C++ 命名空间
ALL IN C 人气:0一、C++ 命名空间
命名空间为了大型项目开发,而引入的一种避免命名冲突的一种机制。比如说,在一个大型项目中,要用到多家软件开发商提供的类库。在事先没有约定的情况下,两套类库可能在存在同名的函数或是全局变量而产生冲突。项目越大,用到的类库越多,开发人员越多,这种冲突就会越明显。
1.默认NameSpace(Global&Function)
Global scope 是一个程序中最大的 scope。也是引起命名冲突的根源。C 语言没有从语言层面提供这种机制来解决。也算是 C 语言的硬伤了。Global scope 是无名的命名空间。
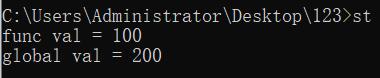
//c 语言中如何访问被局部变量覆盖的全局变量
int val = 200;
int main()
{
int *p = &val;
int val = 100;
printf("func val = %d\n",val);
printf("global val = %d\n",*p);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int val = 200;
void func()
{
return ;
}
int main()
{
int val = 100;
cout<<"func val = "<<val<<endl;
cout<<"global val = "<<::val<<endl;
::func(); //因为不能在函数内定义函数。所以前而的::没有意义。
return 0;
}
2.语法规则
NameSpace是对全局(Global scope)区域的再次划分。
1.声明
命令空间的声明及namespace中可以包含的内容
namespace NAMESPACE
{
全局变量 int a;
数据类型 struct Stu{};
函数 void func();
其它命名空间 namespace
}
2.使用方法
1.直接指定 命名空间: Space::a = 5;
2.使用 using+命名空间+空间元素:using Space::a;
3.使用 using +namespace+命名空间: using namespace Space;
3.支持嵌套
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace MySpace
{
int x = 1;
int y = 2;
namespace Other {
int m = 3;
int n = 4;
}
}
int main()
{
using namespace MySpace::Other;
cout<<m<<n<<endl;
return 0;
}
4.协作开发
同名命名空间自动合并,对于一个命名空间中的类,要包含声明和实现。
a.h
#ifndef A_H
#define A_H
namespace XX {
class A
{
public:
A();
~A();
};
}
#endif // A_H
a.cpp
#include "a.h"
using namespace XXX
{
A::A()
{
}
A::~A()
{
}
}
b.h
#ifndef B_H
#define B_H
namespace XX
{
class B
{
public:
B();
~B();
};
}
#endif // B_
b.cpp
#include "b.h"
namespace XX {
B::B()
{
}
B::~B()
{
}
}
main.cpp
include <iostream>
#include "a.h"
#include "b.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace XX;
int main()
{
A a;
B b;
return 0;
}
总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能够给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注的更多内容!
加载全部内容