Python 图片转字符画 Python简单实现图片转字符画的实例项目
David 612 人气:01. 原理
利用 PIL 库来获取图片并修改大小,
利用灰度值转换公式把每一个像素的 RGB 值转为灰度值
gray = int(0.2126*r+0.7152*g+0.0722*b)
再从字符集里获取对应的字符
asciis = list('M%$@#&WNBRwm8S5A4E3KXFPH69nsxeazgpqbdoctfhkyvuGZYVTUCI2QOD0L7Jjl1ri!^{}[]()/|;:*<>_~-,. ')
最后将字符连接起来并保存就完成了
2. 开始制作
2.1 导入所需的库
在这个工程中,我们需要的第三方库是 PIL 库
但我们不用 pip install PIL 来安装它,而是使用 pip install pillow
pip install pillow
导入库
在导入 PIL 库时,不能用 import pillow,应使用 import PIL
from PIL import Image as Image
2.2 获取图片路径和选项
inputfile = input('inputfile:')
outputfile = input('outputfile:')
distance = {'y':' ','':' ','n':''}
distance = distance[input('distance?(Y/n):')]
re = input("resize?:")
字母占用的位置是矩形的,因此生成出来的字符画会被“挤压”。我们可以在字母与字母之间添加空格来防止这种情况的发生。
如果图片太大了,会导致耗费时间过长、乱码等问题。我们应该对图片进行必要的缩放。在询问“resize?”时,可以设置以下几种回答:
| 回答方式 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| “”,啥也不输入 | 不缩放 |
| “100”,边长 | 输入单个数字时,会按比例缩放为较长边为此长度的矩形 |
| “100,200”,宽和高 | 缩放为指定宽高的矩形 |
2.3 图片获取
使用 PIL 的 open 函数打开图片
image = Image.open(inputfile)
注意:这里的 open 函数不要和 python 内置函数 open 混淆
2.4 调整图片大小
获取图片大小
w, h = image.size
获取变量 re 中存储的大小信息,并用函数 split 分割
nwh = re.split(',')
for i in range(len(nwh)):
nwh[i] = int(nwh[i])
调整图片大小
if len(nwh) == 1:
#如果项数为1,表示用户只输入了一个数字。即按比例缩放为较长边为此长度的矩形
ww = int(nwh[0] / max(w,h) * w) #max函数获取较大值
hh = int(nwh[0] / max(w,h) * h)
image = image.resize((ww,hh),Image.ANTIALIAS)
#改变图片大小
#第一个参数放入一个元组,指定宽高
#第二个参数 Image.ANTIALIAS 表示获取高质量图片
else:
#项数不为1,缩放为指定宽高的矩形
image = image.resize((nwh[0],nwh[1]),Image.ANTIALIAS)
2.5 转换字符
指定转换的字符集
asciis = list('M%$@#&WNBRwm8S5A4E3KXFPH69nsxeazgpqbdoctfhkyvuGZYVTUCI2QOD0L7Jjl1ri!^{}[]()/|;:*<>_~-,. ')
#list函数将字符串转换为列表
定义转换字符的函数
def getasc(r,g,b,t=100): #t为透明度
if t == 0:
return(' ') #如果是透明的,则直接返回空值
else:
asc = ''
gray = int(0.2126*r+0.7152*g+0.0722*b) #转灰度值
asc = asciis[int(len(asciis)/256*(gray))] #获取字符
return(asc)
开始转换字符
for i in range(h):
for o in range(w): #按行读取每一个像素的RGB值
p = image.getpixel((o,i))
g = getasc(*p) # * 将参数列表转换为多个项
txt = txt + g + distance #连接字符
txt = txt + '\n' #换行
函数 getpixel 获取指定位置的 RGB 值,它的第一个参数为元组,传入像素位置 (x,y),如果图片是 JPG 格式的,它会返回含三项的列表 [r,g,b],如果图片是 PNG 格式的,它会返回含四项的列表 [r,g,b,t],t 是透明度
2.6 保存文本
使用 python 内置函数 open 保存文件
with open(outputfile,'w') as f: # 'w' 表示写入
f.write(txt)
2.7 效果
================== RESTART: D:\Python38-32\Files\ji2a\ji2a.py ==================
=====image to ascii=====
inputfile:
dora.png
outputfile:
dora.txt
distance?(Y/n):
y
resize?(needn't:'', square:side length, restangle:width,height):
100Opening 'dora.png'...
