C语言 单链表基本功能 C语言实现单链表的基本功能详解
我是一个小小孩 人气:0想了解C语言实现单链表的基本功能详解的相关内容吗,我是一个小小孩在本文为您仔细讲解C语言 单链表基本功能的相关知识和一些Code实例,欢迎阅读和指正,我们先划重点:C语言 单链表,C语言 单链表基本功能,下面大家一起来学习吧。
1.首先简单了解一下链表的概念:
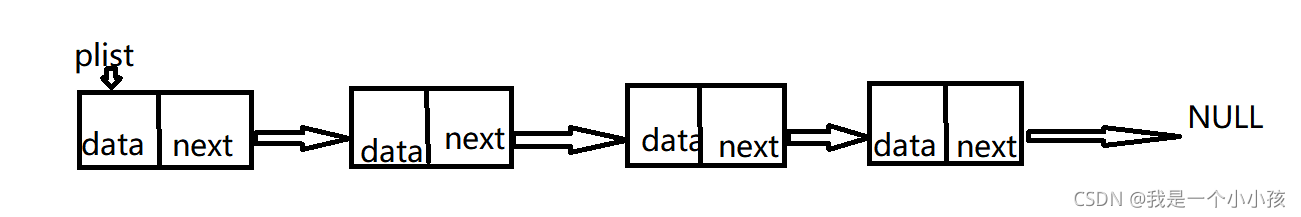
要注意的是链表是一个结构体实现的一种线性表,它只能从前往后,不可以从后往前(因为next只保存下一个节点的地址).在实现单链表的操作时,需要用指针来操作.很简单,注释写的很详细,欢迎大家指正哈哈哈哈~之前写的太烂了重新写了一下.....
2.代码展示:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct linklist {
int data;
struct linklist* next;
}node;
//目录
//1.动态申请节点
node* Creatnode(int x);
//2.单链表的尾插
void PushBack(node** plist, int x);
//3.单链表的打印
void Printlist(node** plist);
//4.单链表尾删
void Popback(node** plist);
//5.单链表的头插
void PushFront(node** plist, int x);
//6.单链表的头删
void PopFrount(node** plist);
//7.单链表的查找
node* Findpos(node* plist, int x);
//8.单链表在pos位置之后插入x
void Insertlinstafter(node* pos, int x);
//9.单链表删除pos位置之后的元素
void PopPosAfter(node* pos);
//10.单链表的销毁
void Destorylist(node** plist);
//1.动态申请节点
node* Creatnode(int x) {
node* t = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
if (t == NULL) {
assert(0);
return NULL;
}
else {
t->next = NULL;
t->data = x;
return t;
}
}
//2.单链表的尾插
void PushBack(node** plist, int x) {
assert(plist);
if (*plist == NULL) {
*plist = Creatnode(x);
}
else {
node* p = *plist;
while (p->next) {
p = p->next;
}
p->next = Creatnode(x);
}
}
//3.单链表的打印
void Printlist(node** plist) {
assert(plist);
node* p =* plist;
while (p) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
}
//4.单链表尾删
void Popback(node** plist) {
assert(plist);
if (*plist == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
node* p = *plist;
node* q = NULL;
while (p->next) {
q = p;
p = p->next;
}
q->next =NULL;
free(p);
}
//5.单链表的头插
void PushFront(node** plist, int x) {
assert(plist);
node* t = Creatnode(x);
if (NULL == *plist) {
*plist = t;
}
else {
t->next = *plist;
*plist = t;
}
}
//6.单链表的头删
