Python os包
渴望力量的哈士奇 人气:0今天我们来学习一下 python 的内置包 —> OS 包。OS 包拥有着普遍的操作系统功能,拥有着各种各样的函数来操作系统的驱动功能。其中最常用的就是对 路径 与 文件的操作,比如检查某个路径下是否存在某个文件,某个路径是否存在等。也可以创建、删除文件等,接下来我们就详细的看一看 OS 中关于文件的操作功能与用法。
os 模块
文件与目录函数介绍
| 函数名 | 参数 | 介绍 | 举例 | 返回值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| getcwd | 没有参数 | 返回当前路径 | os.getcwd() | 字符串 |
| listdir | path | 返回指定路径下所有的文件或文件夹 | os.listdir(‘c://windows’) | 返回一个列表 |
| makedir | path mode | 创建多级文件夹 | os.makedirs(‘d://pycharm/py’) | 无返回值 |
| removedirs | path | 删除多级路径下的文件夹 | os.removedirs(‘d://pycharm/py’) | 无返回值 |
| rename | oldname、newname | 将文件或文件夹重命名 | os.rename(‘d://pycharm’,‘d://pycharm01’) | 无返回值 |
| rmdir | path | 只能删除空文件夹 | os.rmdir(‘d://pycharm’) | 无返回值 |
示例如下:
import os current_path = os.getcwd() print(current_path) new_path = '%s/test01' % current_path os.makedirs(new_path) list_dir = os.listdir(current_path) print(list_dir) # >>> 执行结果如下: # >>> /Users/user_name/PycharmProjects/XXXXX/python_package/animal 这是当前Mac系统的绝对路径,如果是WIN系统会显示磁盘符 # >>> ['cat', 'dog', 'test_time.py', '__init__.py', 'test.py', 'package_os.py', 'test01'] # >>> 列出来当前路径下的所有文件,并创建 'test01' 文件夹成功
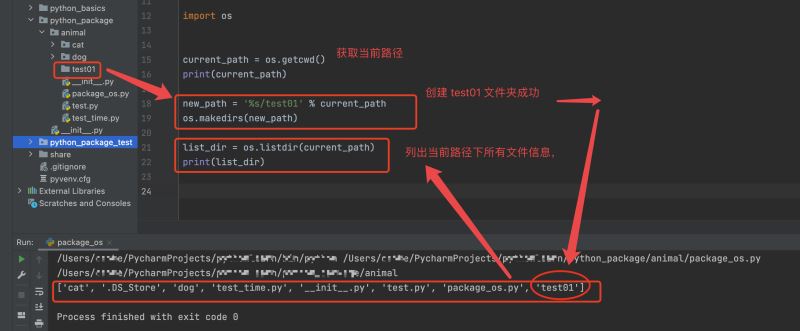
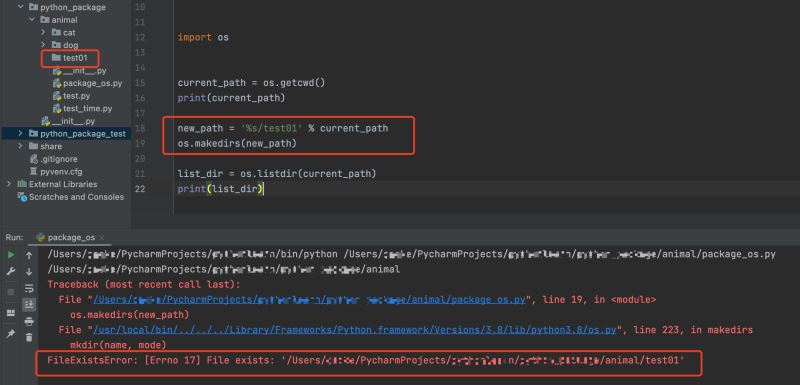
这里有个需要注意的地方,如果当前路径下已经存在了要创建的 文件夹或者文件会出现如下报错。
上面我们只演示了创建一个文件夹,如果我们尝试创建多层级的文件夹呢?
