Python 文件创建 写入
渴望力量的哈士奇 人气:0在前面章节我们通过 os包学习了如何创建、读取一个文件夹,但是并没有学习如何创建、读写一个文件,接下来我们就学习关于文件的处理。当我们学习完文件处理之后,就可以随意读写文件。
内置函数 - open 获取文件对象
open() 函数
open()函数是是python的读写文件的基本函数,它可以生成文件对象可以创建,也可以操作文件的读写。
用法:
open(path, mode)
参数说明:
path:文件路径
mode:操作模式;比如读文件的模式,写文件的模式。下文有详细介绍
返回值:
文件对象
示例用法如下:
file = open('d://test.txt', 'w')
# >>> 代码释义:使用 open() 函数 对 D 磁盘下的 'test.txt' 文件执行写入的操作 ( w 为写入的操作 ) 并赋值给变量 file
利用文件对象进行创建与写入
文件操作的写入模式
| 模式 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
| w | 创建文件(w为写入的操作,当文件不存在时,则会创建文件;已创建文件,则内容会被覆盖) |
| w+ | 创建文件并读取文件 |
| wb | 二进制形式创建文件(与 w 的功能相同,只不过 web 的写入类型为 byte ) |
| wb+ | 二进制形式创建或追加内容(如果文件存在不会覆盖原本的内容,而是以 byte 类型进行追加) |
| a | 在文件中追加内容,如果没有该文件则会创建文件 |
| a+ | 读写模式追加(同样是追加内容,只不过赋予了读取的功能) |
| ab+ | 二进制形式读写追加(可以追加并读取 byte 类型的模式) |
文件对象的写入操作方法
