Python opencv医学处理 Python opencv医学处理的实现过程
Dream丶Killer 人气:0想了解Python opencv医学处理的实现过程的相关内容吗,Dream丶Killer在本文为您仔细讲解Python opencv医学处理的相关知识和一些Code实例,欢迎阅读和指正,我们先划重点:Python,opencv医学处理,Python,opencv医学,下面大家一起来学习吧。
题目描述
利用opencv或其他工具编写程序实现医学处理。
实现过程
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
作者 : 丁毅
开发时间 : 2021/5/9 16:30
'''
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 图像细化
def VThin(image, array):
rows, cols = image.shape
NEXT = 1
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
if NEXT == 0:
NEXT = 1
else:
M = int(image[i, j - 1]) + int(image[i, j]) + int(image[i, j + 1]) if 0 < j < cols - 1 else 1
if image[i, j] == 0 and M != 0:
a = [0]*9
for k in range(3):
for l in range(3):
if -1 < (i - 1 + k) < rows and -1 < (j - 1 + l) < cols and image[i - 1 + k, j - 1 + l] == 255:
a[k * 3 + l] = 1
sum = a[0] * 1 + a[1] * 2 + a[2] * 4 + a[3] * 8 + a[5] * 16 + a[6] * 32 + a[7] * 64 + a[8] * 128
image[i, j] = array[sum]*255
if array[sum] == 1:
NEXT = 0
return image
def HThin(image, array):
rows, cols = image.shape
NEXT = 1
for j in range(cols):
for i in range(rows):
if NEXT == 0:
NEXT = 1
else:
M = int(image[i-1, j]) + int(image[i, j]) + int(image[i+1, j]) if 0 < i < rows-1 else 1
if image[i, j] == 0 and M != 0:
a = [0]*9
for k in range(3):
for l in range(3):
if -1 < (i-1+k) < rows and -1 < (j-1+l) < cols and image[i-1+k, j-1+l] == 255:
a[k*3+l] = 1
sum = a[0]*1+a[1]*2+a[2]*4+a[3]*8+a[5]*16+a[6]*32+a[7]*64+a[8]*128
image[i, j] = array[sum]*255
if array[sum] == 1:
NEXT = 0
return image
array = [0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1,\
1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,\
0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1,\
