session C++服务端 Seesion在C++服务端如何使用
CPP后台服务器开发 人气:0前面介绍了cookie和session两种机制的产生和使用过程(可以关注 CPP后台服务器 公众号查看),但是,似乎在我们C++后台开发过程中遇见的很少;
那session在我们服务端是怎么使用的呢?
首先,我们看一个需求:
客户第一次设置登陆后,以后再次登陆的时候,想要使用快捷登陆或者是一键登陆,比如我们使用指纹登陆,即可获取我们的账户信息
根据这个需求我们做一个方案进行解决,底层实现我们可以使用session的思想;

方案:
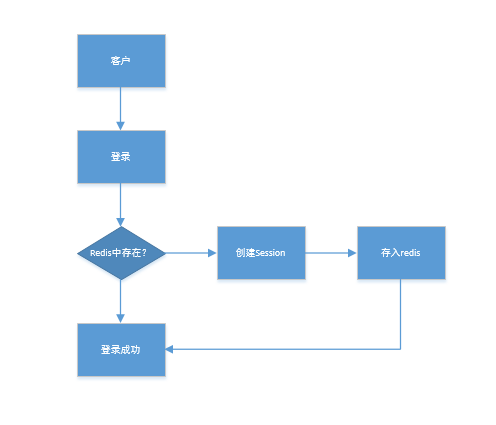
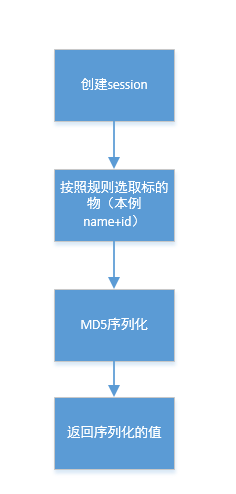

说明 :
- 用户快捷登陆时,根据快捷登陆的ID码在redis中查找
- 如果再redis中不存在,则创建session,与用户的id绑定;如果存在,则登陆成功,调用相关功能显示用户信息
- session的产生一般每个公司都会有自己改造的一套方案,这样可以提升安全性,这里就使用原生的MD5接口
关于redis键值对的设计,一般都比较简单,建议大家可以自己设计一套,并且实现这个功能;
这里,简单展示一下 sessionid 的生成:
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <openssl/md5.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Md5
{
public:
Md5();
~Md5();
bool SetMd5(string data);
unsigned char* GetMd5();
private:
MD5_CTX ctx;
unsigned char outMd5[16];
};
#include "Md5.h"
Md5::Md5()
{
}
Md5::~Md5()
{
}
unsigned char* Md5::GetMd5()
{
//数组初始化
memset(outMd5,0x00,sizeof(outMd5));
int res = MD5_Final(outMd5,&ctx);
if(res != 1)
{
cout<<"Md5_Final is errpr"<<endl;
}
return outMd5;
}
bool Md5::SetMd5(string data)
{
//初始化Md5
MD5_Init(&ctx);
//计算Md5
int res = MD5_Update(&ctx,data.c_str(),5);
if(res != 1)
{
cout<<"Md5_Update is errpr"<<endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "string.h"
#include "Md5.h"
using namespace std;
class Session
{
public:
Session();
~Session();
Session(string UserName,int ID);
bool SetId();
int GetId();
bool SetUserName();
string GetUserName();
bool SetSessionId();
bool SetSessionData();
string GetSessionData();
unsigned char* GetSessionId();
private:
string name;
int id;
string SessionData;
Md5 md5;
};
#include "session.h"
Session::Session()
{
}
Session::~Session()
{
}
Session::Session(string UserName,int ID)
{
this->id = ID;
this->name = UserName;
}
int Session::GetId()
{
return this->id;
}
string Session::GetUserName()
{
return this->name;
}
bool Session::SetSessionData()
{
char str[20];
memset(str,0,sizeof(str));
//这里使用name+id的方式,生成最终的sessionid
sprintf(str,"%d",GetId());
SessionData = GetUserName()+str;
return true;
}
string Session::GetSessionData()
{
if(!SessionData.empty())
return SessionData;
}
unsigned char* Session::GetSessionId()
{
return md5.GetMd5();
}
bool Session::SetSessionId()
{
bool res = md5.SetMd5(GetSessionData());
if(!res)
return false;
return true;
}
#include "session.h"
int main()
{
unsigned char* str = new unsigned char[16];
Session session("test",10);
session.SetSessionData();
session.SetSessionId();
str = session.GetSessionId();
for(int i=0;i<16;i++)
{
printf("%02X",str[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
CXX = g++ -std=c++11
CFLAG = -g -lssl -lcrypto
target = test
OBJ = Md5.cpp main.cpp session.cpp
$(target):$(OBJ)
$(CXX) -o $@ $^ $(CFLAG)
clean:
rm -f $(target)
补充知识点:
session原理:
用户使用浏览器第一次向服务器发送请求,服务器在接受到请求后,调用对应的 Servlet 进行处理。在处理过程中会给用户创建一个session 对象,用来存储用户请求处理相关的公共数据,并将此 session 对象的 JSESSIONID 以 Cookie 的形式存储在浏览器中 (临时存储,浏览器关闭即失效)。用户在发起第二次请求及后续请求时,请求信息中会附带JSESSIONID,服务器在接收到请求后, 调用对应的Servlet 进行请求处理,同时根据 JSESSIONID 返回其对应的session 对象。
特点:
由服务器进行创建
每个用户独立拥有一个session
默认存储时间为 30 分钟作用:
解决了一个用户的不同请求的数据共享问题。
使用:
创建Session 对象
存储数据到session 对象获取session 对象
获取数据从session 对象
如果获取session 中不存在的数据返回null。
总结
加载全部内容