void PopFrount(node** plist) {
assert(plist);
if (plist == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
else {
node* p = *plist;
*plist = p->next;
free(p);
}
}
//7.单链表的查找
node* Findpos(node* plist, int x) {
node* cur = plist;
while (cur) {
if (cur->data == x) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//8.单链表在pos位置之后插入x
void Insertlinstafter(node* pos, int x) {
assert(pos);
if (NULL == pos) {
return ;
}
node* t = Creatnode(x);
t->next = pos->next;
pos->next = t;
}
//9.单链表删除pos位置之后的元素
void PopPosAfter(node* pos) {
assert(pos);
if (pos->next == NULL) {
return;
}
else{
node* p = pos->next;
pos->next = p->next;
free(p);
}
}
//10.单链表的销毁
void Destorylist(node** plist) {
assert(plist);
node* p = *plist;
while (p) {
*plist = p->next;
free(p);
p = *plist;
}
*plist = NULL;
}
void test1() {
node* plist=NULL;//创建头指针
PushBack(&plist, 1);//尾插元素
PushBack(&plist, 2);
PushBack(&plist, 3);
PushBack(&plist, 4);
PushBack(&plist, 5);
Printlist(&plist);//打印链表元素 1 2 3 4 5
printf("\n");
Popback(&plist); //尾删元素
PushFront(&plist, 0);//首插元素0
Printlist(&plist);//打印链表 0 1 2 3 4
printf("\n");
PopFrount(&plist);//首删元素0
Printlist(&plist);//打印链表 1 2 3 4
printf("\n");
Findpos(plist,1);//寻找链表中1的地址,不方便演示,下面会演示
Insertlinstafter(Findpos(plist, 4), 5);//在4后面插入5,用到上面的Findpos函数
Printlist(&plist);//打印链表 1 2 3 4 5
printf("\n");
PopPosAfter(Findpos(plist, 4));//删除指定位置后面的元素(删除4后面的5)
Printlist(&plist);//打印链表 1 2 3 4
printf("\n");
Destorylist(&plist);//销毁链表
Printlist(&plist);//打印链表
}
void test() {
test1();
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
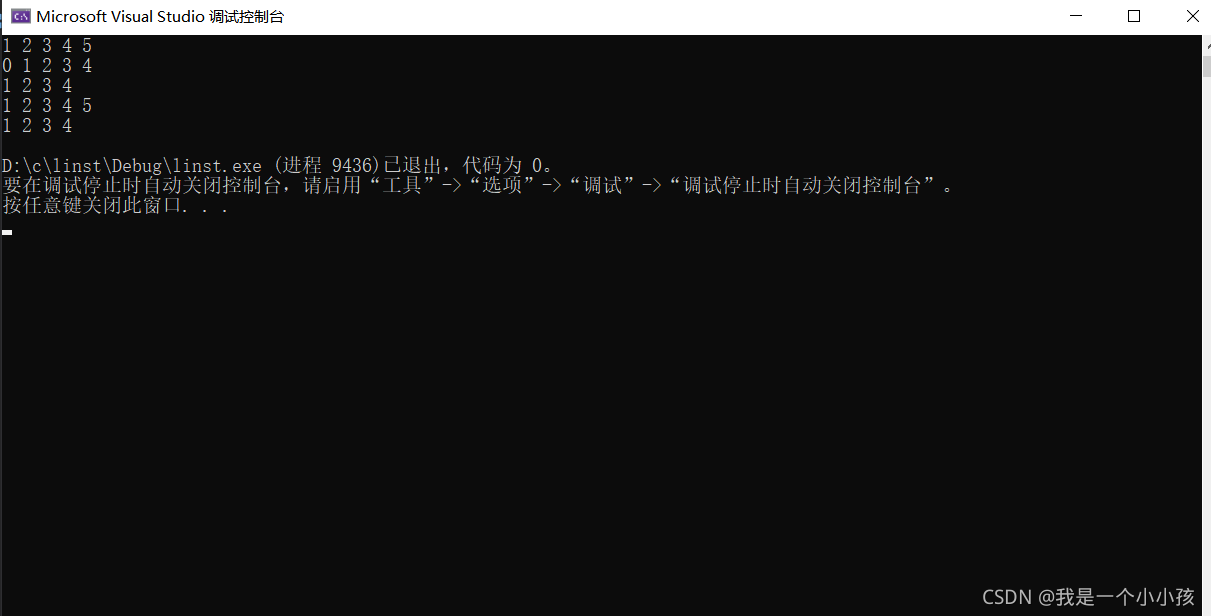
3.测试结果:
a.先创建了头指针plist
b.尾插1 2 3 4 5
c. 尾删元素5
d.首插元素0
e.首删元素0
f.在元素4 后面插入5
g.删除4元素后面的5
h.销毁链表
到此这篇关于C语言实现单链表的基本功能详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关单链表基本功能内容请搜索以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持!
加载全部内容