1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,\
1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,\
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,\
1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1,\
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,\
0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1,\
1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,\
0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1,\
1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,\
1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,\
1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,\
1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0,\
1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0]
# 显示灰度图
img = cv2.imread(r"C:\Users\pc\Desktop\vas0.png",0)
cv2.imshow("img1",img)
# 自适应阈值分割
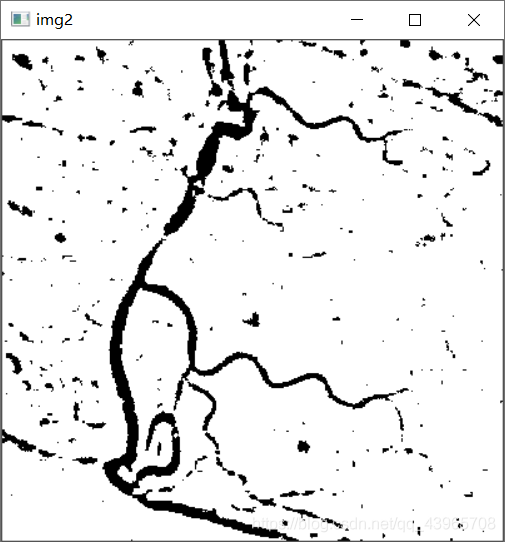
img2 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(img, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 17, 4)
cv2.imshow('img2', img2)
# 图像反色
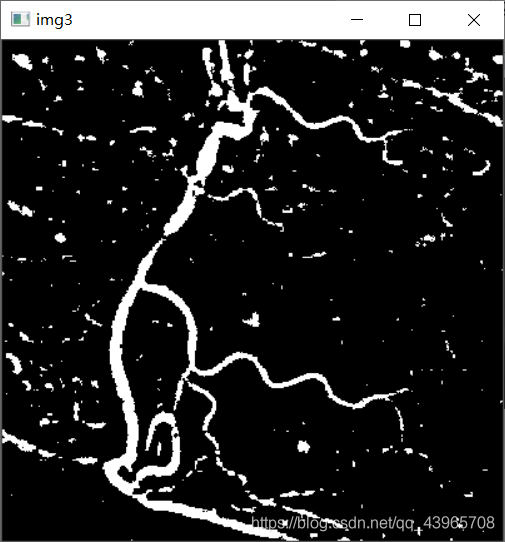
img3 = cv2.bitwise_not(img2)
cv2.imshow("img3", img3)
# 图像扩展
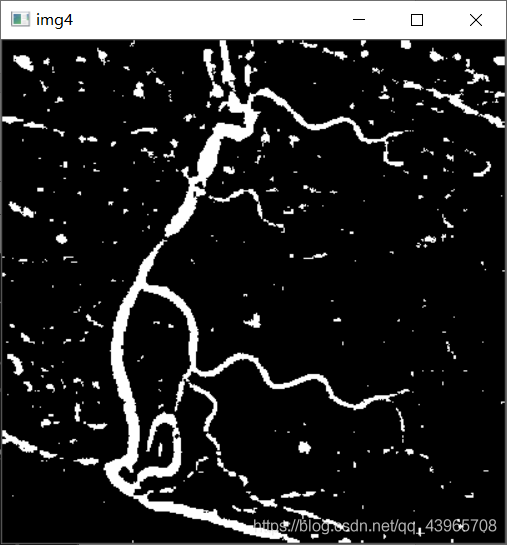
img4 = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img3, 1, 1, 1, 1, cv2.BORDER_REFLECT)
cv2.imshow("img4", img4)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(img4, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# 消除小面积
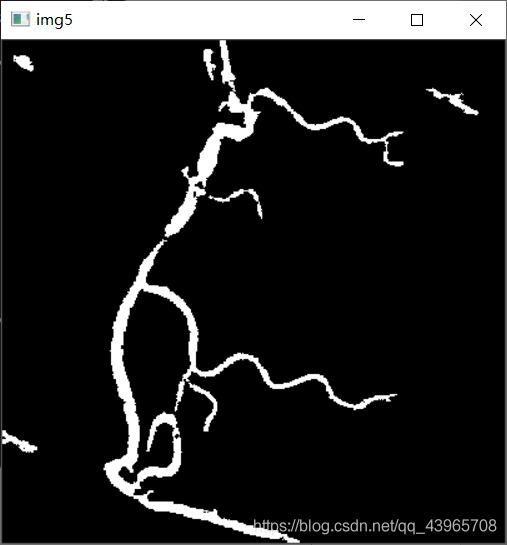
img5 = img4
for i in range(len(contours)):
area = cv2.contourArea(contours[i])
if (area < 80) | (area > 10000):
cv2.drawContours(img5, [contours[i]], 0, 0, -1)
cv2.imshow("img5", img5)
num_labels, labels, stats, centroids = cv2.connectedComponentsWithStats(img5, connectivity=8, ltype=None)
