Java CharArrayWriter流使用
咕噜是个大胖子 人气:0Java CharArrayWriter流
一、CharArrayWriter流定义
API说明:该类实现了一个可用作字符输出流的字符缓冲区,当数据写入流时,缓冲区自动增长,请注意在此类上调用close()无效,并且可以在流关闭后调用此类的方法而不生成IOException。
二、CharArrayWriter流构造函数
根据指定缓冲区大小或者默认缓冲区大小创建CharArrayWriter流对象
/**
*创造默认缓冲区大小的CharArrayWriter对象
*/
public CharArrayWriter() {
this(32);
}
/**
* 创造指定缓冲区大小的CharArrayWriter对象
*/
public CharArrayWriter(int initialSize) {
if (initialSize < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative initial size: "
+ initialSize);
}
buf = new char[initialSize];
}
三、CharArrayWriter流实例域
/**
* 字符缓冲区
*/
protected char buf[];
/**
* 缓冲区中的当前位置
*/
protected int count;
四、CharArrayWriter流方法
1)write(int c):写一个字符到缓冲区中
/**
* 写一个单个字符到缓冲区中
*/
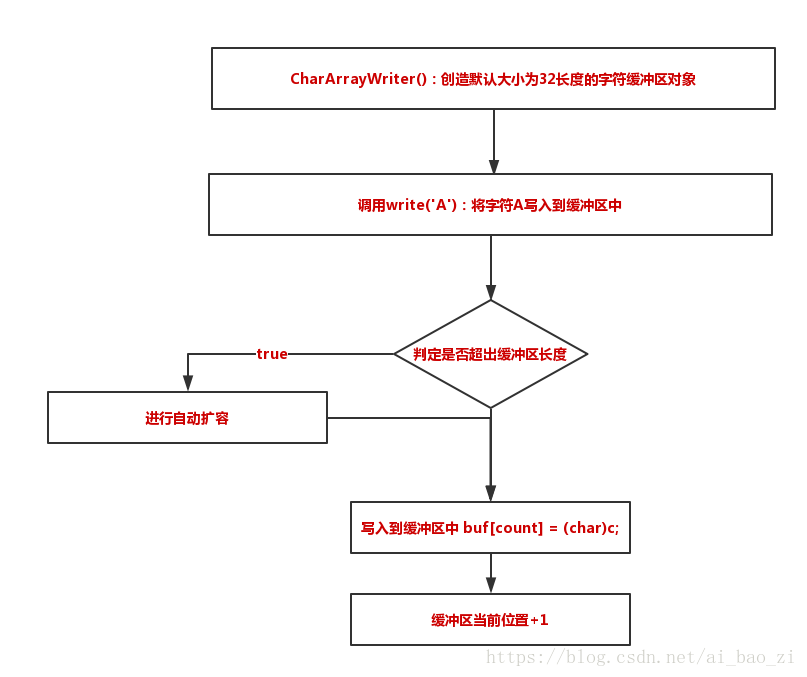
public void write(int c) {
synchronized (lock) {
int newcount = count + 1;
//判定写入的下个元素是否超出缓冲区长度
if (newcount > buf.length) {
//进行扩容
buf = Arrays.copyOf(buf, Math.max(buf.length << 1, newcount));
}
buf[count] = (char)c;
count = newcount;
}
}
实际流程:
2)write(char c[], int off, int len):从字符数组中写len个字符到缓冲区中
/**
* 将字符数组的一部分写入到缓冲区中,自动扩容增长
*/
public void write(char c[], int off, int len) {
if ((off < 0) || (off > c.length) || (len < 0) ||
((off + len) > c.length) || ((off + len) < 0)) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return;
}
synchronized (lock) {
int newcount = count + len;
//判定缓冲区写入len个字符后长度是否超出限制
if (newcount > buf.length) {
buf = Arrays.copyOf(buf, Math.max(buf.length << 1, newcount));
}
System.arraycopy(c, off, buf, count, len);
count = newcount;
}
}
实际流程:

3)write(String str, int off, int len):将字符串的一部分写入到缓冲区中
public void write(String str, int off, int len) {
synchronized (lock) {
int newcount = count + len;
if (newcount > buf.length) {
buf = Arrays.copyOf(buf, Math.max(buf.length << 1, newcount));
}
str.getChars(off, off + len, buf, count);
count = newcount;
}
}
4)writeTo(Writer out):将缓冲区的内容写入到另一个字符输出流中
public void writeTo(Writer out) throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
out.write(buf, 0, count); //本质理解为将缓冲区的内容给写了出去
}
}
5)检索缓冲区中的数据
/**
* 将缓冲区中的数据转成字符串
* @return the string.
*/
public String toString() {
synchronized (lock) {
return new String(buf, 0, count);
}
}
/**
* 将缓冲区的数据转成字符数组
*/
public char toCharArray()[] {
synchronized (lock) {
return Arrays.copyOf(buf, count);
}
}
6)close():关闭流无效,本质没有做任何操作
/**
* 刷新流--无效
*/
public void flush() { }
/**
* 关闭流--无效
*/
public void close() { }
四、CharArrayWriter流的作用
与CharArrayReader流一样,待后期理解加深、实际项目运用过后再来补充
Java基础之什么是CharArrayWriter
CharArrayWriter 实现了以数组作为目标的输出流。CharArrayWriter 有两个构造函数:
CharArrayWriter( ) CharArrayWriter(int numChars)
第一种形式,创建了一个默认长度的缓冲器。
第二种形式,缓冲器长度由numChars指定。
缓冲器保存在CharArrayWriter的buf 成员中。缓冲器大小在需要的情况下可以自动增长。缓冲器保持的字符数包含在CharArrayWriter的count 成员中。buf 和count 都是受保护的域。
下面的例子阐述了CharArrayWriter
我们继续使用前面显示的ByteArrayOutputStream 例子中演示的程序。它的输出与以前的例子输出相同:
// Demonstrate CharArrayWriter.
import java.io.*;
class CharArrayWriterDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
CharArrayWriter f = new CharArrayWriter();
String s = "This should end up in the array";
char buf[] = new char[s.length()];
s.getChars(0, s.length(), buf, 0);
f.write(buf);
System.out.println("Buffer as a string");
System.out.println(f.toString());
System.out.println("Into array");
char c[] = f.toCharArray();
for (int i=0; i<c.length; i++) {
System.out.print(c[i]);
}
System.out.println("\nTo a FileWriter()");
FileWriter f2 = new FileWriter("test.txt");
f.writeTo(f2);
f2.close();
System.out.println("Doing a reset");
f.reset();
for (int i=0; i<3; i++)
f.write('X');
System.out.println(f.toString());
}
}
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持。
加载全部内容