springcloud Zuul动态路由 springcloud Zuul动态路由的实现
下一秒升华 人气:0前言
Zuul 是Netflix 提供的一个开源组件,致力于在云平台上提供动态路由,监控,弹性,安全等边缘服务的框架。也有很多公司使用它来作为网关的重要组成部分,碰巧今年公司的架构组决定自研一个网关产品,集动态路由,动态权限,限流配额等功能为一体,为其他部门的项目提供统一的外网调用管理,最终形成产品(这方面阿里其实已经有成熟的网关产品了,但是不太适用于个性化的配置,也没有集成权限和限流降级)。
不过这里并不想介绍整个网关的架构,而是想着重于讨论其中的一个关键点,并且也是经常在交流群中听人说起的:动态路由怎么做?
再阐释什么是动态路由之前,需要介绍一下架构的设计。
传统互联网架构图
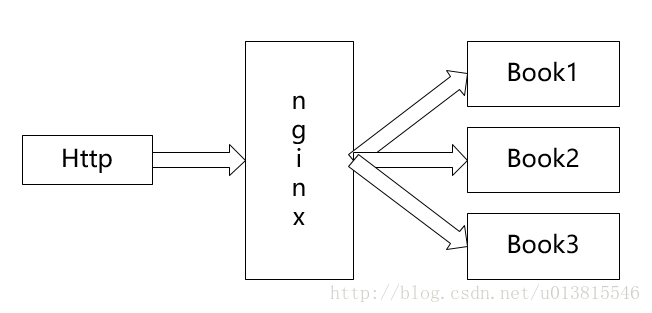
上图是没有网关参与的一个最典型的互联网架构(本文中统一使用book代表应用实例,即真正提供服务的一个业务系统)
加入eureka的架构图
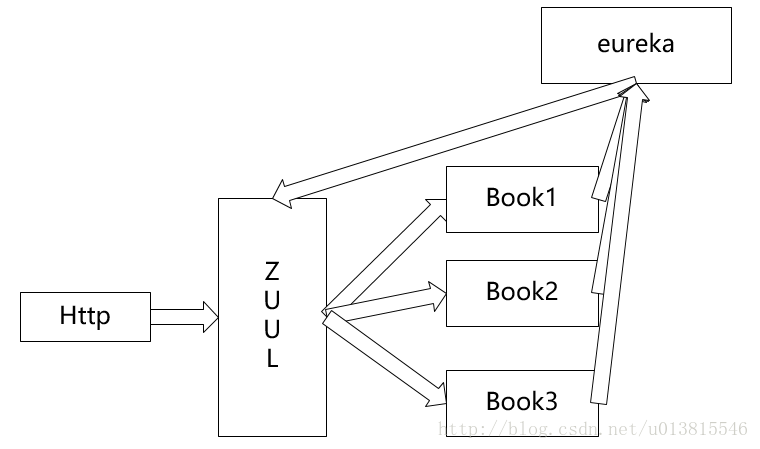
book注册到eureka注册中心中,zuul本身也连接着同一个eureka,可以拉取book众多实例的列表。服务中心的注册发现一直是值得推崇的一种方式,但是不适用与网关产品。因为我们的网关是面向众多的其他部门的已有或是异构架构的系统,不应该强求其他系统都使用eureka,这样是有侵入性的设计。
最终架构图
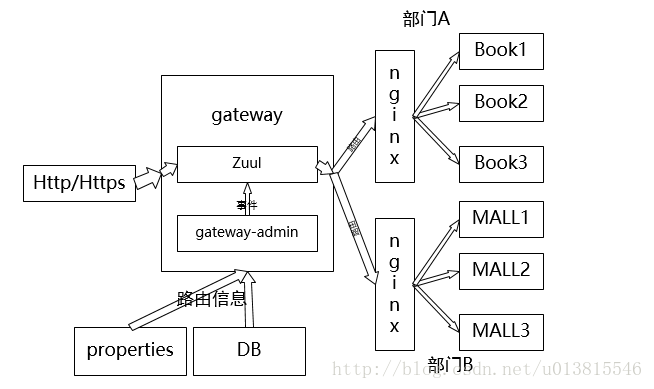
要强调的一点是,gateway最终也会部署多个实例,达到分布式的效果,在架构图中没有画出,请大家自行脑补。
本博客的示例使用最后一章架构图为例,带来动态路由的实现方式,会有具体的代码。
动态路由
动态路由需要达到可持久化配置,动态刷新的效果。如架构图所示,不仅要能满足从spring的配置文件properties加载路由信息,还需要从数据库加载我们的配置。另外一点是,路由信息在容器启动时就已经加载进入了内存,我们希望配置完成后,实施发布,动态刷新内存中的路由信息,达到不停机维护路由信息的效果。
zuul–HelloWorldDemo
项目结构
<groupId>com.sinosoft</groupId>
<artifactId>zuul-gateway-demo</artifactId>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<version>1.0</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<modules>
<module>gateway</module>
<module>book</module>
</modules>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Camden.SR6</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
tip:springboot-1.5.2对应的springcloud的版本需要使用Camden.SR6,一开始想专门写这个demo时,只替换了springboot的版本1.4.0->1.5.2,结果启动就报错了,最后发现是版本不兼容的锅。
gateway项目:
启动类:GatewayApplication.java
@EnableZuulProxy
@SpringBootApplication
public class GatewayApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(GatewayApplication.class, args);
}
}
配置:application.properties
#配置在配置文件中的路由信息 zuul.routes.books.url=http://localhost:8090 zuul.routes.books.path=/books/** #不使用注册中心,会带来侵入性 ribbon.eureka.enabled=false #网关端口 server.port=8080
book项目:
启动类:BookApplication.java
@RestController
@SpringBootApplication
public class BookApplication {
@RequestMapping(value = "/available")
public String available() {
System.out.println("Spring in Action");
return "Spring in Action";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/checked-out")
public String checkedOut() {
return "Spring Boot in Action";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BookApplication.class, args);
}
}
配置类:application.properties
server.port=8090
测试访问:http://localhost:8080/books/available
上述demo是一个简单的静态路由,简单看下源码,zuul是怎么做到转发,路由的。
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ ZuulProperties.class })
@ConditionalOnClass(ZuulServlet.class)
@Import(ServerPropertiesAutoConfiguration.class)
public class ZuulConfiguration {
@Autowired
//zuul的配置文件,对应了application.properties中的配置信息
protected ZuulProperties zuulProperties;
@Autowired
protected ServerProperties server;
@Autowired(required = false)
private ErrorController errorController;
@Bean
public HasFeatures zuulFeature() {
return HasFeatures.namedFeature("Zuul (Simple)", ZuulConfiguration.class);
