springboot启动事件监听
字母哥哥 人气:6一、简介
Spring Boot提供了两个接口:CommandLineRunner、ApplicationRunner,用于启动应用时做特殊处理,这些代码会在SpringApplication的run()方法运行完成之前被执行。相对于之前章节为大家介绍的Spring的ApplicationListener接口自定义监听器、Servlet的ServletContextListener监听器。使用二者的好处在于,可以方便的使用应用启动参数,根据参数不同做不同的初始化操作。
二、常用场景介绍
实现CommandLineRunner、ApplicationRunner接口。通常用于应用启动前的特殊代码执行,比如:
- 将系统常用的数据加载到内存
- 应用上一次运行的垃圾数据清理
- 系统启动成功后的通知的发送等
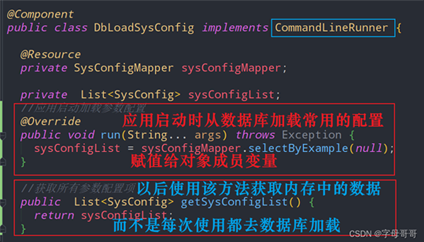
如下图是我实现了CommandLineRunner接口,在应用启动时将系统内常用的配置数据。从数据库加载到内存,以后使用该数据的时候只需要调用getSysConfigList方法,不需要每次使用该数据都去数据库加载。节省系统资源、缩减数据加载时间。
二、代码小实验 通过@Component定义方式实现
CommandLineRunner:参数是字符串数组
@Slf4j
@Component
public class CommandLineStartupRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args){
log.info("CommandLineRunner传入参数:{}", Arrays.toString(args));
}
}
ApplicationRunner:参数被放入ApplicationArguments,通过getOptionNames()、getOptionValues()、getSourceArgs()获取参数
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AppStartupRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) {
log.info("ApplicationRunner参数名称: {}", args.getOptionNames());
log.info("ApplicationRunner参数值: {}", args.getOptionValues("age"));
log.info("ApplicationRunner参数: {}", Arrays.toString(args.getSourceArgs()));
}
}
通过@Bean定义方式实现
这种方式可以指定执行顺序,注意前两个Bean是CommandLineRunner,最后一个Bean是ApplicationRunner 。
@Configuration
public class BeanRunner {
@Bean
@Order(1)
public CommandLineRunner runner1(){
return new CommandLineRunner() {
@Override
public void run(String... args){
System.out.println("BeanCommandLineRunner run1()" + Arrays.toString(args));
}
};
}
@Bean
@Order(2)
public CommandLineRunner runner2(){
return new CommandLineRunner() {
@Override
public void run(String... args){
System.out.println("BeanCommandLineRunner run2()" + Arrays.toString(args));
}
};
}
@Bean
@Order(3)
public ApplicationRunner runner3(){
return new ApplicationRunner() {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args){
System.out.println("BeanApplicationRunner run3()" + Arrays.toString(args.getSourceArgs()));
}
};
}
}
可以通过@Order设置执行顺序
三、执行测试
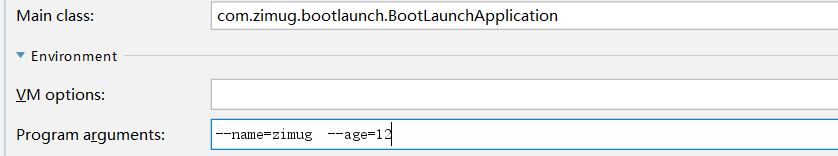
在IDEA Springboot启动配置中加入如下参数,保存后启动应用
测试输出结果:
c.z.boot.launch.config.AppStartupRunner : ApplicationRunner参数名称: [name, age]
c.z.boot.launch.config.AppStartupRunner : ApplicationRunner参数值: [18]
c.z.boot.launch.config.AppStartupRunner : ApplicationRunner参数: [--name=zimug, --age=18]BeanApplicationRunner run3()[--name=zimug, --age=18]
c.z.b.l.config.CommandLineStartupRunner : CommandLineRunner传入参数:[--name=zimug, --age=18]
BeanCommandLineRunner run1()[--name=zimug, --age=18]
e=18]
BeanCommandLineRunner run2()[--name=zimug, --age=18]
从测试结果上看(笔者目前不敢确定这个优先级顺序是不是常态,但从我的多次测试效果,顺序一直是这样的):
- ApplicationRunner执行优先级高于CommandLineRunner
- 以Bean的形式运行的Runner优先级要低于Component注解加implements Runner接口的方式
- Order注解只能保证同类的CommandLineRunner或ApplicationRunner的执行顺序,不能跨类保证顺序
四、总结
CommandLineRunner、ApplicationRunner的核心用法是一致的,就是用于应用启动前的特殊代码执行。ApplicationRunner的执行顺序先于CommandLineRunner;ApplicationRunner将参数封装成了对象,提供了获取参数名、参数值等方法,操作上会方便一些。
五、问题总结
这是笔者在实践中真实遇到的问题,就是我定义了多个CommandLineRunner的实现。出现奇怪的问题是:当你定义多个CommandLineRunner的实现的时候,其中一个或者几个将不会执行。
分析一下:下面的代码是SpringBootApplication启动项目之后会执行的代码,大家看代码中通过一个遍历来启动CommandLineRunner或者ApplicationRunner。也就是说,只有上一个CommandLineRunner执行完成之后,才会执行下一个CommandLineRunner,是同步执行的。
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}
所以,如果在CommandLineRunner某个实现run 方法体中调用了同步阻塞的API或者是一个 while(true) 循环,在遍历中处于该CommandLineRunner之后的其他实现将不会被执行。
加载全部内容