Vue event对象
.NET开发菜鸟 人气:0一、什么是event对象
event对象:代表的是事件的状态。比如获取当前的元素:e.Target。
二、事件冒泡
什么是事件冒泡呢?百度百科的解释如下:
当事件发生后,这个事件就要开始传播(从里到外或者从外向里)。为什么要传播呢?因为事件源本身(可能)并没有处理事件的能力,即处理事件的函数(方法)并未绑定在该事件源上。例如我们点击一个按钮时,就会产生一个click事件,但这个按钮本身可能不能处理这个事件,事件必须从这个按钮传播出去,从而到达能够处理这个事件的代码中(例如我们给按钮的onclick属性赋一个函数的名字,就是让这个函数去处理该按钮的click事件),或者按钮的父级绑定有事件函数,当该点击事件发生在按钮上,按钮本身并无处理事件函数,则传播到父级去处理。
可能下面的例子会更容易理解一些:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>事件冒泡</title>
<!--引入vue.js-->
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js" ></script>
<script>
window.onload=function(){
// 构建vue实例
new Vue({
el:"#my",
data:{
},
// 方法
methods:{
play1:function(){
console.log("我的div1");
},
play2:function(){
console.log("我的div2");
},
play3:function(){
console.log("我的div3");
}
}
})
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="my">
<div @click="play1">我的div1
<div @click="play2">我的div2
<div @click="play3">
我的div3
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>效果:
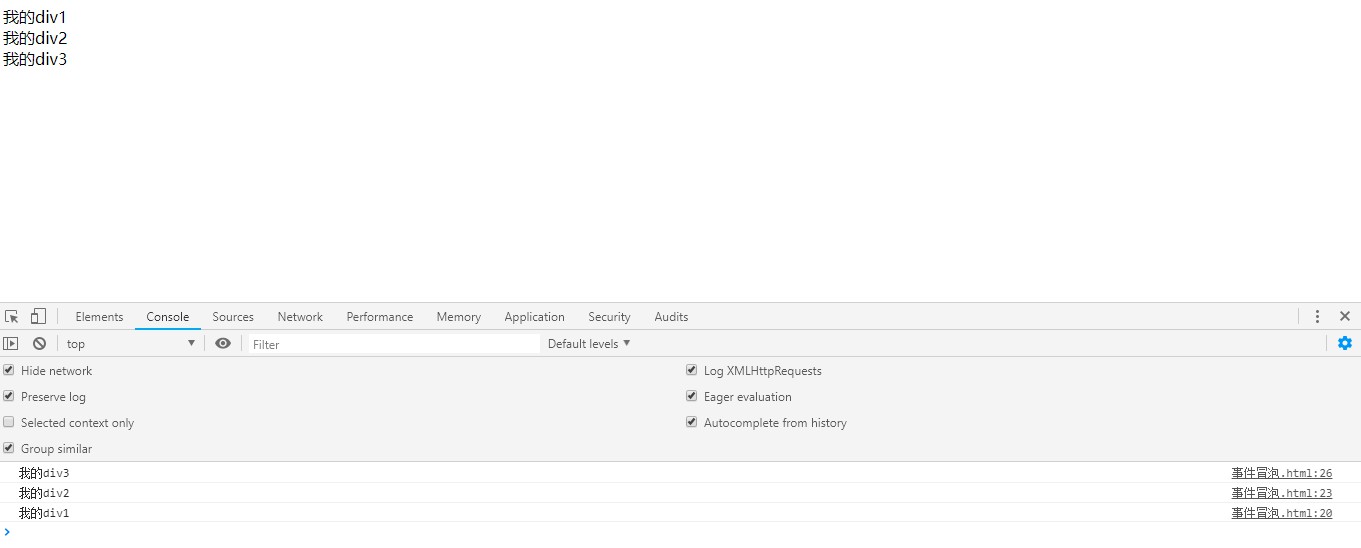
在上面的代码中,3个div分别绑定了3个不同的事件,点击"我的div3"的时候
那么该如何阻止事件冒泡呢?
