VueRouter4.x入门
一碗周 人气:0写在前面
Vue Router是Vue团队的研发的一款与Vue.js核心深度集成的一款路由插件,使Vue构建单页面程序变得非常的简单;Vue Router目前最新版本是4.X,也是Vue3推荐使用的版本,这篇文章我们就来学习一下Vue Router4.X。
URL.hash与History
Vue Router中存在两种history(记录历史路由),分别是URL.hash和HTML5中提供的History两种。
hash历史记录对于没有主机的Web应用程序(例如file://),或当配置服务器不能处理任意的URL时非常有用,但是hash的SEO非常差劲;
History历史是HTML5中新增的,对于IE来说不是很友好,但是Vue3都放弃IE了,你也就不用考虑IE了;这种方式是目前最常见的一种方式,但是应用程序必须通过http协议被提供服务。
安装与使用流程
首先我们安装Vue Router,命令如下:
npm i vue-router
然后在main.js中写入如下代码:
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 1 引入 createRouter
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router'
// 2 定义路由映射表
const routes = [
/* more router */
]
// 3 创建路由实例,并传递对应配置
const router = createRouter({
// history 模式 这里使用createWebHistory
history: createWebHistory(),
// 传递路由映射表
routes
})
createApp(App).use(router).mount('#app')上面的代码中的routes如果多的话,可以定义一个router.js文件,将其进行抽离,示例代码如下:
router.js
export default [ /* more router */ ]
main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 2 引入路由映射表
import routes from './router'
// 1 引入 createRouter
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router'
// 3 创建路由实例,并传递对应配置
const router = createRouter({
// history 模式 这里使用createWebHistory
history: createWebHistory(),
// 传递路由映射表
routes
})
createApp(App).use(router).mount('#app')或者**直接在****router.js中直接导出一个路由实例,在main.js**中使用即可(这种方式更常用)。
router-link和router-view
router-link
<router-link>是Vue提供的自定义组件,用于创建链接,在Vue中并没有使用原生的<a>,因为<a>改变URL后会重新加载页面而<router-link>不会;关于<router-link>组件的细节支持哪些属性,可以参考文档。
router-view
<router-view>组件用于与URL对应的组件,例如下面这段代码:
<template>
<router-link to="/hello"
><img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png"
/></router-link>
<router-view></router-view>
</template>然后我们的router.js的代码如下:
import RootComponent from './components/root.vue'
export default [
{
path: '/',
// 引入组件
component: RootComponent
},
{
path: '/hello',
// 路由懒加载引入组件
component: () => import('./components/HelloWorld.vue')
}
]关于其他配置项,可以参考文档。
代码运行结果如下所示:

路由懒加载
当我们的应用越来越大时,打包后的JavaScript代码也会特别的大,这个时候需要我们将整个应用拆分为不同的块,而Vue Router就支持这个功能,我们只需要使用动态导入替换静态导入即可,就比如上面那段代码:
component: () => import('./components/HelloWorld.vue')然后打包(webpack、Vite)工具就会将这些动态导入的组件单独打包,如下图所示:
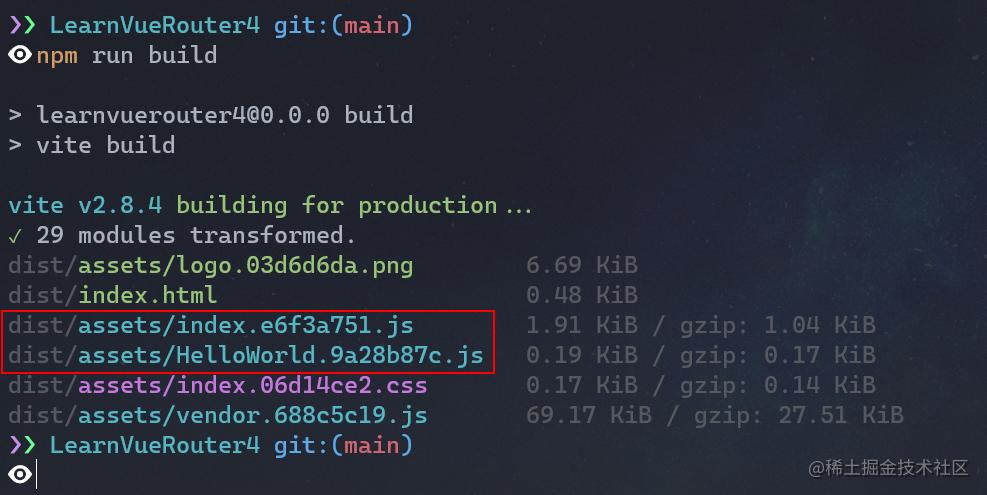
动态路由
VueRouter允许我们动态的去设置路由匹配规则,例如我们现在有一个User组件,组件的内容会根据不同的ID展示不同的内容,设置方法只需要通过:参数名的形式去设置即可。
例如:
{
path: '/user/:id',
component: () => import('@/components/User')
}在模板中跳转如下:
<router-link to="/user/10010"></router-link>
或者通过useRouter这个hook提供的push方法,例如:
import { useRouter } from 'vue-router'
const {push} = useRouter()
push({
path: '/user',
params: { id: 10010 }
})
// 或者
let id = 10010
push('/user/' + id)获取路由地址可以通过useRoute这个hook,用法与useRouter一致。
匹配所有路由
VueRouter的动态路由允许我们匹配哪些没有匹配到的路由,示例代码如下:
{
path: '/:pathMatch(.*)',
component: () => import('./components/Page404.vue'),
},当前面的路由匹配未成功时,就会匹配这个路由。
路由嵌套
现在我们有一个需求,就是在HelloWorld组件下存两个组件,需要切换着两个组件。
这个时候路由嵌套的就发挥作用了,其实路由嵌套比较简单,就是通过路由配置中的一个children属性来实现,示例代码如下:
HelloWorld.vue
<template>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<div
style="
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
width: 240px;
margin: 0 auto;
"
>
<router-link to="about">about</router-link>
<router-link to="user">user</router-link>
</div>
<router-view></router-view>
</template>router.js
{
path: '/hello',
// 路由懒加载引入组件
component: () => import('./components/HelloWorld.vue'),
children: [
{
path: 'about',
component: () => import('./components/about.vue'),
},
{
path: 'user',
component: () => import('./components/user.vue'),
},
],
},子组件比较简单,只有一个<h1>标签,最终效果如下:

写在最后
加载全部内容