Java private方法
JavaEdge. 人气:0现在产品期望用户创建和保存逻辑分离:把User实例的创建和保存逻辑拆到两个方法分别进行。然后,把事务的注解 @Transactional 加在保存数据库的方法上。
@Service
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
public void saveStudent(String realname) throws Exception {
Student student = new Student();
student.setRealname(realname);
studentService.doSaveStudent(student);
}
@Transactional
private void doSaveStudent(Student student) throws Exception {
studentMapper.saveStudent(student);
if (student.getRealname().equals("小明")) {
throw new RuntimeException("该用户已存在");
}
}
}
执行程序,异常正常抛出

事务未回滚

源码解析
debug:
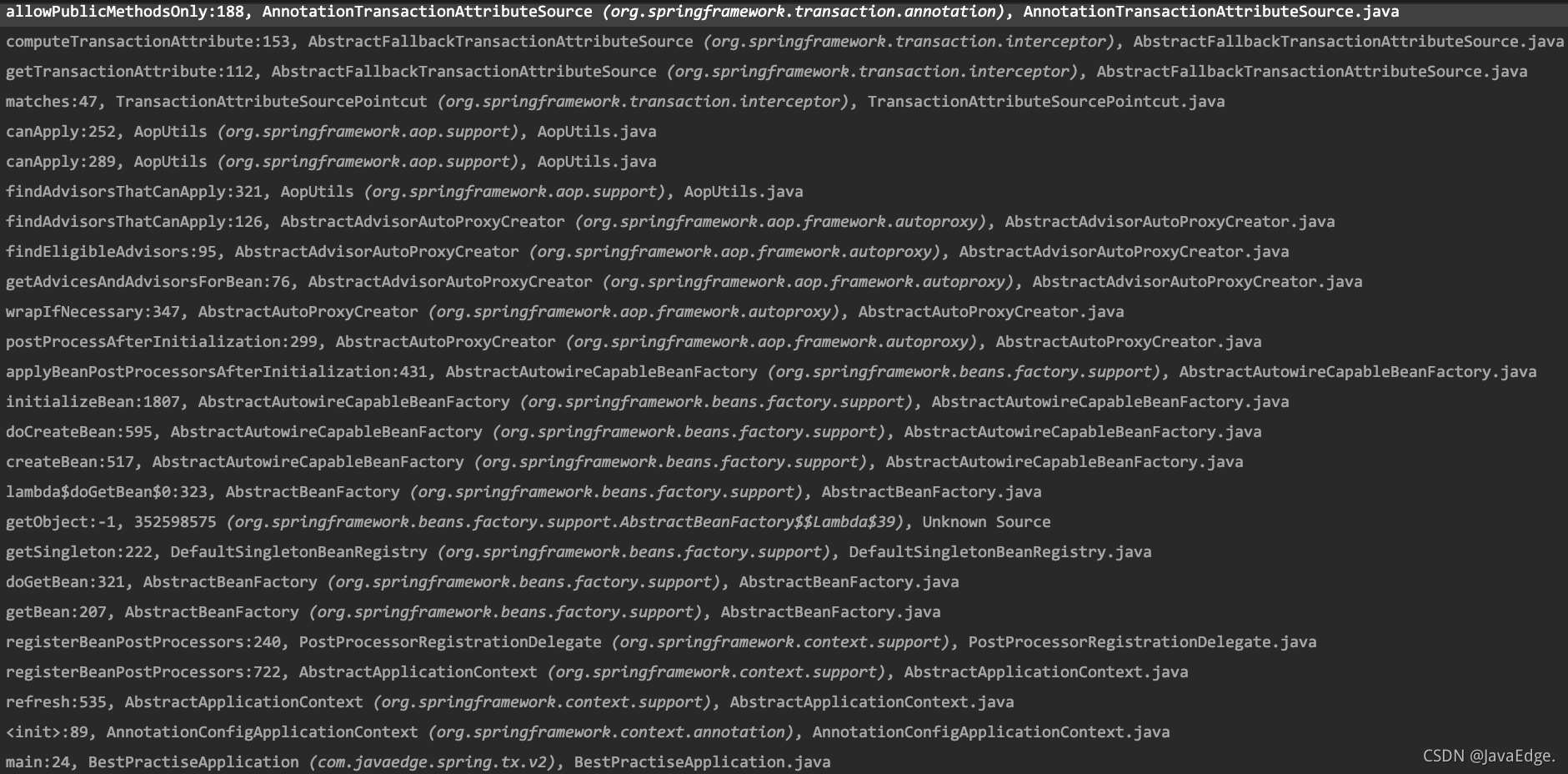
前一段是 Spring 创建 Bean 的过程。当 Bean 初始化之后,开始尝试代理操作,这是从如下方法开始处理的:
AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
继续 debug,直到
AopUtils#canApply
针对切面定义里的条件,确定这个方法是否可被应用创建成代理。有段 methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass) 判断这个方法是否符合这样的条件:
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
// ...
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) :
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}

从 matches() 调用到
AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource#getTransactionAttribute
获取注解中的事务属性,根据属性确定事务的策略。

接着调用到
computeTransactionAttribute
根据方法和类的类型确定是否返回事务属性:

当上图中条件判断结果为 true,则返回 null,表明该方法不会被代理,从而导致事务注解不会生效。
那到底是不是 true 呢?
条件1:allowPublicMethodsOnly()
AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource#publicMethodsOnly属性值

publicMethodsOnly 是通过 AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource 的构造方法初始化的,默认为 true。

条件2:Modifier.isPublic()
根据传入的 method.getModifiers() 获取方法的修饰符,该修饰符是 java.lang.reflect.Modifier 的静态属性,对应的几类修饰符分别是:
- PUBLIC: 1
- PRIVATE: 2
- PROTECTED: 4
这里做了一个位运算,只有当传入的方法修饰符是 public 类型的时候,才返回 true

综上两个条件,只有当注解为事务方法为 public 才会被 Spring 处理。
修正
只需将修饰符从 private 改成 public,其实该问题 IDEA 也会告警,一般都会避免。

调用这个加了事务注解的方法,必须是调用被 Spring AOP 代理过的方法:不能通过类的内部调用或通过 this 调用。所以我们的案例的StudentService,它Autowired了自身(StudentService)的一个实例来完成代理方法的调用。
加载全部内容