从redis读数据时优先从从节点读取
package com.wl.demo.config;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.config.FastJsonConfig;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonRedisSerializer;
import io.lettuce.core.ReadFrom;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.LettuceClientConfigurationBuilderCustomizer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
/**
* @author wl
* @date 2022/3/28
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public LettuceClientConfigurationBuilderCustomizer lettuceClientConfigurationBuilderCustomizer() {
return builder -> builder.readFrom(ReadFrom.REPLICA_PREFERRED);
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
FastJsonRedisSerializer<Object> fastJsonRedisSerializer = new FastJsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
FastJsonConfig fastJsonConfig = fastJsonRedisSerializer.getFastJsonConfig();
SerializerFeature[] serializerFeatures = new SerializerFeature[] {SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue};
fastJsonConfig.setSerializerFeatures(serializerFeatures);
StringRedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(fastJsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(fastJsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setEnableTransactionSupport(true);
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
}编写一个测试接口
package com.wl.demo.controller;
import com.wl.demo.common.result.HttpResult;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author wl
* @date 2022/4/14
*/
@RestController
public class TestController {
private final StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Autowired
public TestController(StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate) {
this.stringRedisTemplate = stringRedisTemplate;
}
@GetMapping("/set/{key}/{value}")
public HttpResult setValue(@PathVariable("key") String key, @PathVariable("value") String value) {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value);
return HttpResult.success();
}
@GetMapping("/get/{key}")
public HttpResult getValue(@PathVariable("key") String key) {
return HttpResult.success(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key));
}
}启动springboot,调用set接口
查看redis
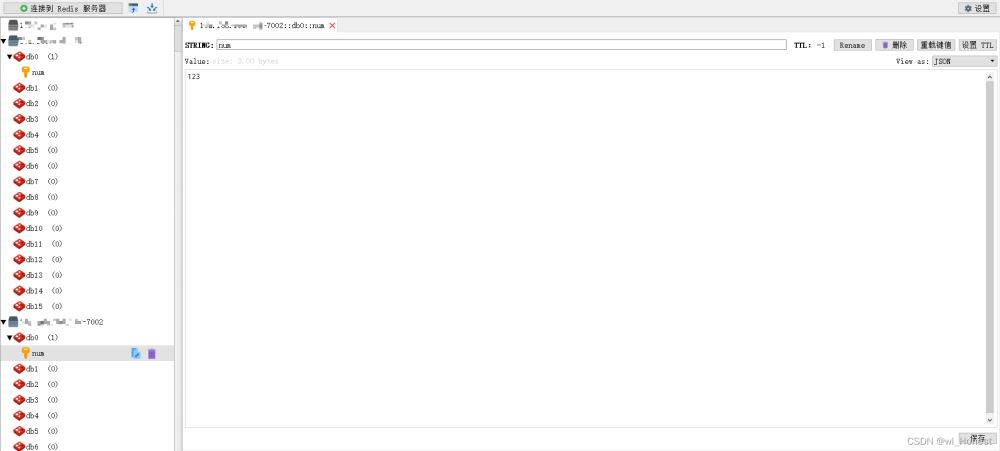
7002主节点有值了,并且它的从节点也同步到了数据
然后调用get接口

数据也成功获取到了
最后测试一下哨兵自动切换主从节点,这里关闭7002的redis
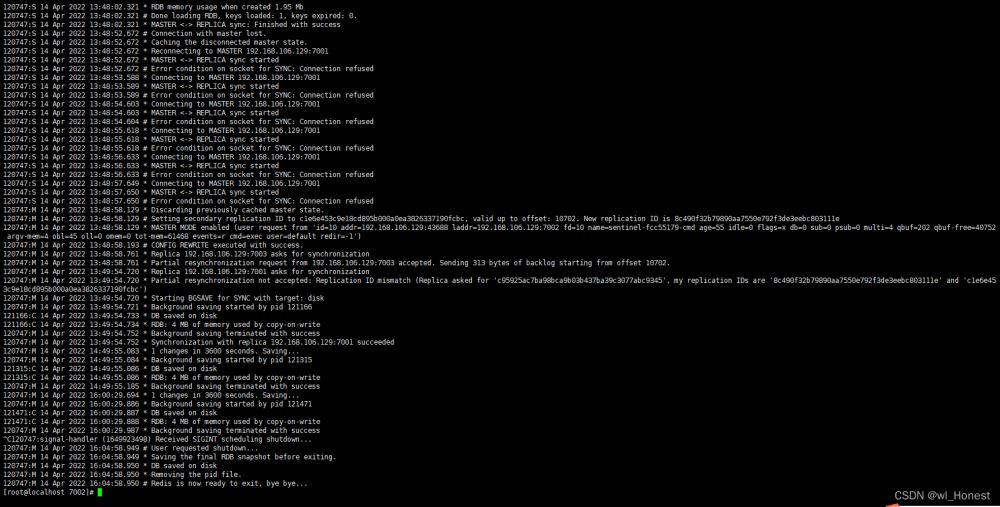
接着查看27002哨兵打印的日志
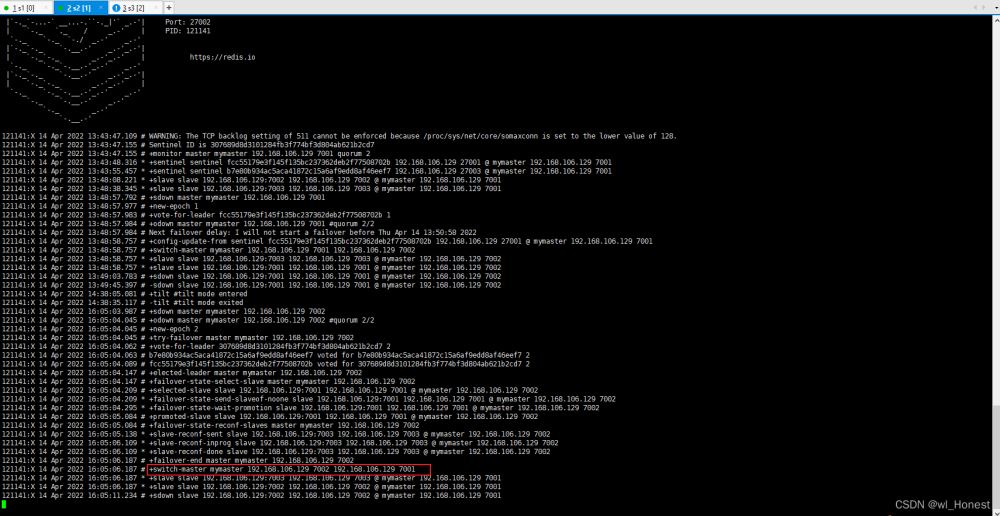
从日志中可以看到关闭7002的redis后,哨兵自动将主节点切换到了7001的redis
现在启动7002的redis
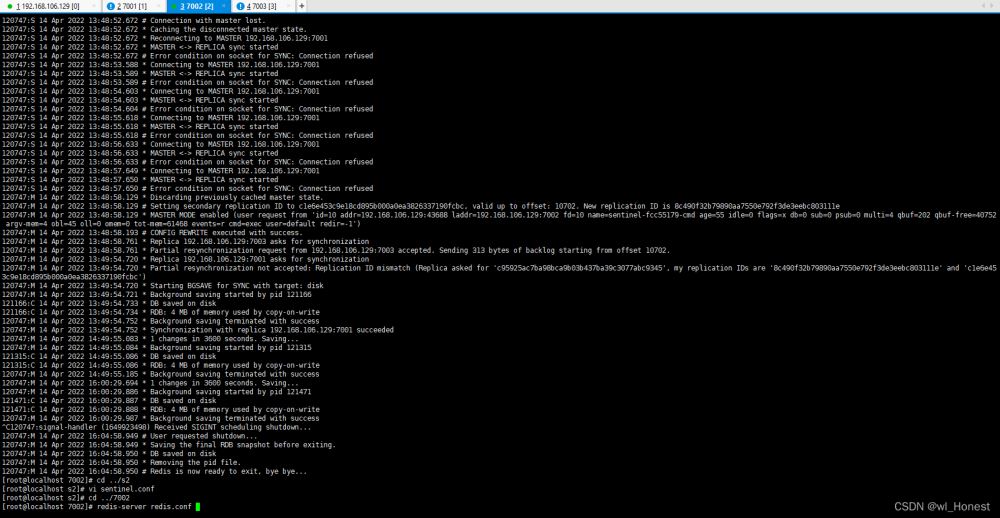
查看哨兵27001的日志
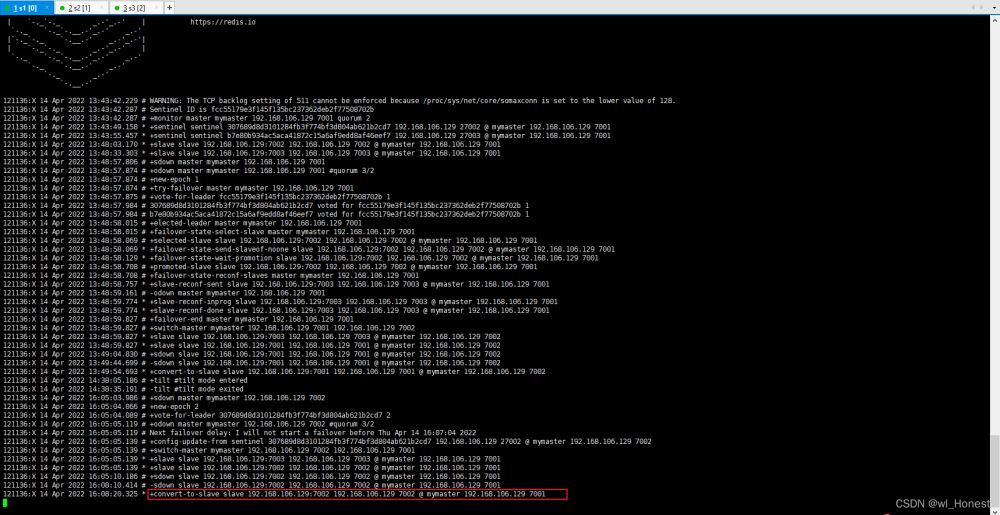
可以发现由将7002加入到了自己的从节点中
自此,Redis哨兵模式的简单搭建就完成了
加载全部内容