# print(stats)
s = sum(stats)
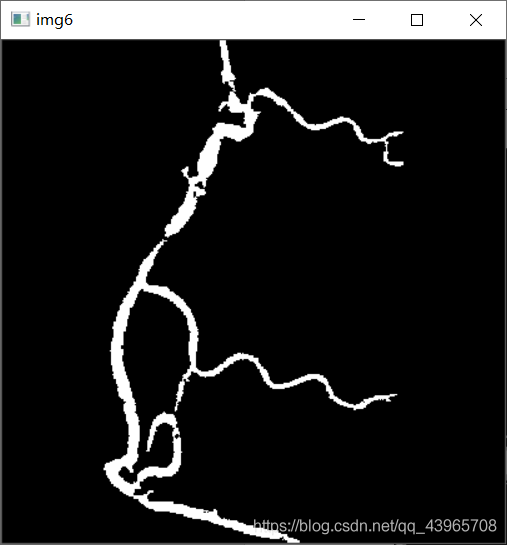
img6 = np.ones(img5.shape, np.uint8) * 0
for (i, label) in enumerate(np.unique(labels)):
# 如果是背景,忽略
if label == 0:
# print("[INFO] label: 0 (background)")
continue
numPixels = stats[i][-1]
div = (stats[i][4]) / s[4]
# print(div)
# 判断区域是否满足面积要求
if round(div, 3) > 0.002:
color = 255
img6[labels == label] = color
cv2.imshow("img6", img6)
# 图像反色
img7 = cv2.bitwise_not(img6)
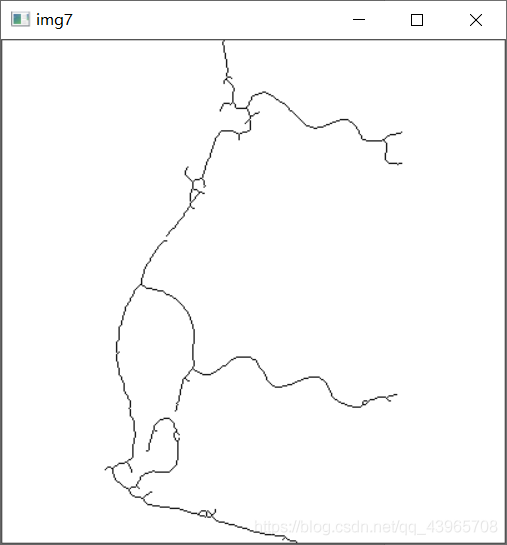
# 图像细化
for i in range(10):
VThin(img7, array)
HThin(img7, array)
cv2.imshow("img7",img7)
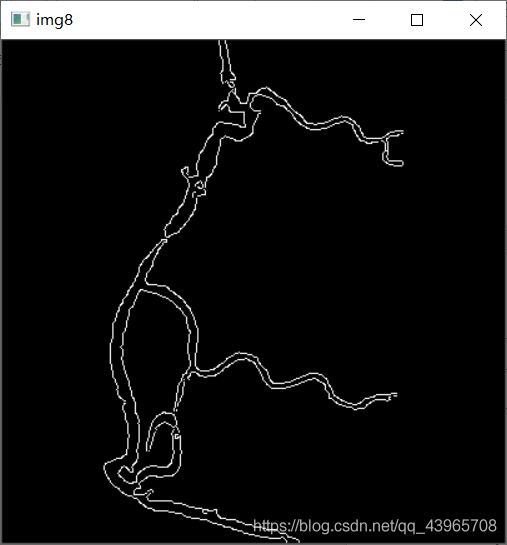
# 边缘检测
img8 = cv2.Canny(img6, 80, 255)
cv2.imshow("img8", img8)
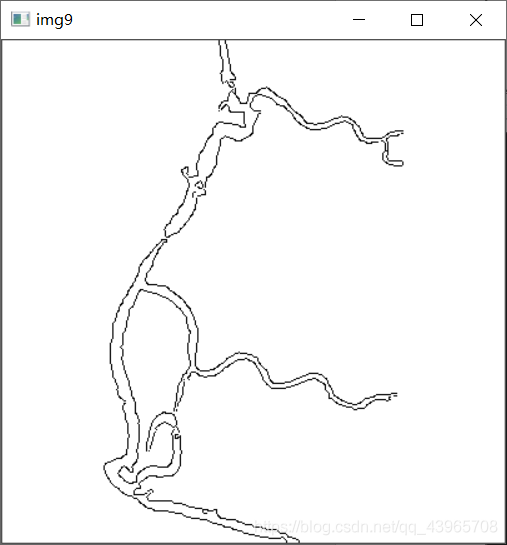
# 使灰度图黑白颠倒
img9 = cv2.bitwise_not(img8)
cv2.imshow("img9", img9)
cv2.waitKey(0)
运行结果


问题及解决方法
1.自适应阈值处理运行报错
参考链接
解决方式:
void adaptiveThreshold(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, double
maxValue, int adaptiveMethod, int thresholdType, int bolckSize, double C)
src:InputArray类型的src,输入图像,填单通道,单8位浮点类型Mat即可。dst:函数运算后的结果存放在这。即为输出图像(与输入图像同样的尺寸和类型)。maxValue:预设满足条件的最大值。adaptiveMethod自适应阈值算法。ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C或ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C两种。thresholdType:指定阈值类型。可选择THRESH_BINARY或者THRESH_BINARY_INV两种(即二进制阈值或反二进制阈值)。bolckSize:表示邻域块大小,用来计算区域阈值,一般选择为3、5、7......等。C:参数C表示与算法有关的参数,它是一个从均值或加权均值提取的常数,可以是负数。- 根据报错提示及参数解释,
blockSize的取值需要大于1且为奇数。
2.图像扩展
参考链接
方式:使用cv2.copyMakeBorder()函数。
主要参数:
src: 输入的图片。top, bottom, left, right:相应方向上的边框宽度。borderType:定义要添加边框的类型,详情参考链接。
3.面积选择
参考链接
方式:选择满足面积80-10000的图像输出, 去除噪声位置元素。
4.图像细化
参考链接
方式:经过一层层的剥离,从原来的图中去掉一些点,但仍要保持原来的形状,直到得到图像的骨架。骨架,可以理解为图像的中轴。
加载全部内容