C++ LRU 与 LFU 缓存算法 C++ 实现LRU 与 LFU 的缓存算法
Ito Schum 人气:0想了解C++ 实现LRU 与 LFU 的缓存算法的相关内容吗,Ito Schum在本文为您仔细讲解C++ LRU 与 LFU 缓存算法的相关知识和一些Code实例,欢迎阅读和指正,我们先划重点:C++,LRU,缓存算法,C++,LFU,缓存算法,下面大家一起来学习吧。
一、LRU (Least Recently Used) 缓存
详见 LeetCode Q146
https:// leetcode.com/problems/l ru-cache/
https:// leetcode-cn.com/problem s/lru-cache/
问题描述:
LRUCache(int capacity)以正整数作为容量capacity初始化LRU缓存int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回 -1 。void put(int key, int value)如果关键字已经存在,则变更其数据值;如果关键字不存在,则插入该组「关键字-值」。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。- 在
O(1)时间复杂度内完成这两种操作
所用数据结构:
为了使 get 与 put 操作的平均时间复杂度为 O(1) ,
使用双向链表 (STL list ) 储存缓存内容 (使用 STL pair {key, value} 表示),
使用哈希表 (STL unordered_map ) 储存 “key” 到 “pair iterator ” 的关系映射
typedef std::unordered_map<int, std::list<std::pair<int, int> >::iterator > CacheMap; typedef std::list<std::pair<int, int> > LRUList;
流程图:
- get function
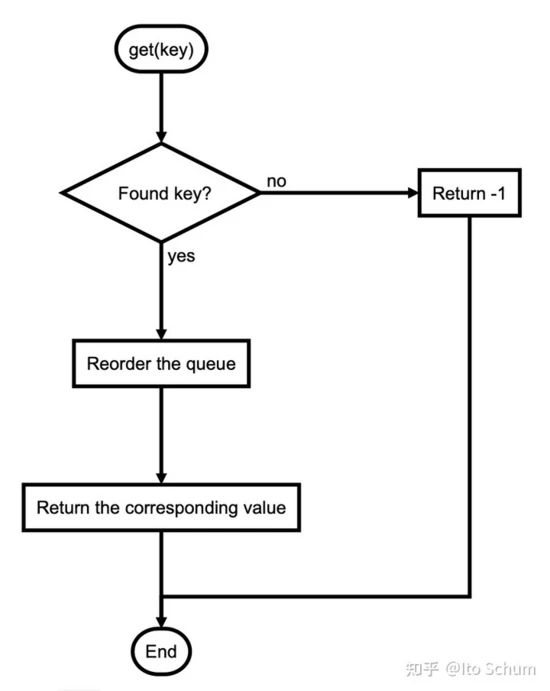
- put function
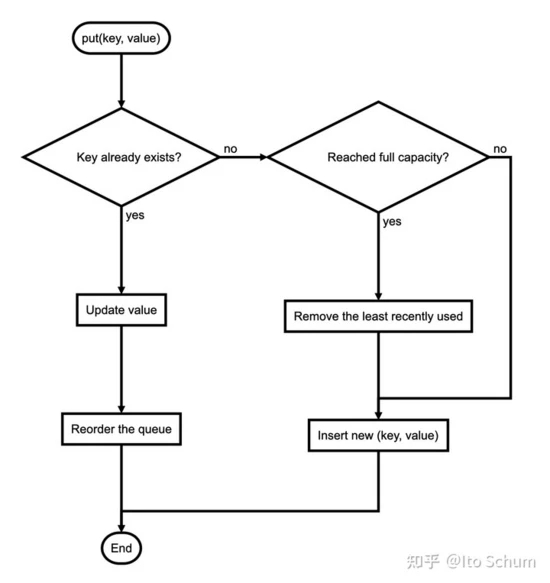
代码实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <unordered_map>
typedef std::unordered_map<int, std::list<std::pair<int, int> >::iterator > CacheMap;
typedef std::list<std::pair<int, int> > LRUList;
class LRUCache {
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) {
_capacity = capacity;
}
int get(int key) {
CacheMap::iterator cache_itr = _cacheMap.find(key);
if (cache_itr == _cacheMap.end() ) {
return -1;
}
makeMostRecent(key, _cacheMap[key]->second);
LRUList::iterator list_itr = _LRUList.end();
--list_itr;
return list_itr->second;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if (_cacheMap.find(key) != _cacheMap.end()) {
makeMostRecent(key, value);
return;
}
if (_LRUList.size() >= _capacity) {
removeLeastRecentTask(key);
}
addMostRecentTask(key, value);
}
private:
void makeMostRecent(int key, int value) {
_LRUList.erase(_cacheMap[key]);
_LRUList.push_back(std::make_pair(key, value) );
LRUList::iterator list_itr = _LRUList.end();
_cacheMap[key] = --list_itr;
}
void removeLeastRecentTask(int key) {
int keyToRemove = _LRUList.begin()->first;
_LRUList.erase(_LRUList.begin());
_cacheMap.erase(keyToRemove);
}
void addMostRecentTask(int key, int value) {
_LRUList.push_back(std::make_pair(key, value) );
LRUList::iterator list_itr = _LRUList.end();
_cacheMap[key] = --list_itr;
}
int _capacity;
LRUList _LRUList;
CacheMap _cacheMap;
};
// n = item number of the LRU list, aka capacity
// Time: O(1)
// Space: O(n)
运行测试:
Accepted
22/22 cases passed (412 ms)
Your runtime beats 69.45 % of cpp submissions
Your memory usage beats 48.08 % of cpp submissions (174 MB)
二、LFU (Least Frequently Used) 缓存
详见 LeetCode Q460
https:// leetcode.com/problems/l fu-cache/
https:// leetcode-cn.com/problem s/lru-cache/
问题描述:
