RestTemplate发送HTTP GET请求用法
字母哥哥 人气:0前言
本文是精讲RestTemplate第3篇,前篇的blog访问地址如下:
RestTemplate在Spring或非Spring环境下使用精讲
RestTemplate实现多种底层HTTP客户端类库的切换用法
RestTemplate可以发送HTTP GET请求,经常使用到的方法有两个:
getForObject()
getForEntity()
二者的主要区别在于,getForObject()返回值是HTTP协议的响应体。getForEntity()返回的是ResponseEntity,ResponseEntity是对HTTP响应的封装,除了包含响应体,还包含HTTP状态码、contentType、contentLength、Header等信息。
为了方便后续开发测试,首先介绍一个网站给大家。JSONPlaceholder是一个提供免费的在线REST API的网站,我们在开发时可以使用它提供的url地址测试下网络请求以及请求参数。或者当我们程序需要获取一些模拟数据、模拟图片时也可以使用它。
一、 getForObject() 方法
1.1.以String的方式接受请求结果数据
在Spring Boot环境下写一个单元测试用例,以String类型接收响应结果信息
@SpringBootTest
class ResttemplateWithSpringApplicationTests {
@Resource
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@Test
void testSimple() {
String url = "http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1";
String str = restTemplate.getForObject(url, String.class);
System.out.println(str);
}
}getForObject第二个参数为返回值的类型,String.class以字符串的形式接受getForObject响应结果,
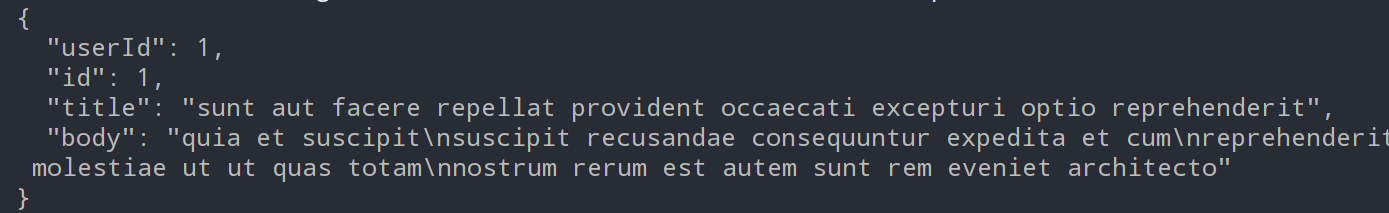
1.2.以POJO对象的方式接受结果数据
在Spring Boot环境下写一个单元测试用例,以java POJO对象接收响应结果信息
@Test
public void testPoJO() {
String url = "http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1";
PostDTO postDTO = restTemplate.getForObject(url, PostDTO.class);
System.out.println(postDTO.toString());
}输出打印结果如下:
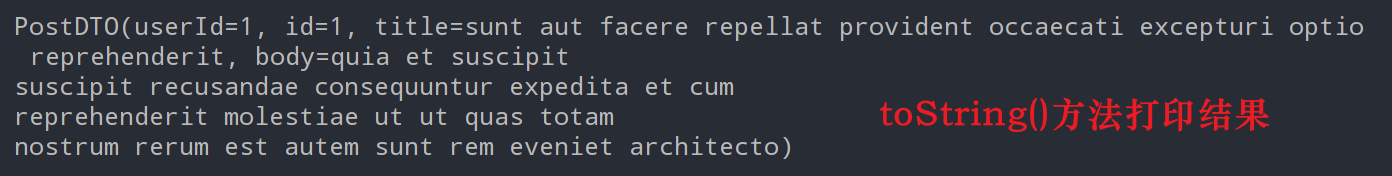
POJO的定义如下,根据JSON String的数据格式定义。
@Data
public class PostDTO {
private int userId;
private int id;
private String title;
private String body;
}1.3.以数组的方式接收请求结果
访问http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts 可以获得JSON数组方式的请求结果

下一步就是我们该如何接收,使用方法也很简单。在Spring Boot环境下写一个单元测试用例,以数组的方式接收请求结果。
@Test
public void testArrays() {
String url = "http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts";
PostDTO[] postDTOs = restTemplate.getForObject(url, PostDTO[].class);
System.out.println("数组长度:" + postDTOs.length);
}请求的结果被以数组的方式正确接收,输出如下:
数组长度:100
1.4.使用占位符号传参的几种方式