| 方法名 | 参数 | 介绍 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| write | Message(字符串) | 写入信息 如果是带有b的模式,则会变为 byte 类型 | f.write(‘hello\n’) |
| writelines | Message_list(列表) | 批量写入 列表内须是字符串,按照索引位置依次写入; 若为b的模式,同上 | f.writelines([‘a\n’, ‘b\n’]) |
| close | 无 | 关闭并保存文件 | f.close() |
注意:操作文件完成后,必须使用 close 方法!!!不然可能会造成内存占用,如果反复生成文件对象进行写入操作,可能会造成内存溢出,我们的程序就会出问题了。
使用 w 模式 执行 write 方法
import os
import os.path
current_path = os.getcwd()
# print(current_path)
file_test = open(current_path + '/' + 'test.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
# 注意如果是在WIN系统,在写入中文时,需要设置编码格式;如果不是WIN系统,则不需要设置编码格式
file_test.write('Python 是一门优雅的编程语言')
file_test.close()
上文脚本我们提及,如果是在WIN系统,在写入中文时,需要设置编码格式。如果不设置编码格式,虽然不会报错,也可以写入成功。但是打开写入的文件,就如同下图:
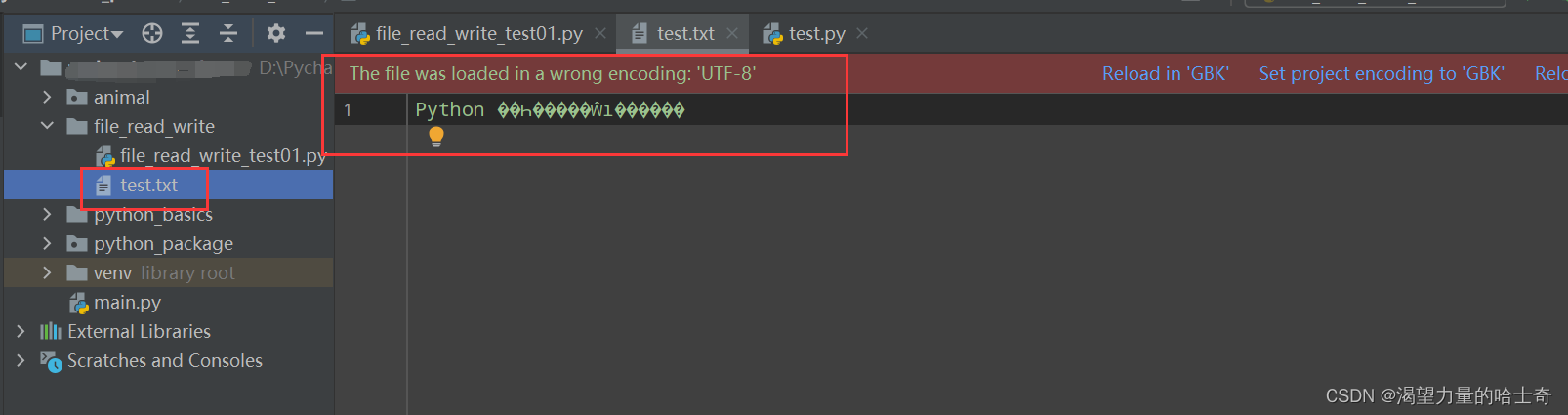
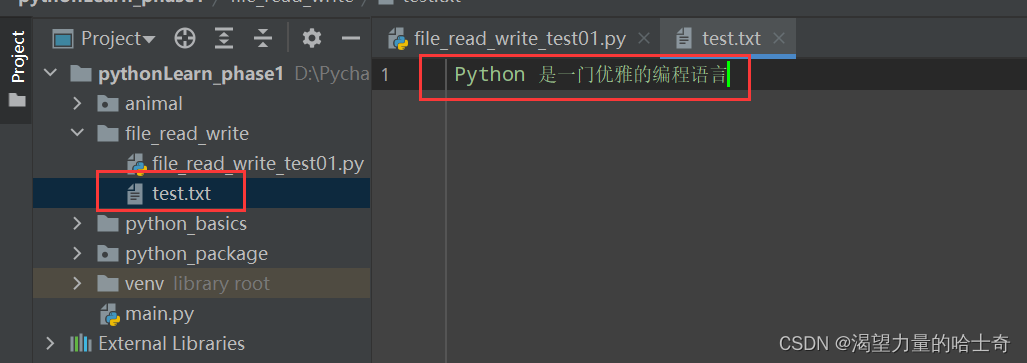
我们继上面演示的案例,在 text.txt 文件的基础上,继续演示 w 模式的功能。