1、原始JS中的处理方法
代码示例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>事件冒泡</title>
<!--引入vue.js-->
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js" ></script>
<script>
window.onload=function(){
// 构建vue实例
new Vue({
el:"#my",
data:{
},
// 方法
methods:{
play1:function(){
console.log("我的div1");
},
play2:function(){
console.log("我的div2");
},
play3:function(e){
console.log("我的div3");
e.stopPropagation();
}
}
})
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="my">
<div @click="play1">我的div1
<div @click="play2">我的div2
<div @click="play3($event)">
我的div3
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>效果:
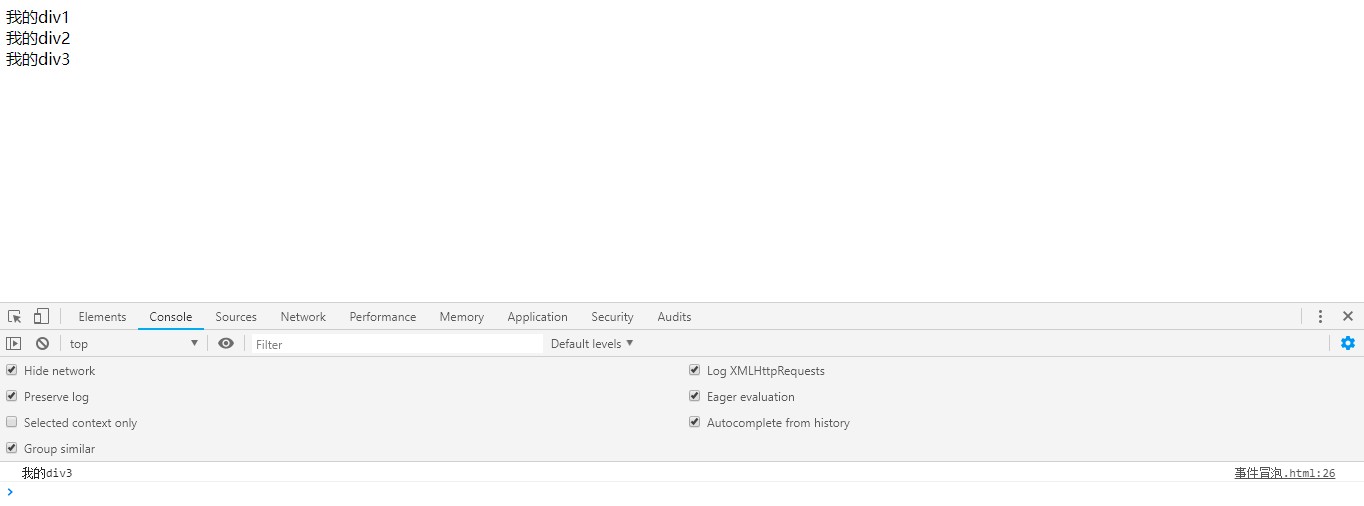
2、vue中处理方法
代码示例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>事件冒泡</title>
<!--引入vue.js-->
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js" ></script>
<script>
window.onload=function(){
// 构建vue实例
new Vue({
el:"#my",
data:{
},
// 方法
methods:{
play1:function(){
console.log("我的div1");
},
play2:function(){
console.log("我的div2");
},
play3:function(e){
console.log("我的div3");
//e.stopPropagation();
}
}
})
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="my">
<div @click="play1">我的div1
<div @click="play2">我的div2
<div @click="play3($event)">
我的div3
</div>
<!--Vue中使用事件修饰符阻止冒泡-->
<div @click.stop="play3($event)">
我的div4
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>效果:
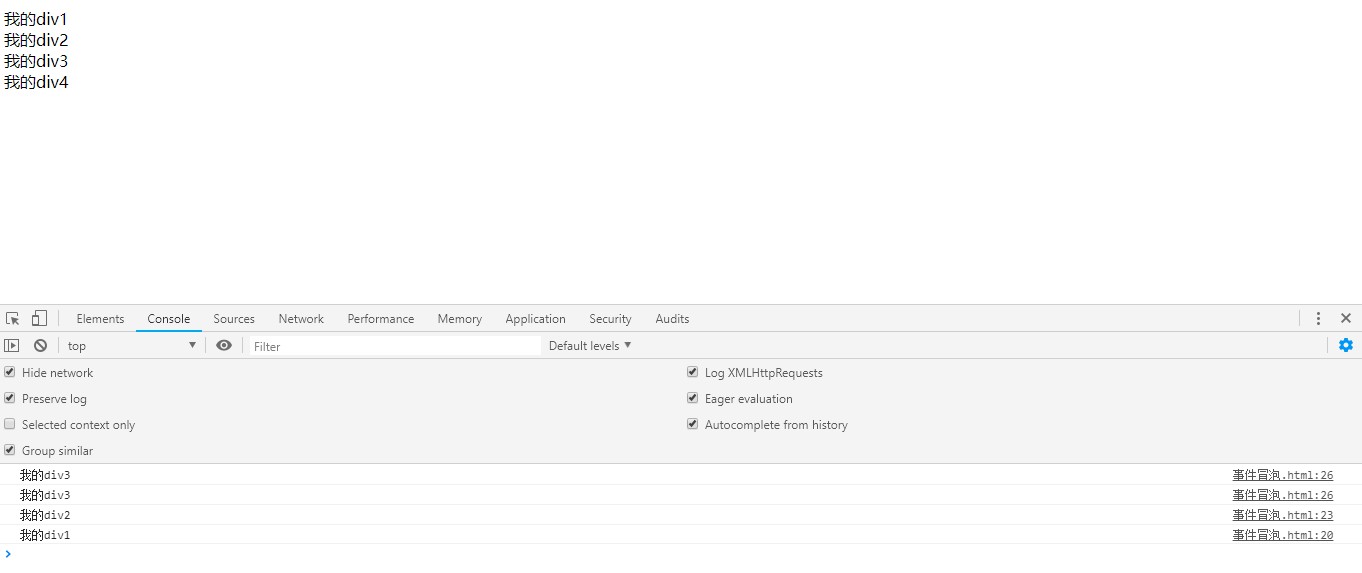
点击"我的div4"的时候会阻止事件冒泡,但点击"我的div3"的时候不会阻止事件冒泡。
