Java CAS
温文艾尔 人气:0开端
在学习源码之前我们先从一个需求开始
需求
我们开发一个网站,需要对访问量进行统计,用户每发送一次请求,访问量+1.如何实现?我们模拟有100个人同时访问,并且每个人对咱们的网站发起10次请求,最后总访问次数应该是1000次
1.代码
package day03;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* Description
* User:
* Date:
* Time:
*/
public class Demo {
//总访问量
static int count = 0;
//模拟访问的方法
public static void request() throws InterruptedException {
//模拟耗时5毫秒
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(5);
count++;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
int threadSize=100;
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(threadSize);
for (int i=0;i<threadSize;i++){
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//每个用户访问10次网站
try {
for (int j=0;j<10;j++) {
request();
}
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}
});
thread.start();
}
//怎么保证100个线程执行之后,执行后面的代码
countDownLatch.await();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"耗时:"+(endTime-startTime)+",count:"+count);
}
}
我们多输出几次结果
main耗时:66,count:950
main耗时:67,count:928
发现每一次count都不相同,和我们期待的1000相差一点,这里就牵扯到了并发问题,我们的count++在底层实际上由3步操作组成
- 获取count,各个线程写入自己的工作内存
- count执行+1操作
- 将+1后的值写回主存中
这并不是一个线程安全的过程,如果有A、B两个线程同时执行count++,同时执行到第一步,得到的count是一样的,三步操作完成后,count只加1,导致count结果不正确
那么怎么解决这个问题呢?
我们可以考虑使用synchronized关键字和ReentrantLock对资源加锁,保证并发的正确性,多线程的情况下,可以保证被锁住的资源被串行访问
1.1修改后的代码
package day03;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* Description
* User:
* Date:
* Time:
*/
public class Demo02 {
//总访问量
static int count = 0;
//模拟访问的方法
public static synchronized void request() throws InterruptedException {
//模拟耗时5毫秒
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(5);
count++;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
int threadSize=100;
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(threadSize);
for (int i=0;i<threadSize;i++){
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//每个用户访问10次网站
try {
for (int j=0;j<10;j++) {
request();
}
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}
});
thread.start();
}
//怎么保证100个线程执行之后,执行后面的代码
countDownLatch.await();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"耗时:"+(endTime-startTime)+",count:"+count);
}
}
执行结果
main耗时:5630,count:1000
可以看到,由于sychronized锁住了整个方法,虽然结果正确,但因为线程执行方法均为串行执行,导致运行效率大大下降
那么我们如何才能使程序执行无误时,效率还不会降低呢?
缩小锁的范围,升级上述3步中第三步的实现
- 获取锁
- 获取count最新的值,记作LV
- 判断LV是否等于A,如果相等,则将B的值赋值给count,并返回true,否则返回false
- 释放锁
1.2代码改进:CAS模仿
package day03;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* Description
* User:
* Date:
* Time:
*/
public class Demo03 {
//总访问量
volatile static int count = 0;
//模拟访问的方法
public static void request() throws InterruptedException {
//模拟耗时5毫秒
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(5);
// count++;
int expectCount;
while (!compareAndSwap(expectCount=getCount(),expectCount+1)){}
}
/**
* @param expectCount 期待的值,比如最刚开始count=3
* @param newCount 新值 count+1之后的值,4
* @return
*/
public static synchronized boolean compareAndSwap(int expectCount,int newCount){
if (getCount()==expectCount){
count = newCount;
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static int getCount(){return count;}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
int threadSize=100;
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(threadSize);
for (int i=0;i<threadSize;i++){
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//每个用户访问10次网站
try {
for (int j=0;j<10;j++) {
request();
}
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}
});
thread.start();
}
//怎么保证100个线程执行之后,执行后面的代码
countDownLatch.await();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"耗时:"+(endTime-startTime)+",count:"+count);
}
}
main耗时:67,count:1000
2.CAS分析
CAS全称“CompareAndSwap”,中文翻译过来为“比较并替换”
定义:
- CAS操作包含三个操作数——
内存位置(V)、期望值(A)和新值(B)。如果内存位置的值和期望值匹配,那么处理器会自动将该位置值更新为新值。否则处理器不作任何操作。无论哪种情况,它都会在CAS指令之前返回该位置的值。 - CAS在一些特殊情况下仅返回CAS是否成功,而不提取当前值,CAS有效的说明了我认为位置V应该包含值A,如果包含该值,将B放到这个位置,否则不要更改该位置的值,只告诉我这个位置现在的值即可
2.1Java对CAS的支持
java中提供了对CAS操作的支持,具体在sun.misc.unsafe类中,声明如下
public final native boolean compareAndSwapObject(Object var1, long var2, Object var4, Object var5); public final native boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object var1, long var2, int var4, int var5); public final native boolean compareAndSwapLong(Object var1, long var2, long var4, long var6);
- 参数var1:表示要操作的对象
- 参数var2:表示要操作属性地址的偏移量
- 参数var4:表示需要修改数据的期望的值
- 参数var5:表示需要修改的新值
2.2CAS实现原理是什么?
CAS通过调用JNI的代码实现,JNI:java native interface,允许java调用其他语言。而compareAndSwapxxx系列的方法就是借助C语言来调用cpu底层指令实现的
以常用的Intel x86平台为例,最终映射到cpu的指令为"cmpxchg",这是一个原子指令,cpu执行此命令时,实现比较并替换的操作
现代计算机动不动就上百核心,cmpxchg怎么保证多核心下的线程安全?