import os
import os.path
current_path = os.getcwd()
# print(current_path)
file_test = open(current_path + '/' + 'test.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
file_test.write('Python 是一门优雅的编程语言')
file_test.close()
file_path = os.path.join(current_path, 'test.txt')
file_test = open(file_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8')
file_test.write('Python 不仅是一门优雅的编程语言,还不掉头发')
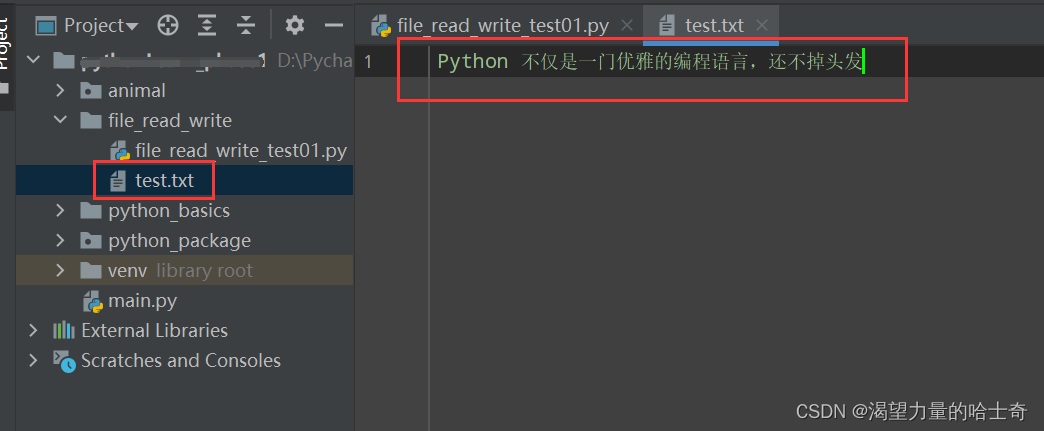
可以看到我们针对 text.txt 文件的基础上,继续演示的 w 模式 新传入的 Python 不仅是一门优雅的编程语言,还不掉头发 已经覆盖了 text.txt 文件原本的内容。
使用 w+ 模式 执行 write 方法
这里我们先 利用 w+ 模式 写入内容
import os.path
current_path = os.getcwd()
file_path = os.path.join(current_path, 'test.txt')
file_test = open(file_path, 'w+', encoding='utf-8')
file_test.write('人生苦短 我用Python')
file_test.close()
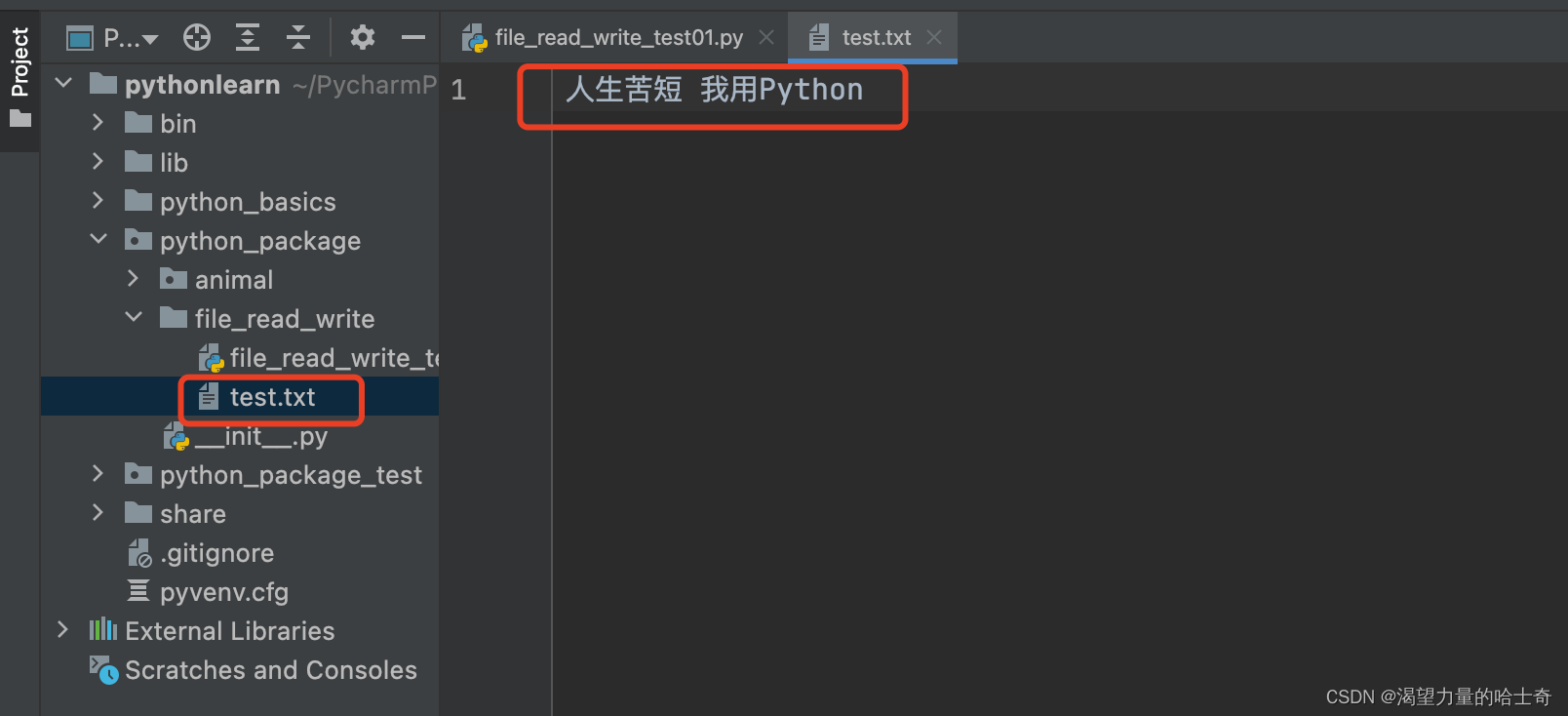