三、事件的默认动作
看下面的代码示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>事件冒泡</title>
<!--引入vue.js-->
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js" ></script>
<script>
window.onload=function(){
// 构建vue实例
new Vue({
el:"#my",
data:{
},
// 方法
methods:{
play1:function(){
console.log("我的div1");
},
play2:function(){
console.log("我的div2");
},
play3:function(e){
console.log("我的div3");
//e.stopPropagation();
},
play4:function(e){
console.log("我是超链接");
}
}
})
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="my">
<div @click="play1">我的div1
<div @click="play2">我的div2
<div @click="play3($event)">
我的div3
</div>
<!--Vue中使用事件修饰符阻止冒泡-->
<div @click.stop="play3($event)">
我的div4
</div>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" @click="play4($event)">click</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>效果:
点击“click”的时候会发现页面跳转到了百度,不会进入play4事件,如果调试代码想进入play4事件该如何处理呢?
1、使用原生JS处理
代码示例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>事件冒泡</title>
<!--引入vue.js-->
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js" ></script>
<script>
window.onload=function(){
// 构建vue实例
new Vue({
el:"#my",
data:{
},
// 方法
methods:{
play1:function(){
console.log("我的div1");
},
play2:function(){
console.log("我的div2");
},
play3:function(e){
console.log("我的div3");
//e.stopPropagation();
},
play4:function(e){
console.log("我是超链接");
// 取消事件的默认动作
e.preventDefault();
}
}
})
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="my">
