C++拷贝构造函数
骆驼胡杨 人气:0拷贝构造函数
拷贝构造函数,它只有一个参数,参数类型是本类的引用。
复制构造函数的参数可以是 const 引用,也可以是非 const 引用。 一般使用前者,这样既能以常量对象(初始化后值不能改变的对象)作为参数,也能以非常量对象作为参数去初始化其他对象。一个类中写两个复制构造函数,一个的参数是 const 引用,另一个的参数是非 const 引用,也是可以的。
1. 手动定义的拷贝构造函数
Human.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <Windows.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Human {
public:
Human();
Human(int age, string name, string sex);
//手动定义了一个拷贝构造函数
Human(const Human &other);
string getName() const;
string getSex() const;
int getAge() const;
void description() const; //描述信息
private:
string name; //姓名
string sex; //性别
int age; //年龄
};
Human.cpp
#include "Human.h"
Human::Human() {
}
Human::Human(int age, string name, string sex) {
this->name = name;
this->sex = sex;
this->age = age;
}
//拷贝构造函数
Human::Human(const Human& other){
//把other对象的数据拷贝到另一个对象的私有数据
this->name = other.name;
this->sex = other.sex;
this->age = other.age;
}
string Human::getName() const {
return name;
}
string Human::getSex() const {
return sex;
}
int Human::getAge() const {
return age;
}
void Human::description() const {
cout << "姓名: " << getName() << endl;
cout << "年龄: " << getAge() << endl;
cout << "性别: " << getSex() << endl;
}
main.cpp
#include "Human.h"
Human::Human() {
}
Human::Human(int age, string name, string sex) {
this->name = name;
this->sex = sex;
this->age = age;
}
//拷贝构造函数
Human::Human(const Human& other){
//把other对象的数据拷贝到另一个对象的私有数据
this->name = other.name;
this->sex = other.sex;
this->age = other.age;
}
string Human::getName() const {
return name;
}
string Human::getSex() const {
return sex;
}
int Human::getAge() const {
return age;
}
void Human::description() const {
cout << "姓名: " << getName() << endl;
cout << "年龄: " << getAge() << endl;
cout << "性别: " << getSex() << endl;
}
2. 合成的拷贝构造函数
当程序员没有定义拷贝构造函数时, 编译器会自动生成合成的拷贝构造函数
说明:
合成的拷贝构造函数的缺点: 使用“浅拷贝”
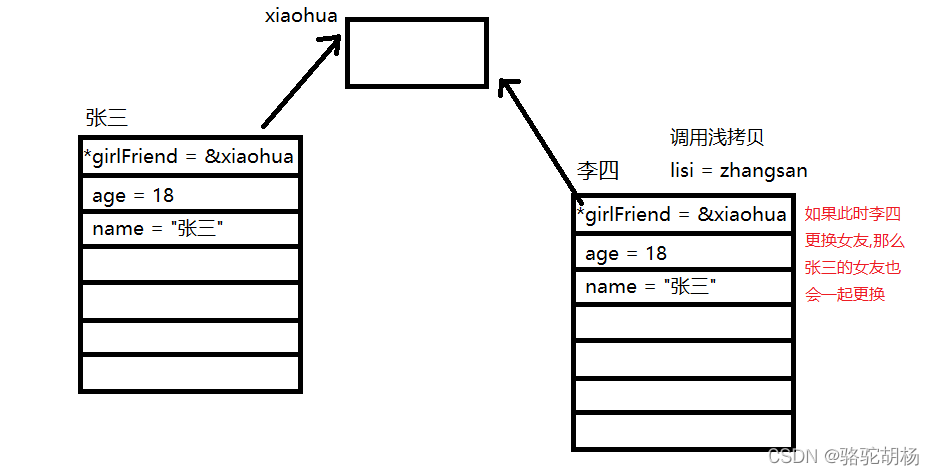
解决方案:在自定义的拷贝构造函数中,使用‘深拷贝
Human.h
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <Windows.h>
using namespace std;
class Human {
public:
Human();
//定义了一个拷贝构造函数
Human(const Human & man);
string getName() const;
string getSex() const;
int getAge() const;
const char* getAddr();
void setAddr(char* addr); //设置地址
private:
string name; //姓名
string sex; //性别
int age; //年龄
char* addr; //地址
};
Human.cpp
#include "Human.h"
#define ADDR_LEN 64
Human::Human() {
name = "无名";
sex = "未知";
age = 18;
const char* addr_s = "China";
addr = new char[ADDR_LEN];
strcpy_s(addr, ADDR_LEN, addr_s);
}
//拷贝构造函数
Human::Human(const Human& other){
cout << "调用拷贝构造函数" << endl;
//把other对象的数据拷贝到私有数据
this->name = other.name;
this->sex = other.sex;
this->age = other.age;
//使用深拷贝, 单独分配一个内存
this->addr = new char[ADDR_LEN];
strcpy_s(this->addr, ADDR_LEN, other.addr);
}
string Human::getName() const {
return name;
}
string Human::getSex() const {
return sex;
}
int Human::getAge() const {
return age;
}
const char* Human::getAddr(){
return addr;
}
void Human::setAddr(char* addr){
if (!addr) return;
strcpy_s(this->addr, ADDR_LEN, addr);
}
#include "Human.h"
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
Human zhangsan;
//初始化调用拷贝构造函数
Human lisi = zhangsan; //自动调用拷贝构造函数
//赋值的时候调用的是赋值构造函数
//lisi = zhangsan;
cout <<"李四地址: " << lisi.getAddr() << endl;
cout <<"张三地址: " << zhangsan.getAddr() << endl;
cout << "张三修改地址" << endl;
zhangsan.setAddr((char*)"美国");
cout << "李四地址: " << lisi.getAddr() << endl;
cout << "张三地址: " << zhangsan.getAddr() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
总结
加载全部内容