区别于 w 模式,w+ 模式 不仅可以创建文件,还可以读取文件。下面我看看看 如何 读取文件。(需要注意的是,读取的操作需要在终端操作,Pycharm 不显示读取的结果)
import os.path
current_path = os.getcwd()
file_path = os.path.join(current_path, 'test.txt')
file_test = open(file_path, 'w+', encoding='utf-8')
file_test.write('人生苦短 我用Python')
file_test.read()
file_test.seek(0)
file_test.read()
file_test.close()
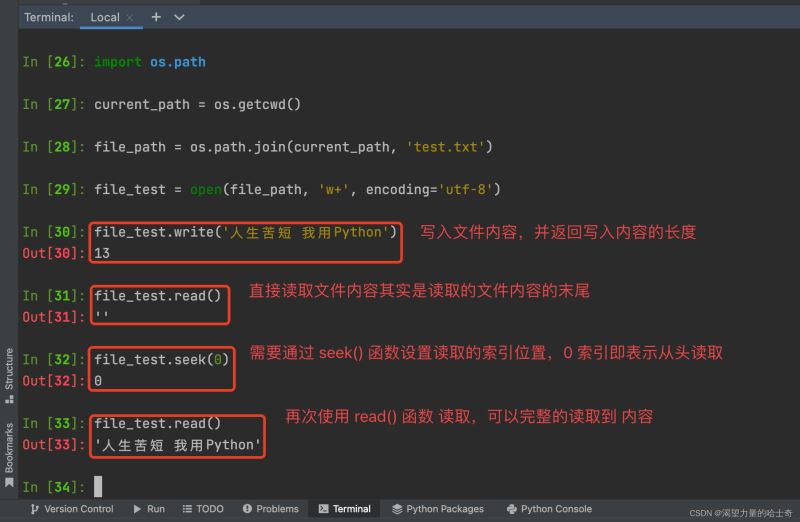
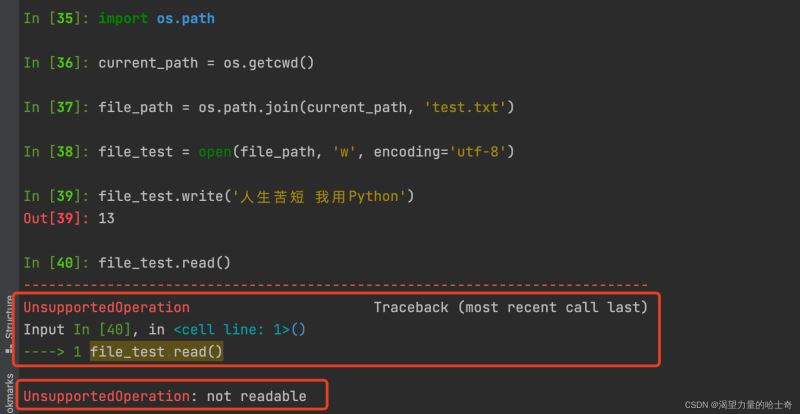
注意:只有 w+ 模式可以使用 read() 与 seek() 函数 读取文件内容 ,w 模式使用 read() 函数 读取文件内容会报错 ,如下图:
使用 ab 模式 执行 write 方法
我们先 使用 ab 模式 尝试将 字符串 通过 write 方法以追加的形式写入文件
import os.path
current_path = os.getcwd()
file_path = os.path.join(current_path, 'test.txt')
file_test = open(file_path, 'ab')
file_test.write('Python 是一种很有意思的编程语言')
终端执行效果如下:
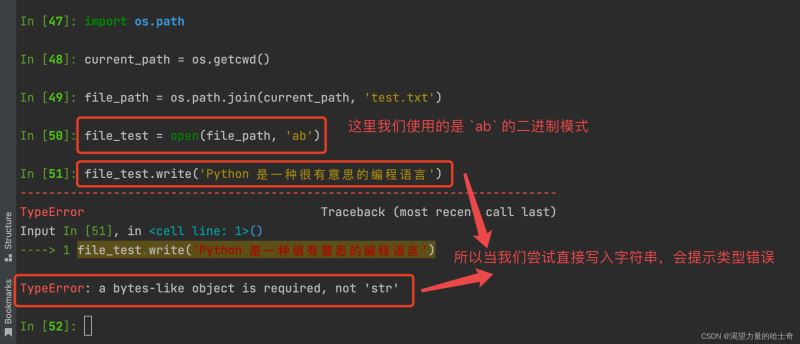
由于我们传入的是 字符串类型 ,无法直接追加写入文件,那么我们 将字符串转为 byte 类型是否能成功呢?
