Android TV 焦点框移动 Android TV 焦点框移动的实现方法
i小康 人气:0Tv开发,最重要的当然是焦点框的移动,有了焦点框我们才能知道当前选中的是哪一个,我们来看下效果图:
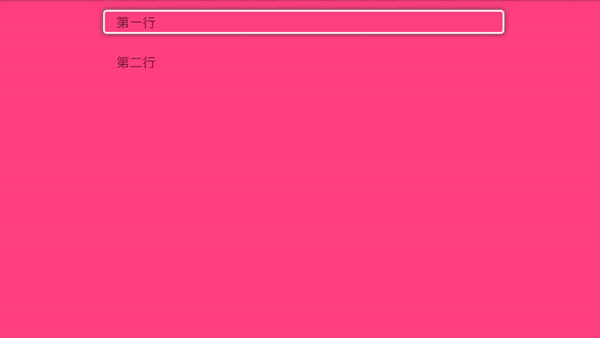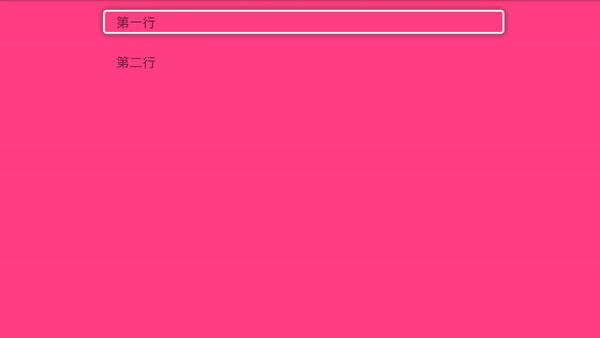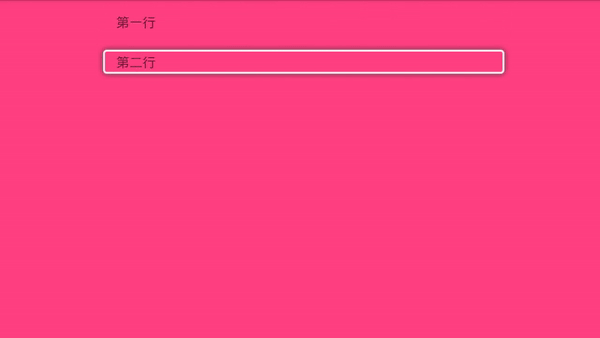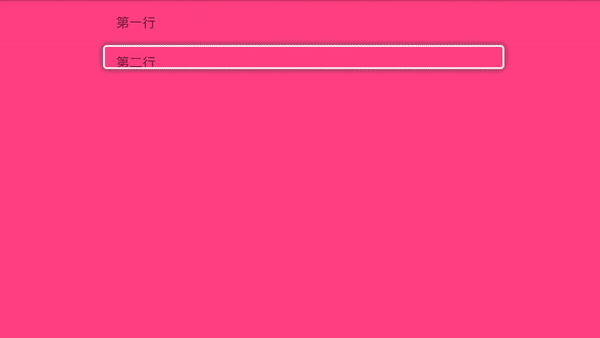
那它是怎么实现的呢,我们一起来看下。
原理
布局上使用一个view,背景是.9图片做焦点框,选中一个控件的时候把这个view移动选中的控件的位置。怎么样,是不是很简单,行动起来。先看下布局
codeing
布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/colorAccent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/id_fl"
android:layout_width="880dp"
android:layout_height="76dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="208dp"
android:layout_marginTop="9dp"
android:focusable="true">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_marginLeft="40dp"
android:text="第一行"
android:textSize="28sp" />
</FrameLayout>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/id_fl_2"
android:layout_width="880dp"
android:layout_height="76dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="208dp"
android:layout_marginTop="9dp"
android:focusable="true">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_marginLeft="40dp"
android:text="第二行"
android:textSize="28sp" />
</FrameLayout>
</LinearLayout>
<View
android:id="@+id/id_focus"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/settings_selector"
android:visibility="gone" />
</FrameLayout>
最底下的View就是我们要用到的焦点框
代码
import android.app.Activity;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.FrameLayout;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements View.OnFocusChangeListener{
private String TAG ="qkmin";
private int Layout1 = R.id.id_fl;
private int Layout2 = R.id.id_fl_2;
private View onFousView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initViews();
}
private void initViews() {
FrameLayout frameLayout=findViewById(Layout1);
FrameLayout frameLayout2=findViewById(Layout2);
onFousView = findViewById(R.id.id_focus);
//设置焦点变化监听
frameLayout.setOnFocusChangeListener(this);
frameLayout2.setOnFocusChangeListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onFocusChange(View v, boolean hasFocus) {
if (hasFocus){
Log.i(TAG,"onFocusChange"+v.getId());
//设置焦点框的位置和动画
Tools.focusAnimator(v,onFousView);
}
}
}
我们来看下Tools 这个类:
import android.animation.Animator;
import android.animation.AnimatorSet;
import android.animation.ObjectAnimator;
import android.animation.ValueAnimator;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class Tools {
private static int mFocusWidth;
private static int mFoucsHeight;
public static void focusAnimator(View v, View onFousView) {
focusAnimator(v, onFousView, -1, 0, 0);
}
public static void focusAnimator(View parentView, final View focusView, int scrollY, int offSetX, int offSetY) {
int[] fromLocation = new int[2];
focusView.getLocationOnScreen(fromLocation);
int fromWidth = focusView.getWidth();
int fromHeight = focusView.getHeight();
float fromX = fromLocation[0];
float fromY = fromLocation[1];
int[] toLocation = new int[2];
parentView.getLocationOnScreen(toLocation);
int toWidth = parentView.getWidth() + offSetX;
int toHeight = parentView.getHeight() + offSetY;
float toX = toLocation[0] - offSetX / 2;
float toY = toLocation[1] - offSetY / 2;
if (scrollY == -1) {
if (focusView.getVisibility() == View.GONE)
focusView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
AnimatorSet animatorSet = new AnimatorSet();
ObjectAnimator translateXAnimator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(focusView, "x", fromX, toX);
translateXAnimator.addListener(new Animator.AnimatorListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) {
}
@Override
public void onAnimationRepeat(Animator animation) {
}
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
if (focusView.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
focusView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
}
@Override
public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) {
if (focusView.getVisibility() == View.GONE)
focusView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
});
ObjectAnimator translateYAnimator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(focusView, "y", fromY, toY);
ValueAnimator scaleWidthAnimator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(focusView, "width", fromWidth, toWidth);
scaleWidthAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
float width = (Float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
mFocusWidth = (int) width;
ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = focusView.getLayoutParams();
layoutParams.width = mFocusWidth;
layoutParams.height = mFoucsHeight;
focusView.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
}
});
ValueAnimator scaleHeightAnimator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(focusView, "height", fromHeight, toHeight);
scaleHeightAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
float height = (Float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
mFoucsHeight = (int) height;
ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = focusView.getLayoutParams();
layoutParams.width = mFocusWidth;
layoutParams.height = mFoucsHeight;
focusView.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
}
});
animatorSet.playTogether(translateXAnimator, translateYAnimator, scaleWidthAnimator, scaleHeightAnimator);
animatorSet.setDuration(150);
animatorSet.start();
}
}
主要方法是focusAnimator(),首先获取focusView的宽、高,以及x ,y 坐标,在得到获取焦点的view的宽、高,以及x ,y 坐标,最会设置动画。这样就Ok了。
加载全部内容