Getting...
Saving...
Seccessfully
原图:

结果:
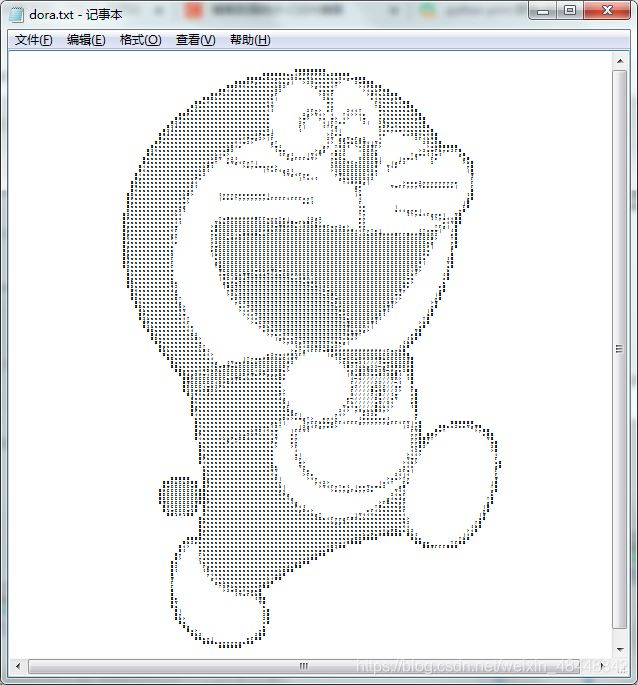
3. 完整代码
from PIL import Image as Image
asciis = list('M%$@#&WNBRwm8S5A4E3KXFPH69nsxeazgpqbdoctfhkyvuGZYVTUCI2QOD0L7Jjl1ri!^{}[]()/|;:*<>_~-,. ')
#gray = int(0.2126*r+0.7152*g+0.0722*b)
def main():
global asciis
print('=====image to ascii=====')
inputfile, outputfile, distance, re = getargs()
image = openfile(inputfile)
image = resize(image,re)
w, h = image.size
txt = gettxt(image,w,h,distance)
savefile(outputfile,txt)
print('Seccessfully')
def getargs():
inputfile = input('inputfile:\n')
outputfile = input('outputfile:\n')
distance = {'':' ','y':' ','n':''}
distance = distance[input('distance?(Y/n):\n')]
re = input("resize?(needn't:'', square:side length, restangle:width,height):\n")
return(inputfile,outputfile,distance,re)
def openfile(inputfile):
print("\nOpening '"+inputfile+"'...")
image = Image.open(inputfile)
return(image)
def resize(image,re):
if re != '':
print('Resizing...')
nwh = re.split(',')
for i in range(len(nwh)):nwh[i]=int(nwh[i])
w, h = image.size
if len(nwh) == 1:
ww = int(nwh[0] / max(w,h) * w)
hh = int(nwh[0] / max(w,h) * h)
image = image.resize((ww,hh),Image.ANTIALIAS)
else:
image = image.resize((nwh[0],nwh[1]),Image.ANTIALIAS)
return(image)
def gettxt(image,w,h,distance):
txt = ''
print('Getting...')
for i in range(h):
for o in range(w):
p = image.getpixel((o,i))
txt = txt + getasc(*p) + distance
txt = txt + '\n'
return(txt)
def getasc(r,g,b,t=100):
if t == 0:
return(' ')
else:
asc = ''
gray = int(0.2126*r+0.7152*g+0.0722*b)
asc = asciis[int(len(asciis)/256*(gray))]
return(asc)
def savefile(outputfile,txt):
print('Saving...')
with open(outputfile,'w') as f:
f.write(txt)
return()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
此代码在 Python3.8 下调试通过
4. 后记
我们的图片转字符画程序完成了!
要想将它打造成一个真正的命令行工具,可以加入命令行参数功能,
利用 sys 模块的 argv 函数获取命令行参数,
利用 getopt 模块的 getop 函数解析命令行参数。
加载全部内容