SpringBoot SpringCache两级缓存 SpringBoot+SpringCache实现两级缓存(Redis+Caffeine)
xfgg 人气:2想了解SpringBoot+SpringCache实现两级缓存(Redis+Caffeine)的相关内容吗,xfgg在本文为您仔细讲解SpringBoot SpringCache两级缓存的相关知识和一些Code实例,欢迎阅读和指正,我们先划重点:SpringBoot,SpringCache缓存,SpringBoot,SpringCache,下面大家一起来学习吧。
1. 缓存、两级缓存
1.1 内容说明
Spring cache:主要包含spring cache定义的接口方法说明和注解中的属性说明
springboot+spring cache:rediscache实现中的缺陷
caffeine简介
spring boot+spring cache实现两级缓存
使用缓存时的流程图

1.2 Sping Cache
spring cache是spring-context包中提供的基于注解方式使用的缓存组件,定义了一些标准接口,通过实现这些接口,就可以通过在方法上增加注解来实现缓存。这样就能够避免缓存代码与业务处理耦合在一起的问题。spring cache的实现是使用spring aop中对方法切面(MethodInterceptor)封装的扩展,当然spring aop也是基于Aspect来实现的。
spring cache核心的接口就两个:Cache和CacheManager
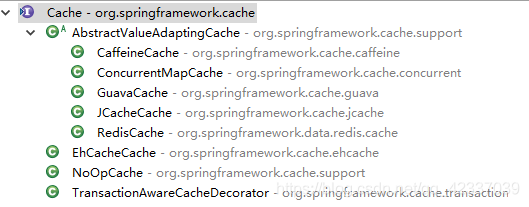
1.2.1 Cache接口
提供缓存的具体操作,比如缓存的放入,读取,清理,spring框架中默认提供的实现有
1.2.2 CacheManager接口
主要提供Cache实现bean的创建,每个应用里可以通过cacheName来对Cache进行隔离,每个CaheName对应一个Cache实现,spring框架中默认提供的实现与Cache的实现都是成对出现的
1.2.3 常用的注解说明
- @Cacheable:主要应用到查询数据的方法上
- @CacheEvict:清除缓存,主要应用到删除数据的方法上
- @CachePut:放入缓存,主要用到对数据有更新的方法上
- @Caching:用于在一个方法上配置多种注解
- @EnableCaching:启用spring cache缓存,作为总的开关,在spring boot的启动类或配置类上需要加入次注解才会生效
2.实战多级缓存的用法
package com.xfgg.demo.config;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Caffeine;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.caffeine.CaffeineCacheManager;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Configuration
@AllArgsConstructor
//把定义的缓存加入到Caffeine中
public class CacheConfig {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(){
CaffeineCacheManager cacheManager = new CaffeineCacheManager();
cacheManager.setCaffeine(Caffeine.newBuilder()
//使用refreshAfterWrite必须要设置cacheLoader
//在5分钟内没有创建/覆盖时,会移除该key,下次取的时候从loading中取【重点:失效、移除Key、失效后需要获取新值】
.expireAfterWrite(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
//初始容量
.initialCapacity(10)
//用来控制cache的最大缓存数量
.maximumSize(150)
);
return cacheManager;
}
}
package com.xfgg.demo.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisPassword;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisStandaloneConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
//生成的redis连接
public class RedisConfig<GenericObjectPoolConfig> {
@Value("${spring.redis1.host}")
private String host;
@Value("${spring.redis1.port}")
private Integer port;
@Value("${spring.redis1.password}")
private String password;
@Value("${spring.redis1.database}")
private Integer database;
@Value("${spring.redis1.lettuce.pool.max-active}")
private Integer maxActive;
@Value("${spring.redis1.lettuce.pool.max-idle}")
private Integer maxIdle;
@Value("${spring.redis1.lettuce.pool.max-wait}")
private Long maxWait;
@Value("${spring.redis1.lettuce.pool.min-idle}")
private Integer minIdle;
@Bean
public RedisStandaloneConfiguration redis1RedisConfig() {
RedisStandaloneConfiguration config = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration();
config.setHostName(host);
config.setPassword(RedisPassword.of(password));
config.setPort(port);
config.setDatabase(database);
return config;
}
//配置序列化器
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory){
RedisTemplate<String,Object>template=new RedisTemplate<>();
//关联
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//设置key的序列化器
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
//设置value的序列化器
template.setValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
return template;
}
}
一个使用cacheable注解,一个使用redistemplate进行缓存
因为公司项目中用到的是jedis和jediscluster所以这里只是做个了解,没有写的很细
加载全部内容