import os current_path = os.getcwd() print(current_path) new_path = '%s/test01' % current_path # os.makedirs(new_path) list_dir = os.listdir(current_path) print(list_dir) new_path02 = '%s/test02/test02-01' % current_path # 尝试创建多级文件夹及文件 os.makedirs(new_path02)
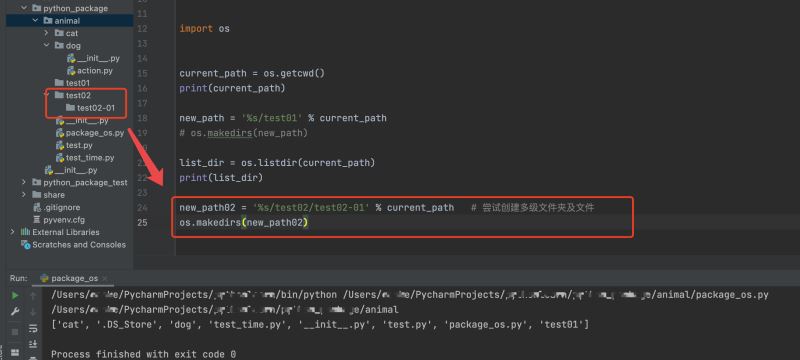
注意:如果不指定创建文件夹的路径,直接利用 os.makedirs('filename') 就可以在当前脚本的默认路径下创建该文件夹,这里就不再进行演示了。大家可以自己在本地试一下。
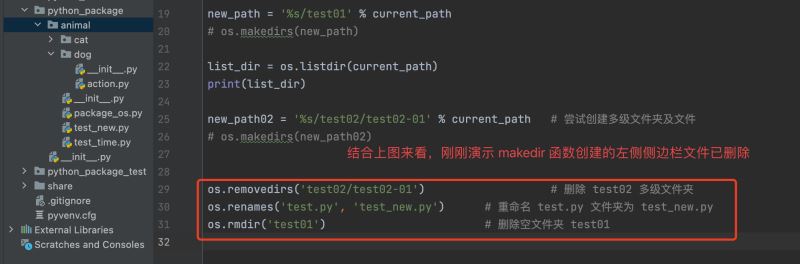
上面我们演示了 getcwd()、listdir()、makedir() 三个函数,接下来我们演示 removedirs()、rename()、rmdir() 三个函数
import os
current_path = os.getcwd()
print(current_path)
new_path = '%s/test01' % current_path
# os.makedirs(new_path)
list_dir = os.listdir(current_path)
print(list_dir)
new_path02 = '%s/test02/test02-01' % current_path # 尝试创建多级文件夹及文件
# os.makedirs(new_path02)
# 之所以要注销 os.makedir() 是因为,我们已经创建好了 'test01'、'test02/test02-01' ,再次执行会报错
os.removedirs('test02/test02-01') # 删除 test02 多级文件夹
os.renames('test.py', 'test_new.py') # 重命名 test.py 文件夹为 test_new.py
os.rmdir('test01') # 删除空文件夹 test01
# >>> 执行效果如下图
注意:当我们使用 os.rmdir() 函数删除非空的文件夹时,是会报错的。比如我们尝试删除 dog 文件夹 就会报错 OSError: [Errno 66] Directory not empty: 'dog' , 该提示的意思是 : OSERROR - dog 是一个非空文件夹 。
以上演示的是 OS 包常用的调用文件的函数,其实OS操作文件的函数还有很多 ,大家可以尝试 使用 dir() 函数查看并尝试练习一下其他函数的应用。
path 模块
os.path 模块同样也是我们在日常开发工作中比较常用的一个模块,接下来我们看看 path 模块都有哪些较常用的函数。
path 模块常用方法
| 函数名 | 参数 | 介绍 | 举例 | 返回值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exists | path | 文件或路径是否存在 | os.path.exists(‘d://test/’) | bool类型 |
| isdir | path | 是否是路径 | os.path.isdir(‘d://test/’) | bool类型 |
| isabs | path | 是否是绝对路径 | os.isabs(‘test’) | bool类型 |
| isfile | path | 是否是文件 | os.path.isfile(‘d://test.py’) | bool类型 |
| join | path, path* | 通过路径的’//'将其用字符串合并 | os.path.join(‘d://’,‘test’) | 字符串 |
| split | path | 通过路径的’//'以最后一层路径为及基准切割成元组 | os.path.split(‘d://test’) | 元组 |
需要注意一点:win电脑和 mac电脑的 路径标识符不一样。 win系统为 // , mac或者linux系统为 / 。
结合我们上文 os 包常用的函数演示案例如下:
import os
import os.path
current_path = os.getcwd() # 定义 current_path 变量获取当前脚本的绝对路径
print(current_path) # 打印 current_path 变量
print(os.path.isabs(current_path)) # 利用 path 模块的 isabs 函数判断 current_path 是否是绝对路径 [返回结果 True]
print(os.path.isabs('animal')) # 利用 path 模块的 isabs 函数判断 animal 是否是绝对路径 [返回结果 False , animal 是相对路径]
new_path = '%s/test1' % current_path
if os.path.exists(new_path): # 判断 new_path 是否存在,如果存在,则删除 new_path
os.makedirs(new_path)
data = os.listdir(current_path)
print(data)
new_path2 = os.path.join(current_path, 'test2', 'test2_01')
print(new_path2)
# 将 'test2'、'test2_01' 与 current_path 拼接在一起,生成一个 路径形式 的字符串赋值给new_path2
# >>> 执行结果为 '/Users/XXX/PycharmProjects/python_package/test2/test2_01'
if os.path.exists(new_path2): # 判断 new_path2 是否存在,如果不存在,则通过 os包 的 makedirs 函数创建
os.makedirs(new_path2)
if os.path.exists('test3'): # 判断 'test3' 是否存在,如果不存在,则通过 os包 的 makedirs 函数创建
os.makedirs('test3')
if os.path.exists('test2/test2_01'): # 判断 'test2/test2_01' 是否存在,如果存在,则删除 'test2/test2_01'
os.removedirs('test2/test2_01')
if os.path.exists('test3'): # 判断 'test3' 是否存在,如果存在,则将 'test3' 重命名为 'test3_new'
os.rename('test3', 'test3_new')
if os.path.exists('test1'): # 判断 'test1' 是否存在,如果存在,则删除 'test1'
os.rmdir('test1')
current_path = current_path + '/package_os.py'
print(os.path.isfile(current_path))
# 利用 path模块 的 isfile函数 判断 current_path 是否是一个文件[返回结果为 True ]
print(os.path.split(current_path))
# 利用 path模块 的 split函数 将 'package_os.py' 与 路径分割开; 实际工作中经常通过这种方式将带有文件的路径进行分割
# >>> 执行结果为:('/Users/XXX/PycharmProjects/python_package', 'package_os.py')
print(os.path.isdir(os.path.split(current_path)[0]))
# 利用 path模块 的 isdir函数 判断 current_path 被 split 函数分割后 第一个元素是不是路径 [返回结果为 True ]
print(dir(os.path))
# 通过 dir()函数 查看 当前 os.path 模块更多的功能;[可以自己尝试一下 os.path 更多的功能]
加载全部内容