LFUCache(int capacity)- 用数据结构的容量capacity初始化对象int get(int key) - 如果键存在于缓存中,则获取键的值,否则返回 -1 。void put(int key,int value) - 如果键已存在,则变更其值;如果键不存在,请插入键值对。当缓存达到其容量时,则应该在插入新项之前,使最不经常使用的项无效。在此问题中,当存在平局(即两个或更多个键具有相同使用频率)时,应该去除 最近最久未使用的键。- 「项的使用次数」就是自插入该项以来对其调用 get 和 put 函数的次数之和。使用次数会在对应项被移除后置为 0 。
- 为了确定最不常使用的键,可以为缓存中的每个键维护一个 使用计数器 。使用计数最小的键是最久未使用的键。
- 当一个键首次插入到缓存中时,它的使用计数器被设置为 1 (由于 put 操作)。对缓存中的键执行 get 或 put 操作,使用计数器的值将会递增。
所用数据结构:
为了使 get 与 put 操作的平均时间复杂度为 O(1) ,
- 使用哈希表 (STL
unordered_map) 储存 “key” 到 “value与frequency” 的关系映射 (使用 STLpair {value, frequency} 表示) - 使用哈希表 (STL
unordered_map) 储存 “frequency” 到 “对应所有的key” 的关系映射 (key 使用双向链表,即 STL list 存储) - 使用哈希表 (STL
unordered_map) 储存 “key” 到 “2 中存储 key 所用 list 中对应iterator” 的关系映射
std::unordered_map<int, std::pair<int, int> > _keyToValFreq; std::unordered_map<int, std::list<int> > _freqToKeyList; std::unordered_map<int, std::list<int>::iterator> _keyToKeyListItr;
流程图:
- get function

- put function

代码实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <unordered_map>
class LFUCache {
public:
LFUCache(int capacity) {
_capacity = capacity;
}
int get(int key) {
// If key doesn't exist
if (_keyToValFreq.find(key) == _keyToValFreq.end() ) {
return -1;
}
// if key exists, increse frequency and reorder
increaseFreq(key);
return _keyToValFreq[key].first;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if (_capacity <= 0) { return; }
// if key exists
if (_keyToValFreq.find(key) != _keyToValFreq.end() ) {
_keyToValFreq[key].first = value;
increaseFreq(key);
return;
}
// if key doesn't exist
// if reached hashmap's max capacity, remove the LFU (LRU if tie)
if (_keyToValFreq.size() >= _capacity) {
int keyToRmove = _freqToKeyList[_minFreq].back();
_freqToKeyList[_minFreq].pop_back();
_keyToKeyListItr.erase(keyToRmove);
_keyToValFreq.erase(keyToRmove);
}
// Then add new item with frequency = 1
addNewTask(key, value);
}
void increaseFreq(int key) {
// Update the freq in the pair
int oldFreq = _keyToValFreq[key].second++;
// Detele the old freq by itr
_freqToKeyList[oldFreq].erase(_keyToKeyListItr[key]);
// Add the new freq and re-assign the itr
_freqToKeyList[oldFreq + 1].emplace_front(key);
_keyToKeyListItr[key] = _freqToKeyList[oldFreq + 1].begin();
// Update minFreq
if (_freqToKeyList[_minFreq].empty() ) {
_minFreq = oldFreq + 1;
}
}
void addNewTask(int key, int value) {
// Add new key-value/freq to all hashmaps
_minFreq = 1;
_keyToValFreq[key] = std::make_pair(value, _minFreq);
_freqToKeyList[_minFreq].emplace_front(key);
_keyToKeyListItr[key] = _freqToKeyList[_minFreq].begin();
}
private:
int _capacity;
int _minFreq;
std::unordered_map<int, std::pair<int, int> > _keyToValFreq;
std::unordered_map<int, std::list<int> > _freqToKeyList;
std::unordered_map<int, std::list<int>::iterator> _keyToKeyListItr;
};
// n = item number of the LFU, aka capacity
// Time: O(1)
// Space: O(n)
运行测试:
Accepted
24/24 cases passed (464 ms)
Your runtime beats 72.37 % of cpp submissions
Your memory usage beats 45.99 % of cpp submissions (186.7 MB)
加载全部内容