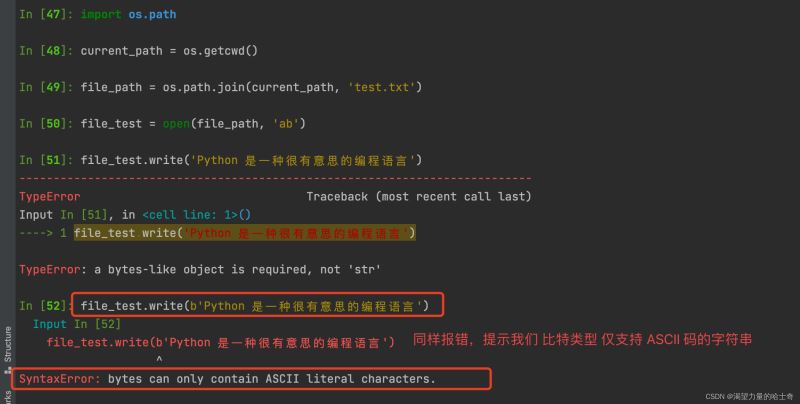
这又是为何?难道我们使用方法的姿势不对?其实不然,这里写入的 byte 类型 我们需要先转为 byte 类型 才可以成功的写入。示例如下:
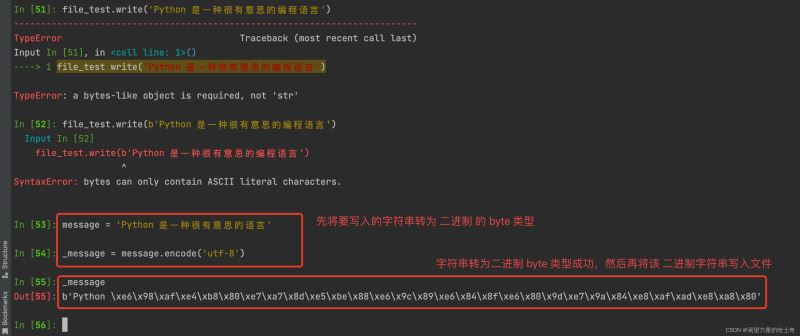
此时我们再次执行写入的动作,就可以将其追加写入文件。
file_test.write(_message) file_test.close()
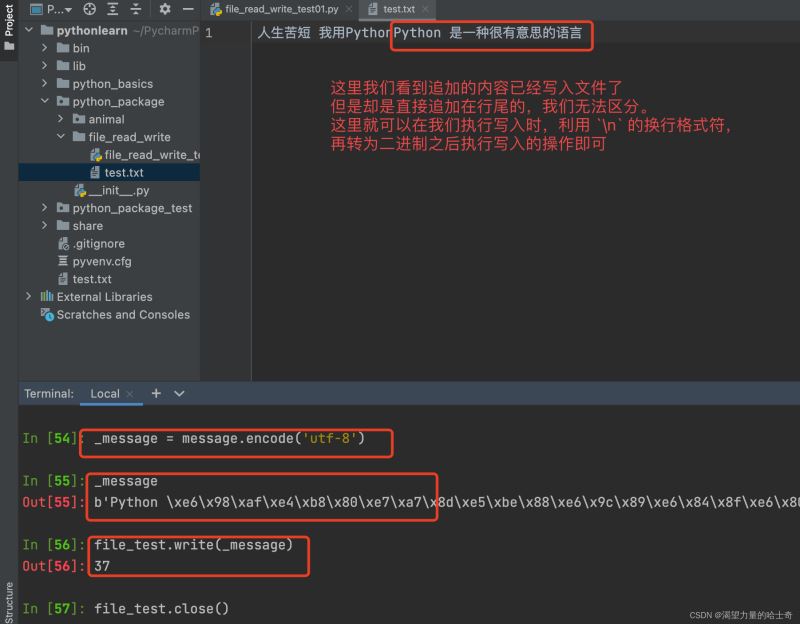
使用 a 模式 执行 writelines 方法
借着上面演示的案例,我们定义一个列表的字符串,然后 通过 open() 函数 的 a模式,使用 writelines 方法将内容写入文件
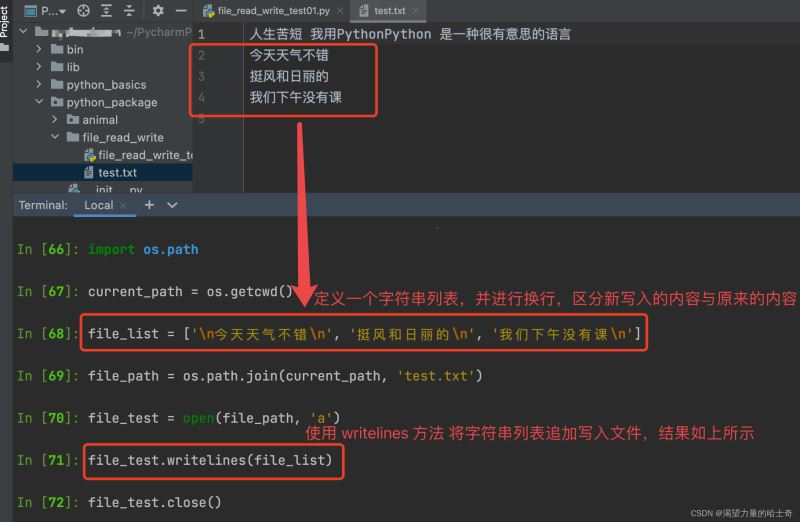
import os.path current_path = os.getcwd() file_path = os.path.join(current_path, 'test.txt') file_list = ['\n今天天气不错\n', '挺风和日丽的\n', '我们下午没有课\n'] file_test = open(file_path, 'a') file_test.writelines(file_list) file_test.close()
执行效果如下图:
实战小案例
需求:实现一个可以自动创建 python 包 的函数
