Spring boot2.x中集成H2数据库代码实例
人气:0这篇文章主要介绍了Spring boot2.x中集成H2数据库代码实例,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友可以参考下
在spring boot中集成
1.添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.h2database</groupId> <artifactId>h2</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency>
2.添加H2相关配置,修改application.properties文件
spring.jpa.database=h2 spring.jpa.show-sql=true #ddl执行方式,update create 等 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:./data/test;AUTO_SERVER=TRUE spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update spring.datasource.username=sa spring.datasource.password=123456 spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver spring.h2.console.path=/h2-console spring.h2.console.enabled=true
说明:
spring.datasource.url
数据库文件
(1)内存数据库
jdbc:h2:mem:DBName
内存数据库的数据存在内存中,当程序停止时,不会被保存会丢失
eg:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:test
(2)文件数据库
jdbc:h2:file:{FilePath} 也可以简化为 jdbc:h2:{FilePath}
FilePath的格式
- a) ./{path}/{fileName} 在当前程序的根目录下创建目录和数据库文件
- b) ~/{path}/{fileName} 在当前用户的根目录下创建目录和数据库文件
- c) C:/{path}/{fileName} 在指定盘符的指定目录下创建数据库文件
(3)远程数据库
jdbc:h2:tcp://<{IP|hostname}>[:{Port}]/[]<{dbName}>
附加参数:
- AUTO_SERVER=TRUE 启动自动混合模式,允许开启多个连接,该参数不支持在内存中运行模式
- DB_CLOSE_ON_EXIT=FALSE,当虚拟机退出时并不关闭数据库
3.代码
domain层,即User类(entity)
package com.example.demo.domain;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "user")
@Data
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.AUTO)
private int id;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
dao层,即UserRepository 接口
package com.example.demo.dao;
import com.example.demo.domain.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User,Integer> {
List<User> getUsersByName(String Name);
}
controller层,即Demo
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.dao.UserRepository;
import com.example.demo.domain.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class Demo {
@Autowired
private UserRepository repo;
@RequestMapping("find")
public List<User> find() {
return (List<User>) repo.findAll();
}
}
编写DemoApplication
package com.example.demo;
import com.example.demo.dao.UserRepository;
import com.example.demo.domain.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
@Bean
InitializingBean saveData(UserRepository repo){
return ()->{
User u = new User();
u.setName("abc");
repo.save(u);
User u1 = new User();
u1.setName("zyx");
repo.save(u1);
};
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
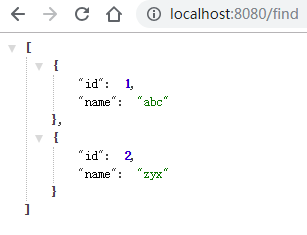
启动项目,打开浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/find
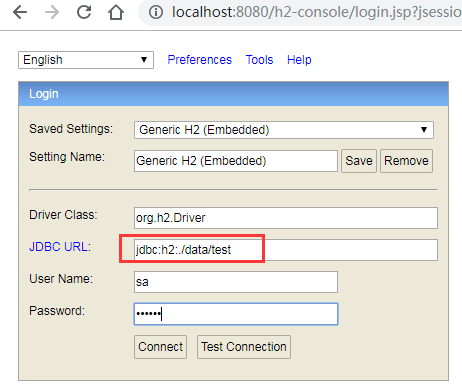
访问http://localhost:8080/h2-console/
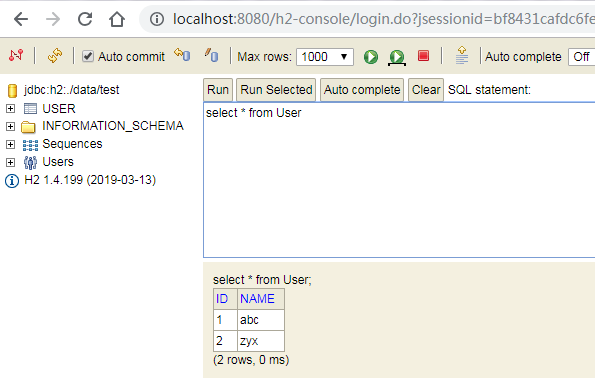
连接上后查询数据
您可能感兴趣的文章:
- Spring Security OAuth2认证授权示例详解
- 基于Spring Security的Oauth2授权实现方法
- springboot2.x实现oauth2授权码登陆的方法
- 详解Springboot Oauth2 Server搭建Oauth2认证服务
- Spring Security OAuth2实现使用JWT的示例代码
- 使用Springboot搭建OAuth2.0 Server的方法示例
- Spring Security OAuth2集成短信验证码登录以及第三方登录
- Spring Cloud下基于OAUTH2认证授权的实现示例
- spring-boot集成spring-security的oauth2实现github登录网站的示例
加载全部内容