搭建Vue从Vue-cli到router路由护卫的实现
人气:0别的不多说,开始动爪把,
首先安装vue-cli mac: sudo npm install -g @vue/cli
github:
https://github.com/XinYueXiao/vue-routes
1、Vue-cli基础使用
1.1 创建测试项目 vue create vue-routes

1.2 创建成功,启动项目 yarn serve
在 http://localhost:8080/ 就可以看到欢迎:clap:页面了
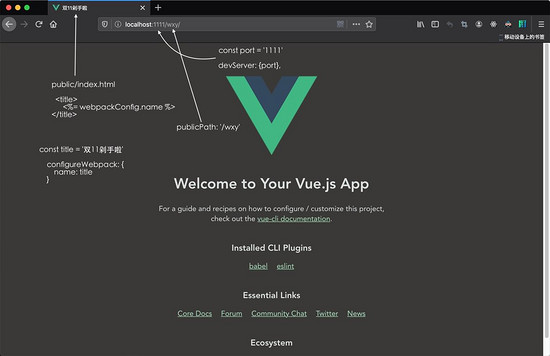
1.3 搞点自定义配置,新建vue.config.js
const title = '双11剁手啦'
const port = '1111'
module.exports = {
publicPath: '/wxy',
//自定义端口号
devServer: {
port
},
//自定义变量
configureWebpack: {
name: title
}
}
配置完成后重新启动 yarn serve 效果图
如何配置svg图标
1)准备一个svg,例如: src/icons/svg/hg.svg
2)安装loader yarn add svg-sprite-loader
3)对config进行链式操作即可修改loader
const path = require('path')
//处理地址
function resolve(dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, dir)
}
module.exports = {
...,
chainWebpack(config) {
//安装loader,对config进行链式操作即可修改loader、plugins
//1.svg rule中要排除icons目录
config.module.rule('svg')
//转换为绝对地址
.exclude.add(resolve('src/icons'))
//查看配置后svg规则 vue inspect --rule svg
//2.添加一个规则icons
config.module.rule('icons')
.test(/\.svg$/)
.include.add(resolve('src/icons')).end()
.use('svg-sprite-loader')
.loader('svg-sprite-loader')
.options({
symbolId: 'icon-[name]'
})
}
}
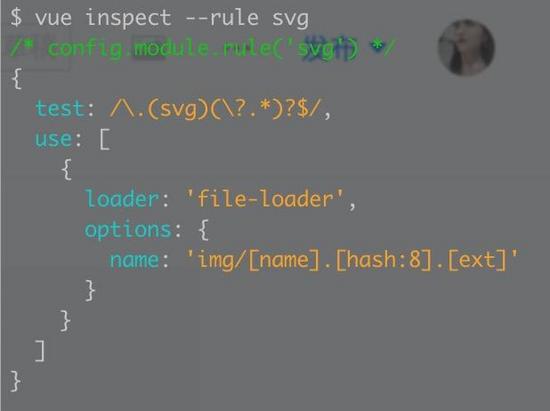
4)svg rule中要排除icons目录后配置
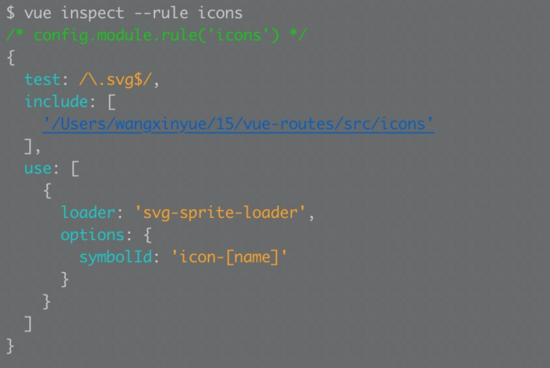
5) 添加一个规则icons配置
6) 新建 src/components/SvgIcon.vue 模板
<template>
<svg :class="svgClass" aria-hidden="true" v-on="$listeners">
<use :xlink:href="iconName" rel="external nofollow" />
</svg>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "SvgIcon",
props: {
iconClass: {
type: String,
required: true
},
className: {
type: String,
default: ""
}
},
computed: {
iconName() {
return `#icon-${this.iconClass}`;
},
svgClass() {
if (this.className) {
return "svg-icon " + this.className;
} else {
return "svg-icon";
}
}
}
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.svg-icon {
width: 1em;
height: 1em;
vertical-align: -0.15em;
fill: currentColor;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
7)新建 src/icons/index.js 在main.js下引入icon
//src/icons/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import SvgIcon from '@/components/SvgIcon'
//图标自动加载
const req = require.context('./svg', false, /\.svg$/)
req.keys().map(req)
Vue.component('svg-icon', SvgIcon)
//main.js
import "./icons";
8)在App.vue引入图标
<svg-icon icon-class="hg"></svg-icon>
效果如下:
2、router路由守卫
何为守卫,即为阻止无身份者进入组织内部
安装yarn add vue-router 控制路由
安装yarn add vuex 存储身份认证
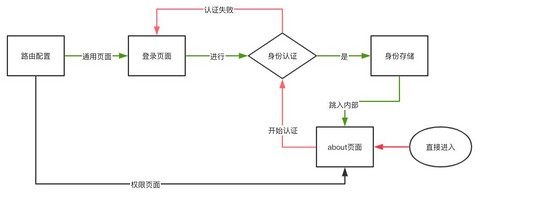
2.1 路由配置
src/router/index.js
import Vue from "vue";
import Router from "vue-router";
import Layout from '@/layout'; // 布局页
Vue.use(Router);
// 通用页面:不需要守卫,可直接访问
export const constRoutes = [
{
path: "/login",
component: () => import("@/views/Login"),
hidden: true // 导航菜单忽略该项
}, {
path: "/",
component: Layout,// 应用布局
redirect: "/home",
children: [
{
path: "home",
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "home" */ "@/views/Home.vue"),
name: "home",
meta: {
title: "Home", // 导航菜单项标题
icon: "hg" // 导航菜单项图标
}
}]
}];
// 权限页面:受保护页面,要求用户登录并拥有访问权限的角色才能访问
export const asyncRoutes = [
{
path: "/about",
component: Layout,
redirect: "/about/index",
children: [
{
path: "index",
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "home" */ "@/views/About.vue"),
name: "about",
meta: {
title: "About",
icon: "hg",
roles: ['admin', 'editor']
},
}
]
}
];
export default new Router({
mode: "history",
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes: constRoutes
});
布局组件 src/layout
<template> <div class="app-wrapper"> <div class="main-container"> <router-view /> </div> </div> </template>
路由展示src/App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<!-- 路由 -->
<div id="nav">
<router-link to="/">
<svg-icon icon-class="wx"></svg-icon>
<!-- <svg>
<use xlink:href="#icon-wx" rel="external nofollow" ></use>
</svg>-->
Home
</router-link>|
<router-link to="/about">
<svg-icon icon-class="hg"></svg-icon>About
</router-link>
</div>
<!-- 4.路由视图 -->
<!-- 问题:router-link和router-view是哪来的 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "app",
components: {}
};
