python游戏地图最短路径 python游戏地图最短路径求解
北落师门XY 人气:0一.题目要求
参考下图完成游戏地图中从起点到目标点的最短路径寻找问题。

二.设计思路
先对游戏地图做了几个设定,以矩阵来模拟游戏地图。将可行的区域位置赋值0,障碍区赋值为inf。考虑到地图大小,将起始点和终点区域赋值99。
从Start点A开始向外层扩展,每扩展一层pathlen加一。List Q存储当前需要扩展的点,list P 存储当前扩展层。当扩展到End点B时扩展结束,路径可规划。当Q为空时,本次层扩展结束,检查P,若P非空,从P层向外扩展,若P为空,则End点B无法到达。
寻找最短路径时,从End点B开始,寻找当前点附近8个点的标记中比当前点标记小的点,直到标记为1为止。
三.程序主体
# -*-coding:gbk -*-
from numpy import *
dirs = [(1,1),(1,0),(1,-1),(0,-1),(-1,-1),(-1,0),(-1,1),(0,1)] # 四邻位置:从右下角开始顺时针得到,是按坐标差得到的
def find_path(oldmap,A,B):
oldmap[A[0], A[1]] = 99
oldmap[B[0], B[1]] = 99
[a,b]=oldmap.shape
pathmap=oldmap.copy()
Q=[]#存储扩展节点
P=[]#往外一层
pathlen=1
if A==B:
print('start point is equal to end point')
return True
current=A
while (True):
for i in range(8):
neighbor=[current[0]+dirs[i][0], current[1]+dirs[i][1]]
if neighbor==B:
print('the way is found')######################wrong
print('中间过程')
print(oldmap)
find_way(oldmap,pathmap,A,B,a,b)#####调用路径函数
return True
if (neighbor[0]>=0 and neighbor[1]>=0 and neighbor[0]<a and neighbor[1]<b and oldmap[neighbor[0],neighbor[1]]==0):
P.append(neighbor)
oldmap[neighbor[0],neighbor[1]]=pathlen
if Q==[]:
if P ==[]:
print(oldmap) ##############
print('No path')
return False
else:
Q.extend(P)
P=[]
pathlen += 1
else:
current=Q.pop()
###################寻找最短路径
def find_way(oldmap,pathmap,A,B,a,b):
currentpos=B
while (oldmap[currentpos[0],currentpos[1]]!=1):
for i in range(8):
neighborpos=[currentpos[0]+dirs[i][0], currentpos[1]+dirs[i][1]]
if (neighborpos[0] >= 0 and neighborpos[1] >= 0 and neighborpos[0] < a and neighborpos[1] < b and oldmap[neighborpos[0],neighborpos[1]]!=0):
if oldmap[neighborpos[0],neighborpos[1]]<oldmap[currentpos[0],currentpos[1]]:
pathmap[neighborpos[0],neighborpos[1]]=oldmap[neighborpos[0],neighborpos[1]]
currentpos=neighborpos
break
print('the way:')
print(pathmap)
四.主函数
def main():
map =mat([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, inf,inf, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0,inf, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[inf,inf,inf, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0,inf, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, inf],
[0, 0,inf, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, inf],
[0, 0,inf, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,inf],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, inf],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],])
print('最初地图')
print(map)
print('**********************************')
A = [5, 0]
# B=[5,0]
B = [3, 12]
find_path(map,A, B)
if __name__=='__main__':
main()
五.运行结果

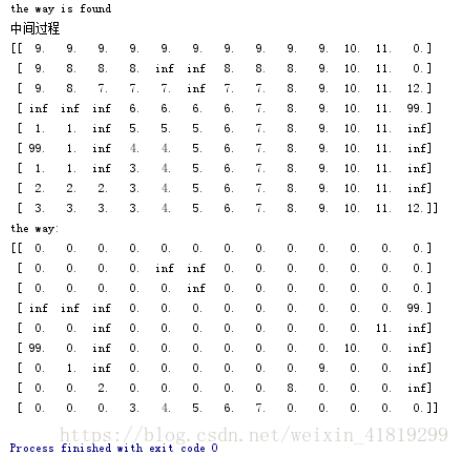
六.结果分析
由中间过程对应的矩阵可知,共经历了12次向外层扩展,第12次扩展即可将目标点包含进去。最短路径如the way对应的矩阵所示,是通过一种类似梯度下降的方法得到的。
加载全部内容