<div @click="play1">我的div1
<div @click="play2">我的div2
<div @click="play3($event)">
我的div3
</div>
<!--Vue中使用事件修饰符阻止冒泡-->
<div @click.stop="play3($event)">
我的div4
</div>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" @click="play4($event)">click</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>效果:
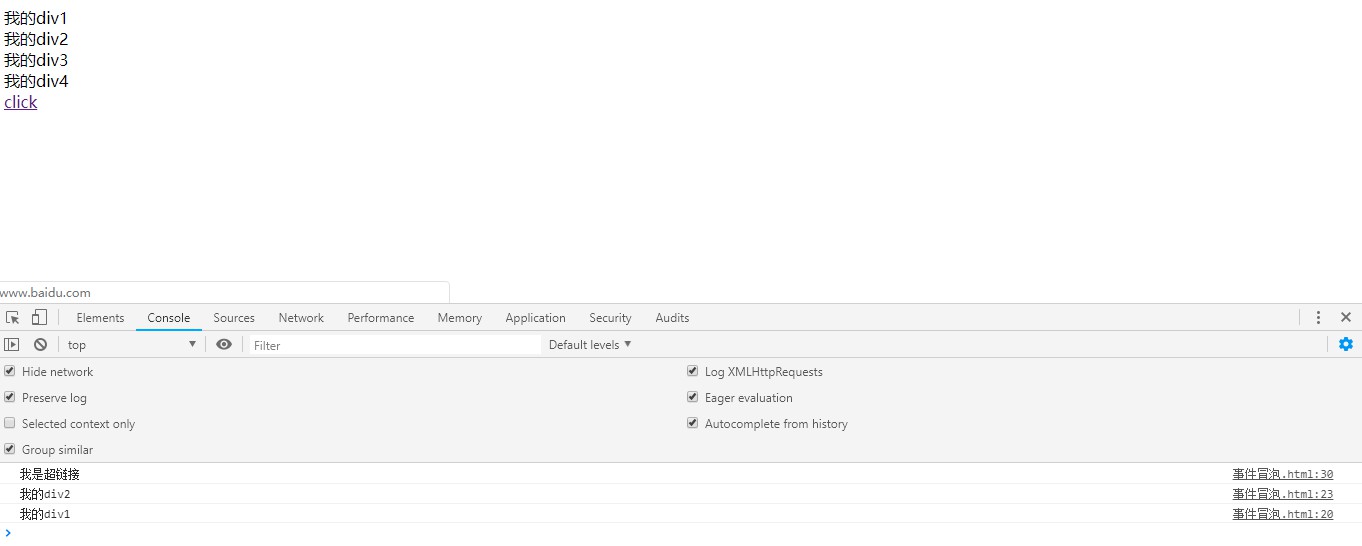
这里在点击“click”的时候就不会进入百度首页了。这里没有处理冒泡,所以会触发play2和play1事件。
2、使用vue处理
代码示例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>事件冒泡</title>
<!--引入vue.js-->
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js" ></script>
<script>
window.onload=function(){
// 构建vue实例
new Vue({
el:"#my",
data:{
},
// 方法
methods:{
play1:function(){
console.log("我的div1");
},
play2:function(){
console.log("我的div2");
},
play3:function(e){
console.log("我的div3");
//e.stopPropagation();
},
play4:function(e){
console.log("我是超链接");
// 取消事件的默认动作
//e.preventDefault();
}
}
})
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="my">
<div @click="play1">我的div1
<div @click="play2">我的div2
<div @click="play3($event)">
我的div3
</div>
<!--Vue中使用事件修饰符阻止冒泡-->
<div @click.stop="play3($event)">
我的div4
</div>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" @click="play4($event)">click</a>
<!--使用vue处理-->
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" @click.prevent.stop="play4($event)">click2</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>效果:
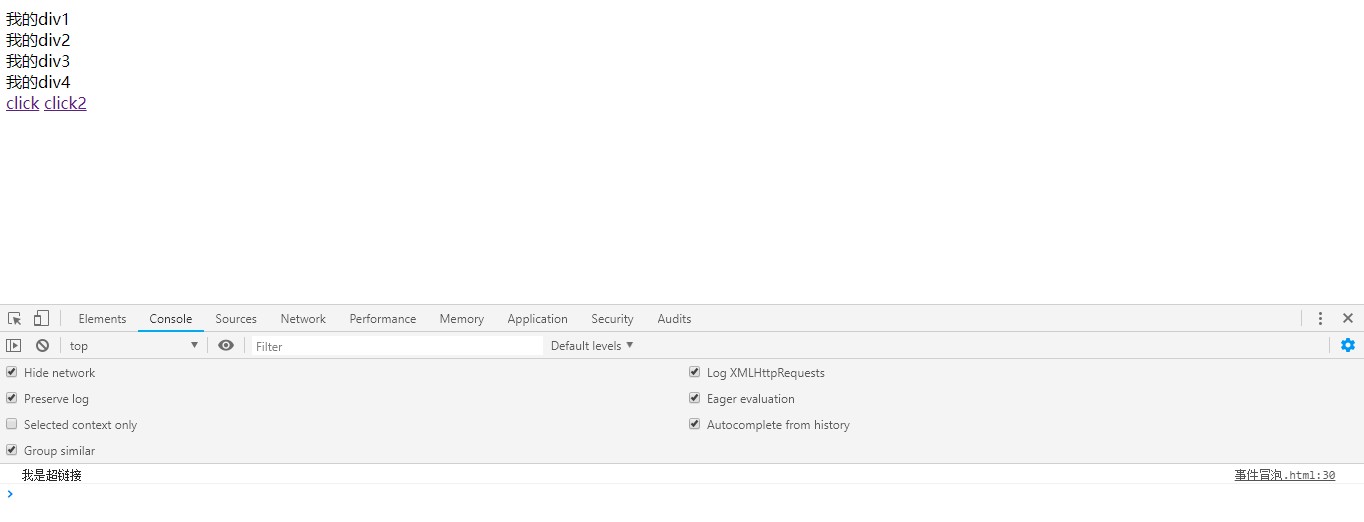
加载全部内容