C++操作符
清风自在 流水潺潺 人气:0一、值得思考的问题
下面的代码有没有区别?为什么?

二、意想不到的事实
- 现代编译器产品会对代码进行优化
- 优化使得最终的二进制程序更加高效
- 优化后的二进制程序丢失了 C/C++ 的原生语义
- 不可能从编译后的二进制程序还原 C/C++ 程序
三、++ 操作符重载
++ 操作符可以重载吗?如何区分前置++ 和后置++?
++ 操作符可以被重载
- 全局函数和成员函数均可进行重载
- 重载前置++操作符不需要额外的参数
- 重载后置++操作符需要一个 int 类型的占位参数
下面来看 ++ 操作符重载的示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int mValue;
public:
Test(int i)
{
mValue = i;
}
int value()
{
return mValue;
}
Test& operator ++ ()
{
++mValue;
return *this;
}
Test operator ++ (int)
{
Test ret(mValue);
mValue++;
return ret;
}
};
int main()
{
Test t(0);
Test m(0);
Test tt = t++;
cout << "tt = " << tt.value() << endl;
cout << "t = " << t.value() << endl;
Test mm = ++m;
cout << "mm = " << mm.value() << endl;
cout << "m = " << m.value() << endl;
return 0;
}输出结果如下:
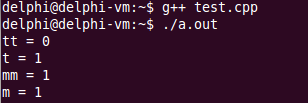
前置++的效率高于后置++,因为前置的++没有生成额外的对象,意味着不需要过多的内存,也就是不需要在栈上生成对象。而后置的++需要创建栈空间上的对象,占用栈空间,并且需要调用构造函数,返回后需要调用析构函数。
四、真正的区别
对于基础类型的变量
- 前置++的效率与后置++的效率基本相同
- 根据项目组编码规范进行选择
对于类类型的对象
- 前置++的效率高于后置++
- 尽量使用前置++操作符提高程序效率
前面写过的复数类可以进一步完善了:
Complex.h:
#ifndef _COMPLEX_H_
#define _COMPLEX_H_
class Complex
{
double a;
double b;
public:
Complex(double a = 0, double b = 0);
double getA();
double getB();
double getModulus();
Complex operator + (const Complex& c);
Complex operator - (const Complex& c);
Complex operator * (const Complex& c);
Complex operator / (const Complex& c);
bool operator == (const Complex& c);
bool operator != (const Complex& c);
Complex& operator = (const Complex& c);
Complex& operator ++ ();
Complex operator ++ (int);
};
#endifComplex.cpp:
#include "Complex.h"
#include "math.h"
Complex::Complex(double a, double b)
{
this->a = a;
this->b = b;
}
double Complex::getA()
{
return a;
}
double Complex::getB()
{
return b;
}
double Complex::getModulus()
{
return sqrt(a * a + b * b);
}
Complex Complex::operator + (const Complex& c)
{
double na = a + c.a;
double nb = b + c.b;
Complex ret(na, nb);
return ret;
}
Complex Complex::operator - (const Complex& c)
{
double na = a - c.a;
double nb = b - c.b;
Complex ret(na, nb);
return ret;
}
Complex Complex::operator * (const Complex& c)
{
double na = a * c.a - b * c.b;
double nb = a * c.b + b * c.a;
Complex ret(na, nb);
return ret;
}
Complex Complex::operator / (const Complex& c)
{
double cm = c.a * c.a + c.b * c.b;
double na = (a * c.a + b * c.b) / cm;
double nb = (b * c.a - a * c.b) / cm;
Complex ret(na, nb);
return ret;
}
bool Complex::operator == (const Complex& c)
{
return (a == c.a) && (b == c.b);
}
bool Complex::operator != (const Complex& c)
{
return !(*this == c);
}
Complex& Complex::operator = (const Complex& c)
{
if( this != &c )
{
a = c.a;
b = c.b;
}
return *this;
}
Complex& Complex::operator ++ ()
{
a = a + 1;
b = b + 1;
return *this;
}
Complex Complex::operator ++ (int)
{
Complex ret(a, b);
a = a + 1;
b = b + 1;
return ret;
}test.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "Complex.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Complex a(0, 0);
Complex b(0, 0);
Complex aa = a++;
Complex bb = ++b;
cout << "aa的实部为: " << aa.getA() << endl;
cout << "aa的实部为: " << aa.getB() << endl;
cout << "bb的实部为: " << bb.getA() << endl;
cout << "bb的实部为: " << bb.getB() << endl;
return 0;
}输出结果如下:
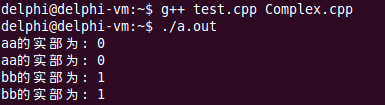
五、小结
- 编译优化使得最终的可执行程序更加高效
- 前置++操作符和后置++操作符都可以被重载
- ++操作符的重载必须符合其原生语义
- 对于基础类型,前置++与后置++的效率几乎相同
- 对于类类型,前置++的效率高于后置++
加载全部内容