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: "Avenir", Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
2.2 准备页面
src/views/About.vue
<template> <div class="about"> <h1>This is an about page</h1> </div> </template>
src/views/Home.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<img alt="Vue logo" src="../assets/logo.png" />
<HelloWorld msg="Welcome to Your Vue.js App" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
// @ is an alias to /src
import HelloWorld from "@/components/HelloWorld.vue";
export default {
name: "home",
components: {
HelloWorld
}
};
</script>
src/views/Login.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>用户登录</h2>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="username" />
<button @click="login">登录</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
username: "admin"
};
},
methods: {
login() {
this.$store
.dispatch("user/login", { username: this.username })
.then(() => {
this.$router.push({
path: this.$route.query.redirect || "/"
});
})
.catch(error => {
alert(error);
});
}
}
};
</script>
2.3 身份认证
import router from "./router";
import store from "./store";
const whiteList = ["/home", "/login"]; // 无需令牌白名单
// 全局路由守卫
router.beforeEach(async (to, from, next) => {
// 获取令牌判断用户是否登录
const hasToken = localStorage.getItem("token");
// 已登录
if (hasToken) {
if (to.path === "/login") {
// 若已登录没有必要显示登录页,重定向至首页
next({ path: "/" });
} else {
// 去其他路由,暂时放过
// next()
// 接下来执行用户角色逻辑, todo
// 1.判断用户是否拥有角色
const hasRoles =
store.state.user.roles && store.state.user.roles.length > 0;
if (hasRoles) {
next();
} else {
// 2.获取用户角色
const roles = await store.dispatch("user/getInfo");
const accessRoutes = await store.dispatch("permission/generateRoutes", roles);
// 动态添加路由到路由器
router.addRoutes(accessRoutes);
// 跳转
next({ ...to });
}
}
} else {
// 未登录
if (whiteList.indexOf(to.path) !== -1) {
// 白名单中路由放过
next();
} else {
// 重定向至登录页
next(`/login?redirect=${to.path}`);
}
}
});
2.4 用户信息设置
import Vue from "vue";
import Vuex from "vuex";
import user from './modules/user'
import permission from './modules/permission'
Vue.use(Vuex);
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
user, permission
}
});
src/store/modules/user.js
const state = {
token: localStorage.getItem("token"),
// 其他用户信息
roles: []
};
const mutations = {
SET_TOKEN: (state, token) => {
state.token = token;
},
SET_ROLES: (state, roles) => {
state.roles = roles;
},
};
const actions = {
// 模拟用户登录
login({ commit }, userInfo) {
const { username } = userInfo;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (username === "admin" || username === "jerry") {
commit("SET_TOKEN", username);
localStorage.setItem("token", username);
resolve();
} else {
reject("用户名、密码错误");
}
}, 1000);
});
},
getInfo({ commit, state }) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
const roles = state.token === 'admin' ? ['admin'] : ['editor']
commit('SET_ROLES', roles)
resolve(roles)
}, 1000);
})
}
};
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions,
};
2.5 用户路由权限 src/store/modules/permission.js
// 导入asyncRoutes,过滤它看当前用户是否拥有响应权限
import {asyncRoutes, constRoutes} from '@/router'
const state = {
routes: [], // 完整路由
addRoutes: [], // 权限路由
}
const mutations = {
// routes: 用户可访问的权限路由
SET_ROUTES: (state, routes) => {
state.addRoutes = routes;
state.routes = constRoutes.concat(routes);
}
}
const actions = {
generateRoutes({commit}, roles) {
// 过滤出能访问的路由表
const routes = filterAsyncRoutes(asyncRoutes, roles)
commit('SET_ROUTES', routes)
return routes;
}
}
function filterAsyncRoutes(routes, roles) {
const res = [];
routes.forEach(route => {
// 复制一份路由
const tmp = {...route};
// 拥有访问权限
if (hasPermission(roles, tmp)) {
if (tmp.children) {
// 递归子路由
tmp.children = filterAsyncRoutes(tmp.children, roles)
}
res.push(tmp);
}
})
return res;
}
function hasPermission(roles, route) {
if (route.meta && route.meta.roles) {
return roles.some(role => route.meta.roles.includes(role))
} else {
// 路由定义中没有roles选项,则不需要权限即可访问
return true;
}
}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions
}
2.6 最终效果图

您可能感兴趣的文章:
加载全部内容