以下的几个请求都是在访问"http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1",只是使用了占位符语法,这样在业务使用上更加灵活。
使用占位符的形式传递参数:
String url = "http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/{1}/{2}";
PostDTO postDTO = restTemplate.getForObject(url, PostDTO.class, "posts", 1);另一种使用占位符的形式:
String url = "http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/{type}/{id}";
String type = "posts";
int id = 1;
PostDTO postDTO = restTemplate.getForObject(url, PostDTO.class, type, id);
我们也可以使用 map 装载参数:
String url = "http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/{type}/{id}";
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("type", "posts");
map.put("id", 1);
PostDTO postDTO = restTemplate.getForObject(url, PostDTO.class, map);二、getForEntity()方法
上面的所有的getForObject请求传参方法,getForEntity都可以使用,使用方法上也几乎是一致的,只是在返回结果接收的时候略有差别。使用ResponseEntity<T> responseEntity来接收响应结果。用responseEntity.getBody()获取响应体。响应体内容同getForObject方法返回结果一致。剩下的这些响应信息就是getForEntity比getForObject多出来的内容。
HttpStatus statusCode = responseEntity.getStatusCode();获取整体的响应状态信息
int statusCodeValue = responseEntity.getStatusCodeValue(); 获取响应码值
HttpHeaders headers = responseEntity.getHeaders();获取响应头等
@Test
public void testEntityPoJo() {
String url = "http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/5";
ResponseEntity<PostDTO> responseEntity
= restTemplate.getForEntity(url, PostDTO.class);
PostDTO postDTO = responseEntity.getBody(); // 获取响应体
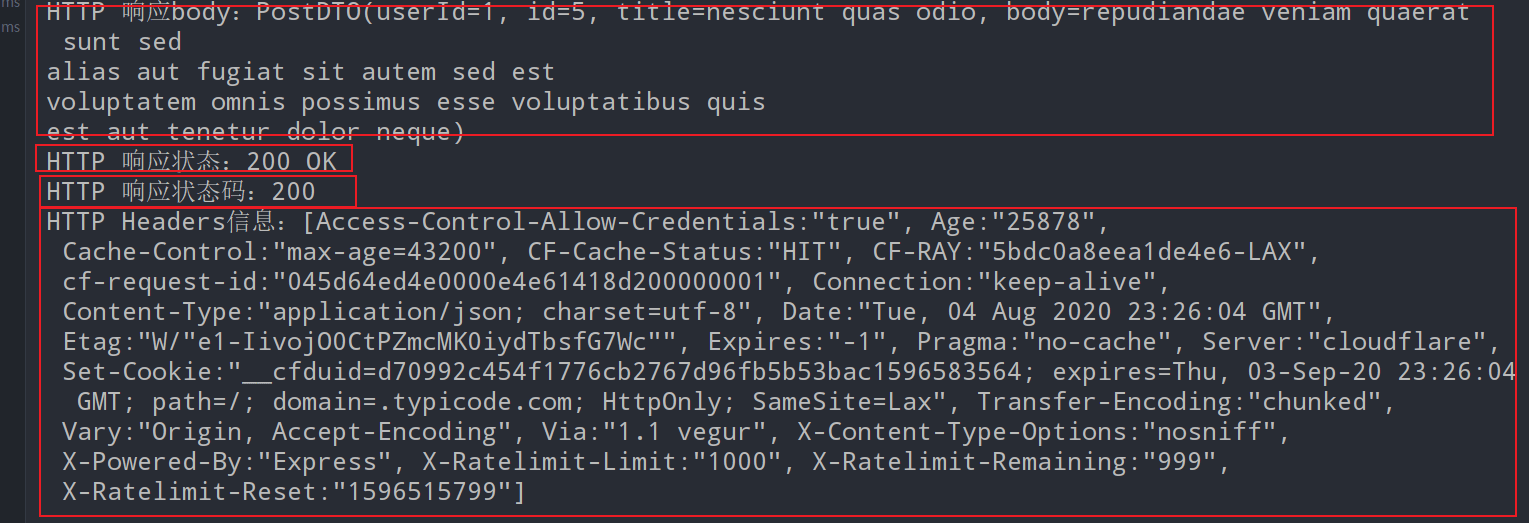
System.out.println("HTTP 响应body:" + postDTO.toString());
//以下是getForEntity比getForObject多出来的内容
HttpStatus statusCode = responseEntity.getStatusCode(); // 获取响应码
int statusCodeValue = responseEntity.getStatusCodeValue(); // 获取响应码值
HttpHeaders headers = responseEntity.getHeaders(); // 获取响应头
System.out.println("HTTP 响应状态:" + statusCode);
System.out.println("HTTP 响应状态码:" + statusCodeValue);
System.out.println("HTTP Headers信息:" + headers);
}输出打印结果
加载全部内容