Opencv EigenFace人脸识别算法详解
人气:0简要:
EigenFace是基于PCA降维的人脸识别算法,PCA是使整体数据降维后的方差最大,没有考虑降维后类间的变化。 它是将图像每一个像素当作一维特征,然后用SVM或其它机器学习算法进行训练。但这样维数太多,根本无法计算。我这里用的是ORL人脸数据库,英国剑桥实验室拍摄的,有40位志愿者的人脸,在不同表情不同光照下每位志愿者拍摄10张,共有400张图片,大小为112*92,所以如果把每个像素当做特征拿来训练的话,一张人脸就有10304维特征,这么高维的数据根本无法处理。所以需要先对数据进行降维,去掉一些冗余的特征。
第一步:将ORL人脸图片的地址统一放在一个文件里,等会通过对该文件操作,将图片全部加载进来。
//ofstream一般对文件进行读写操作,ifstream一般对文件进行读操作
ofstream file;
file.open("path.txt");//新建并打开文件
char str[50] = {};
for (int i = 1; i <= 40; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 10; j++) {
sprintf_s(str, "orl_faces/s%d/%d.pgm;%d", i, j, i);//将数字转换成字符
file << str << endl;//写入
}
}
得到路劲文件如下图所示:
第二步:读入模型需要输入的数据,即用来训练的图像vector<Mat>images和标签vector<int>labels
string filename = string("path.txt");
ifstream file(filename);
if (!file) {
printf("could not load file");
}
vector<Mat>images;
vector<int>labels;
char separator = ';';
string line,path, classlabel;
while (getline(file,line)) {
stringstream lines(line);
getline(lines, path, separator);
getline(lines, classlabel);
images.push_back(imread(path, 0));
labels.push_back(atoi(classlabel.c_str()));//atoi(ASCLL to int)将字符串转换为整数型
}
第三步:加载、训练、预测模型
Ptr<BasicFaceRecognizer> model = EigenFaceRecognizer::create();
model->train(images, labels);
int predictedLabel = model->predict(testSample);
printf("actual label:%d,predict label :%d\n", testLabel, predictedLabel);
补充:
1、显示平均脸
//计算特征值特征向量及平均值
Mat vals = model->getEigenValues();//89*1
printf("%d,%d\n", vals.rows, vals.cols);
Mat vecs = model->getEigenVectors();//10324*89
printf("%d,%d\n", vecs.rows, vecs.cols);
Mat mean = model->getMean();//1*10304
printf("%d,%d\n", mean.rows, mean.cols);
//显示平均脸
Mat meanFace = mean.reshape(1, height);//第一个参数为通道数,第二个参数为多少行
normalize(meanFace, meanFace, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1);
imshow("Mean Face", meanFace);

2、显示前部分特征脸
//显示特征脸
for (int i = 0; i<min(10, vals.rows); i++) {
Mat feature_vec = vecs.col(i).clone();
Mat feature_face= feature_vec.reshape(1, height);
normalize(feature_face, feature_face, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1);
Mat colorface;
applyColorMap(feature_face, colorface, COLORMAP_BONE);
sprintf_s(win_title, "eigenface%d", i);
imshow(win_title, colorface);
}
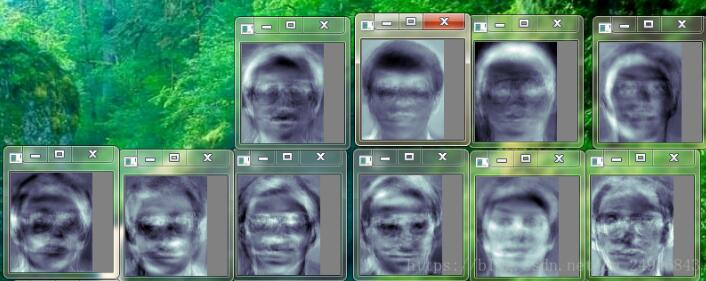
3、对第一张人脸在特征向量空间进行人脸重建(分别基于前10,20,30,40,50,60个特征向量进行人脸重建)
//重建人脸
for (int i = min(10, vals.rows); i <min(61, vals.rows); i+=10) {
Mat vecs_space = Mat(vecs, Range::all(), Range(0, i));
Mat projection = LDA::subspaceProject(vecs_space, mean, images[0].reshape(1, 1));//投影到子空间
Mat reconstruction = LDA::subspaceReconstruct(vecs_space, mean, projection);//重建
Mat result = reconstruction.reshape(1, height);
normalize(result, result, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1);
//char wintitle[40] = {};
sprintf_s(win_title, "recon face %d", i);
imshow(win_title, result);
}

完整代码如下:
#include<opencv2\opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2\face.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace face;
using namespace std;
char win_title[40] = {};
int main(int arc, char** argv) {
namedWindow("input",CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
//读入模型需要输入的数据,用来训练的图像vector<Mat>images和标签vector<int>labels
string filename = string("path.txt");
ifstream file(filename);
if (!file) { printf("could not load file"); }
vector<Mat>images;
vector<int>labels;
char separator = ';';
string line,path, classlabel;
while (getline(file,line)) {
stringstream lines(line);
getline(lines, path, separator);
getline(lines, classlabel);
//printf("%d\n", atoi(classlabel.c_str()));
images.push_back(imread(path, 0));
labels.push_back(atoi(classlabel.c_str()));//atoi(ASCLL to int)将字符串转换为整数型
}
int height = images[0].rows;
int width = images[0].cols;
printf("height:%d,width:%d\n", height, width);
//将最后一个样本作为测试样本
Mat testSample = images[images.size() - 1];
int testLabel = labels[labels.size() - 1];
//删除列表末尾的元素
images.pop_back();
labels.pop_back();
//加载,训练,预测
Ptr<BasicFaceRecognizer> model = EigenFaceRecognizer::create();
model->train(images, labels);
int predictedLabel = model->predict(testSample);
printf("actual label:%d,predict label :%d\n", testLabel, predictedLabel);
//计算特征值特征向量及平均值
Mat vals = model->getEigenValues();//89*1
printf("%d,%d\n", vals.rows, vals.cols);
Mat vecs = model->getEigenVectors();//10324*89
printf("%d,%d\n", vecs.rows, vecs.cols);
Mat mean = model->getMean();//1*10304
printf("%d,%d\n", mean.rows, mean.cols);
//显示平均脸
Mat meanFace = mean.reshape(1, height);//第一个参数为通道数,第二个参数为多少行
normalize(meanFace, meanFace, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1);
imshow("Mean Face", meanFace);
//显示特征脸
for (int i = 0; i<min(10, vals.rows); i++) {
Mat feature_vec = vecs.col(i).clone();
Mat feature_face= feature_vec.reshape(1, height);
normalize(feature_face, feature_face, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1);
Mat colorface;
applyColorMap(feature_face, colorface, COLORMAP_BONE);
sprintf_s(win_title, "eigenface%d", i);
imshow(win_title, colorface);
}
//重建人脸
for (int i = min(10, vals.rows); i <min(61, vals.rows); i+=10) {
Mat vecs_space = Mat(vecs, Range::all(), Range(0, i));
Mat projection = LDA::subspaceProject(vecs_space, mean, images[0].reshape(1, 1));
Mat reconstruction = LDA::subspaceReconstruct(vecs_space, mean, projection);
Mat result = reconstruction.reshape(1, height);
normalize(result, result, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1);
//char wintitle[40] = {};
sprintf_s(win_title, "recon face %d", i);
imshow(win_title, result);
}
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
您可能感兴趣的文章:
加载全部内容