系统底层在进行CAS操作的时候,会判断当前系统是否为多核心系统,如果是就给“总线”加锁,只有一个线程会对总线加锁成功,加锁之后执行CAS操作,也就是说CAS的原子性是平台级别的
2.3CAS存在的问题
2.3.1什么是ABA问题?
CAS需要在操作值的时候检查下值有没有发生变化,如果没有发生变化则更新,但是如果一个值原来是A,在CAS方法执行之前,被其他线程修改为B,然后又修改回了A,那么CAS方法执行检查的时候会发现它的值没有发生变化,但是实际却不是原来的A了,这就是CAS的ABA问题
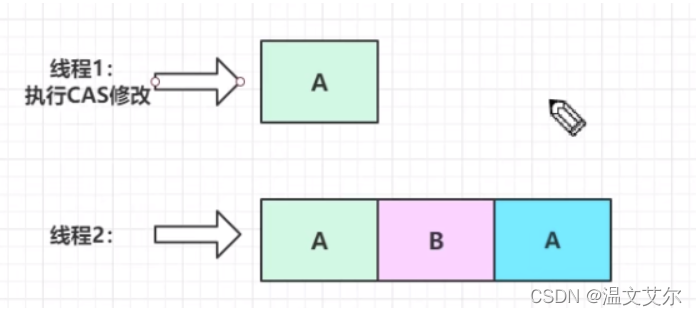
可以看到上图中线程A在真正更改A之前,A已经被其他线程修改为B然后又修改为A了
程序模拟ABA问题
package day04;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* Description
* User:
* Date:
* Time:
*/
public class Test01 {
public static AtomicInteger a = new AtomicInteger();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread main = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行,a的值为:"+a.get());
try {
int expect = a.get();
int update = expect+1;
//让出cpu
Thread.sleep(1000);
boolean b = a.compareAndSet(expect, update);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"CAS执行:"+b+",a的值为:"+a.get());
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"主线程");
// main.start();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(20);
a.incrementAndGet();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"更改a的值为:"+a.get());
a.decrementAndGet();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"更改a的值为:"+a.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"其他线程");
main.start();
thread1.start();
}
}
主线程执行,a的值为:0
其他线程更改a的值为:1
其他线程更改a的值为:0
主线程CAS执行:true,a的值为:1
可以看到,在执行CAS之前,a被其他线程修改为1又修改为0,但是对执行CAS并没有影响,因为它根本没有察觉到其他线程对a的修改
2.3.2如何解决ABA问题
解决ABA问题最简单的方案就是给值加一个修改版本号,每次值变化,都会修改它的版本号,CAS操作时都去对比此版本号
在java中的ABA解决方案(AtomicStampedReference)
AtomicStampedReference主要包含一个对象引用及一个可以自动更新的整数stamp的pair对象来解决ABA问题
AtomicStampedReference源码
/**
* Atomically sets the value of both the reference and stamp
* to the given update values if the
* current reference is {@code ==} to the expected reference
* and the current stamp is equal to the expected stamp.
*
* @param expectedReference the expected value of the reference 期待引用
* @param newReference the new value for the reference 新值引用
* @param expectedStamp the expected value of the stamp 期望引用的版本号
* @param newStamp the new value for the stamp 新值的版本号
* @return {@code true} if successful
*/
public boolean compareAndSet(V expectedReference,
V newReference,
int expectedStamp,
int newStamp) {
Pair<V> current = pair;
return
expectedReference == current.reference &&//期望引用与当前引用保持一致
expectedStamp == current.stamp &&//期望引用版本号与当前版本号保持一致
((newReference == current.reference &&//新值引用与当前引用一致并且新值版本号与当前版本号保持一致
newStamp == current.stamp)
||//如果上述版本号不一致,则通过casPair方法新建一个Pair对象,更新值和版本号,进行再次比较
casPair(current, Pair.of(newReference, newStamp)));
}
private boolean casPair(Pair<V> cmp, Pair<V> val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, pairOffset, cmp, val);
}
使用AtomicStampedReference解决ABA问题代码
package day04;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicStampedReference;
/**
* Description
* User:
* Date:
* Time:
*/
public class Test02 {
public static AtomicStampedReference<Integer> a = new AtomicStampedReference(new Integer(1),1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread main = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行,a的值为:"+a.getReference());
try {
Integer expectReference = a.getReference();
Integer newReference = expectReference+1;
Integer expectStamp = a.getStamp();
Integer newStamp = expectStamp+1;
//让出cpu
Thread.sleep(1000);
boolean b = a.compareAndSet(expectReference, newReference,expectStamp,newStamp);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"CAS执行:"+b);
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"主线程");
// main.start();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(20);
a.compareAndSet(a.getReference(),a.getReference()+1,a.getStamp(),a.getStamp()+1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"更改a的值为:"+a.getReference());
a.compareAndSet(a.getReference(),a.getReference()-1,a.getStamp(),a.getStamp()-1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"更改a的值为:"+a.getReference());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"其他线程");
main.start();
thread1.start();
}
}
主线程执行,a的值为:1
其他线程更改a的值为:2
其他线程更改a的值为:1
主线程CAS执行:false
因为AtomicStampedReference执行CAS会去检查版本号,版本号不一致则不会进行CAS,所以ABA问题成功解决
总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能够给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注的更多内容!
加载全部内容