SQLite和PySqlite的使用方法 以SQLite和PySqlite为例来学习Python DB API
人气:0Python应用编程需要用到的针对不同数据库引擎的数据库接口:http://wiki.python.org/moin/DatabaseInterfaces
Python标准的DB API 2.0见:http://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0249/
本文将以SQLite和PySqlite为例来学习Python DB API。
pysqlite是一个sqlite为python 提供的api接口,它让一切对于sqlit的操作都变得异常简单。
从Python2.5起,pysqlite作为Python的一个标准模块。在使用标准库时,它被简称为sqlite3模块。
sqlite3标准库,详见:http://docs.python.org/3.3/library/sqlite3.html
基本的学习内容如下:
1.创建一张表
# filename:create.py
import sqlite3
# 创建连接对象
conn = sqlite3.connect('E:/code/py/db/test.db')
# 创建一个游标对象
cur = conn.cursor()
# 创建数据表的sql语句
createtb_sql = """create table test(
id integer,
name text,
age integer);"""
# 调用execute()执行create_sql语句
cur.execute(createtb_sql)
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
2.简单的插入数据
# filename:insert.py
import sqlite3
# 创建连接对象
conn = sqlite3.connect('E:/code/py/db/test.db')
# 创建一个游标对象
cur = conn.cursor()
# 向数据表中插入数据的sql语句
'''
insert_sql = """
insert into test values(1, 'huhu', 20);
insert into test values(2, 'hengheng', 18);
insert into test values(3, 'huahua', 18);
"""
'''
insert_sql = """
insert into test values(1, 'huhu', 20);
"""
# 调用execute()执行insert sql语句
# execute一次只能执行一条语句
cur.execute(insert_sql)
# 提交事务
conn.commit()
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
3.查询
# filename:select.py
import sqlite3
# 创建连接对象
conn = sqlite3.connect('E:/code/py/db/test.db')
# 创建一个游标对象
cur = conn.cursor()
# 查询数据表的sql语句
select_sql = """ select * from test;"""
# 调用execute()执行select sql语句
cur.execute(select_sql)
'''
while True:
# fetchone()把查询的结果集的下一行作为序列或者None
row = cur.fetchone()
if row == None:
break
print(row)
'''
'''
# fetchall()把查询的结果集的所有行作为序列的序列
for row in cur.fetchall():
print(row)
'''
# 迭代对象遍历
for row in cur:
print(row)
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
4.删除数据
# filename:delete.py
import sqlite3
# 创建连接对象
conn = sqlite3.connect('E:/code/py/db/test.db')
# 创建一个游标对象
cur = conn.cursor()
# delete语句
delete_sql = """delete from test"""
# execute()执行sql语句
cur.execute(delete_sql)
# commit()提交事务
conn.commit()
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
以上四步的运行结果:
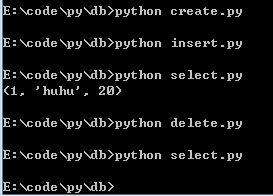
5.一次插入多条数据
# filename:insertmany.py
import sqlite3
# 创建连接对象
conn = sqlite3.connect('E:/code/py/db/test.db')
# 创建一个游标对象
cur = conn.cursor()
# 向数据表中插入数据的sql语句
insert_sql = """insert into test values(?, ?, ?)"""
# 调用execute()执行insert sql语句
# execute一次只能执行一条语句
for line in open('E:/code/py/db/data.txt'):
fields = line.split(',')
vals = [f for f in fields]
cur.execute(insert_sql,vals)
# 提交事务
conn.commit()
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
data.txt:
1,huhu,18
2,hengheng,18
3,lq,20
运行结果:
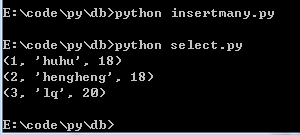
6.插入数据的方法(参数绑定,executemany的使用):
# inserts.py
import sqlite3
# 创建连接对象
conn = sqlite3.connect('E:/code/py/db/test.db')
# 创建一个游标对象
cur = conn.cursor()
# 向数据表中插入数据的sql语句
# 最简单的insert形式
insert_sql1 = """insert into test values(1, 'huhu', 20);"""
# execute()一次只能执行一条语句
cur.execute(insert_sql1)
# 参数绑定
# execute()第二个参数:位置参数或者字典类型参数
insert_sql2 = """insert into test values(?, ?, ?)"""