import os
def create_package(path): # 定义一个创建 包 的函数
if os.path.exists(path): # 判断路径是否存在,若已经存在,则抛出异常
raise Exception('%s 已经存在,不可创建' % path)
else:
os.mkdir(path)
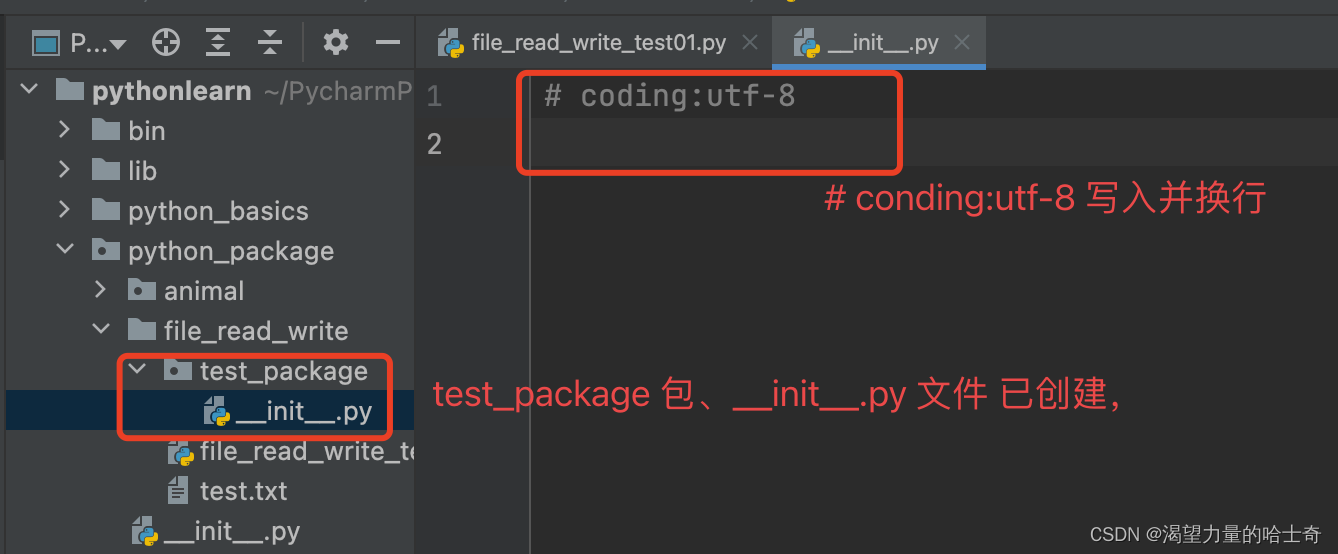
init_path = os.path.join(path, '__init__.py')
file_init = open(init_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8')
file_init.write('# coding:utf-8\n')
file_init.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
current_path = os.getcwd()
path = os.path.join(current_path, 'test_package')
create_package(path)
执行结果如下:
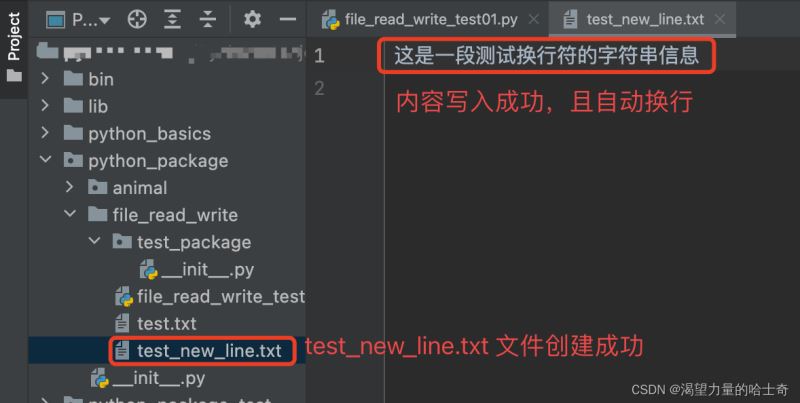
拓展:从上文脚本中,我们可以发现每次,执行写入的时候,都要写入 \n 换行符,很是麻烦,我们可以自定义一个 open 类,从而实现每次我们执行写入操作时的自动换行。
class Open(object):
def __init__(self, path, mode='w', is_return=True): # 这里的 is_return 我们定义的是换行的意思,结合下文的 message 理解
self.path = path
self.mode = mode
self.is_return = is_return
def write(self, message):
file_test = open(self.path, mode=self.mode)
if self.is_return: # 如果返回 Ture 则 在 message 后,增加换行符
message = '%s\n' % message
file_test.write(message)
file_test.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
current_path = os.getcwd()
# path = os.path.join(current_path, 'test_package')
open_path = os.path.join(current_path, 'test_new_line.txt')
# create_package(path)
# create_package(open_path)
open_test = Open(open_path)
open_test.write('这是一段测试换行符的字符串信息')
执行结果如下:
加载全部内容