c++虚函数与虚函数表
考拉爱睡觉鸭~ 人气:01.什么是虚函数?
用virtual 修饰的成员函数叫虚函数
小知识: 没有虚构造函数 不写虚函数,没有默认的虚函数
普通函数不影响类的内存:
class MM
{
public:
void print()
{
cout << "普通函数"<< endl; //普通函数不影响类的内存<--->普通函数存在另一段内存中
}
protected:
};
void testVirtual()
{
//C语言不允许存在空的结构体
cout << sizeof(MM) << endl;/*(没有数据成员的)空的类或者结构体 占用1字节 用1字节标识当
前内存为结构体内存*/
}
int main()
{
testVirtual();
return 0;
}
/*输出*/
/* 1 */
2.虚函数会影响类的内存
增加一个指针的内存,32位操作系统多4个字节 ,64位操作系统多8个字节
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class MM
{
public:
virtual void print1()
{
cout << "虚函数1"<< endl;
}
/*virtual void print2()
{
cout << "虚函数2" << endl;
} 无论多少个虚函数,增加的字节就是一个指针的字节--->多了一个虚函数,还是4个字节*/
protected:
};
void testVirtual()
{
cout << sizeof(MM) << endl;
}
int main()
{
testVirtual();
return 0;
}
/*输出*/
/* 4 */
小知识:一旦有了数据,标识位就不需要存在了
class A
{
int num; //输出4而不是5 (4+1)
};
class B
{
//用1字节标识当前内存为结构体内存
};
void testVirtual()
{
cout << sizeof(A) << endl;
cout << sizeof(B) << endl;
}
int main()
{
testVirtual();
return 0;
}
/*输出*/
/*4
1*/
3.了解虚函数表--->通过虚函数表的指针去访问数据
就是一个指针存储所有虚函数的首地址(虚函数函数名)<--->函数指针
只有指针可以操作一段内存(4字节)
/*无论多少个虚函数,增加的字节就是一个指针的字节*/
所有的虚函数其实是 用一个函数指针去存储的 ,把 这个函数指针指向的这一段内存 称为虚函数表
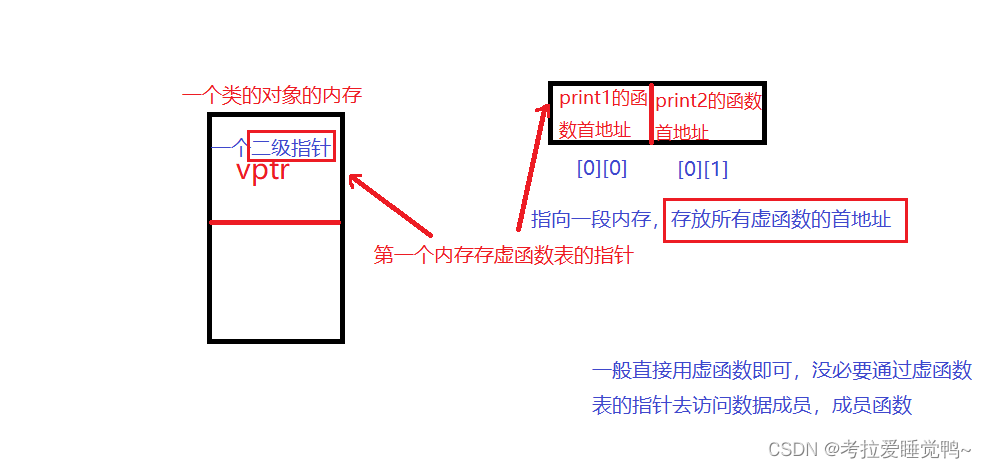
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class MM
{
public:
virtual void print1()
{
cout << "虚函数1"<< endl;
}
virtual void print2()
{
cout << "虚函数2"<< endl;
}
protected:
};
void testVirtual()
{
//虚函数表
MM mm; //构建一个对象
int** vptr = (int** )&mm; //定义一个二级指针&对象的地址 强转类型
typedef void(*PF)(); //函数指针定义别名
PF func = (PF)vptr[0][0]; //把地址转为函数指针,访问第一个函数指针的地址
func(); //通过虚函数表的函数指针调用第一个虚函数
func = (PF)vptr[0][1];
func(); //调用第二个虚函数
}
int main()
{
testVirtual();
return 0;
}
/*输出*/
/*虚函数1
虚函数2*/
4.虚函数声明
虚函数可以在类中声明,在类外实现,不再需要virtual修饰词,只要类名限定就可以了
class MM
{
public:
virtual void print3();
protected:
};
void MM::print3() {
cout << "虚函数3" << endl;
}
int main()
{
MM mm;
mm.print3();
return 0;
}
/*输出*/
/*虚函数3*/
加载全部内容