cur.execute(insert_sql2, (2,'hengheng',18))
insert_sql3 = """insert into test values(:id, :name, :age)"""
cur.execute(insert_sql3, {'id':3, 'name':'lq', 'age':18})
# executemany()第二个参数:列表类型参数,适用于迭代器和生成器
l = [(4, 'huhu', 18), (5, 'hh', 18), (6, 'lq', 18)]
cur.executemany(insert_sql2, l)
# 利用生成器实现
def l_generator():
l = [(7, 'huhu', 18), (8, 'hh', 18), (9, 'lq', 18)]
for t in l:
yield(t)
cur.executemany(insert_sql2, l_generator())
# 提交事务
conn.commit()
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
运行结果:
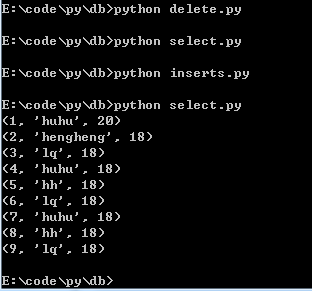
7.带条件的的update、delelte和select语句
(1)update
# filename:update.py
import sqlite3
# 创建连接对象
conn = sqlite3.connect('E:/code/py/db/test.db')
# 创建一个游标对象
cur = conn.cursor()
# update语句
update_sql = """update test set name = 'noname' where id = ?"""
# execute()和executem()执行sql语句
x = (1, )
cur.execute(update_sql, x)
y = (2, )
cur.execute(update_sql, y)
l = [(3, ),(4, ),(5, )]
cur.executemany(update_sql, l)
# commit()提交事务
conn.commit()
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
运行结果:
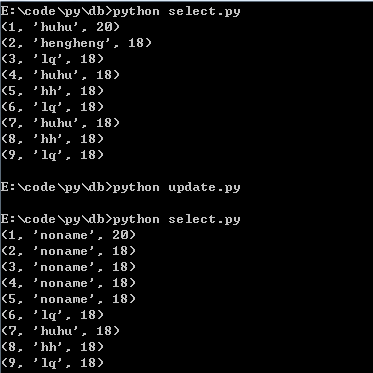
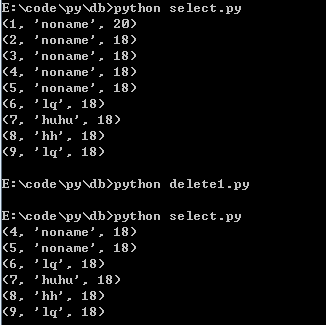
(2)delete
# filename:delete1.py
import sqlite3
# 创建连接对象
conn = sqlite3.connect('E:/code/py/db/test.db')
# 创建一个游标对象
cur = conn.cursor()
# delete语句
delete_sql = """delete from test where id = ?"""
# execute()和executemany()执行sql语句
cur.execute(delete_sql, (1, ))
cur.executemany(delete_sql, [(2, ), (3, )])
# commit()提交事务
conn.commit()
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
运行结果:
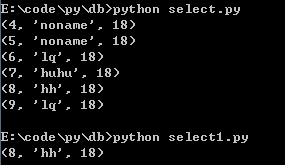
(3)select
# filename:select1.py
import sqlite3
# 创建连接对象
conn = sqlite3.connect('E:/code/py/db/test.db')
# 创建一个游标对象
cur = conn.cursor()
# 查询数据表的sql语句
select_sql = """ select * from test where id = ?;"""
# 调用execute()执行select sql语句
x = (8, )
cur.execute(select_sql, x)
'''
# 在executemany中,不能执行select语句
y = [(2, ), (3, )]
cur.executemany(select_sql, y)
'''
# 迭代对象遍历
for row in cur:
print(row)
# 关闭游标
cur.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
运行结果:
sqlite3标准库相比Python DB API 2.0,增加了一个较为方便的函数executescript函数(一次可以执行多条sql),介绍如下:
This is a nonstandard convenience method for executing multiple SQL statements at once. It issues a COMMIT statement first, then executes the SQL script it gets as a parameter.
sql_script can be an instance of str or bytes.
Example:
import sqlite3
con = sqlite3.connect(":memory:")
cur = con.cursor()
cur.executescript("""
create table person(
firstname,
lastname,
age
);
create table book(
title,
author,
published
);
insert into book(title, author, published)
values (
'Dirk Gently''s Holistic Detective Agency',
'Douglas Adams',
);
""")
好了这篇文章就为大家介绍到这了,希望大家以后多多支持。
您可能感兴趣的文章:
加载全部内容