}
//核心类,路由定位器,最最重要
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(RouteLocator.class)
public RouteLocator routeLocator() {
//默认配置的实现是SimpleRouteLocator.class
return new SimpleRouteLocator(this.server.getServletPrefix(),
this.zuulProperties);
}
//zuul的控制器,负责处理链路调用
@Bean
public ZuulController zuulController() {
return new ZuulController();
}
//MVC HandlerMapping that maps incoming request paths to remote services.
@Bean
public ZuulHandlerMapping zuulHandlerMapping(RouteLocator routes) {
ZuulHandlerMapping mapping = new ZuulHandlerMapping(routes, zuulController());
mapping.setErrorController(this.errorController);
return mapping;
}
//注册了一个路由刷新监听器,默认实现是ZuulRefreshListener.class,这个是我们动态路由的关键
@Bean
public ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> zuulRefreshRoutesListener() {
return new ZuulRefreshListener();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "zuulServlet")
public ServletRegistrationBean zuulServlet() {
ServletRegistrationBean servlet = new ServletRegistrationBean(new ZuulServlet(),
this.zuulProperties.getServletPattern());
// The whole point of exposing this servlet is to provide a route that doesn't
// buffer requests.
servlet.addInitParameter("buffer-requests", "false");
return servlet;
}
// pre filters
@Bean
public ServletDetectionFilter servletDetectionFilter() {
return new ServletDetectionFilter();
}
@Bean
public FormBodyWrapperFilter formBodyWrapperFilter() {
return new FormBodyWrapperFilter();
}
@Bean
public DebugFilter debugFilter() {
return new DebugFilter();
}
@Bean
public Servlet30WrapperFilter servlet30WrapperFilter() {
return new Servlet30WrapperFilter();
}
// post filters
@Bean
public SendResponseFilter sendResponseFilter() {
return new SendResponseFilter();
}
@Bean
public SendErrorFilter sendErrorFilter() {
return new SendErrorFilter();
}
@Bean
public SendForwardFilter sendForwardFilter() {
return new SendForwardFilter();
}
@Configuration
protected static class ZuulFilterConfiguration {
@Autowired
private Map<String, ZuulFilter> filters;
@Bean
public ZuulFilterInitializer zuulFilterInitializer() {
return new ZuulFilterInitializer(this.filters);
}
}
//上面提到的路由刷新监听器
private static class ZuulRefreshListener
implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
@Autowired
private ZuulHandlerMapping zuulHandlerMapping;
private HeartbeatMonitor heartbeatMonitor = new HeartbeatMonitor();
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent
|| event instanceof RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent
|| event instanceof RoutesRefreshedEvent) {
//设置为脏,下一次匹配到路径时,如果发现为脏,则会去刷新路由信息
this.zuulHandlerMapping.setDirty(true);
}
else if (event instanceof HeartbeatEvent) {
if (this.heartbeatMonitor.update(((HeartbeatEvent) event).getValue())) {
this.zuulHandlerMapping.setDirty(true);
}
}
}
}
}
我们要解决动态路由的难题,第一步就得理解路由定位器的作用。
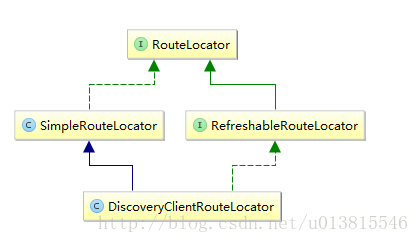
很失望,因为从接口关系来看,spring考虑到了路由刷新的需求,但是默认实现的SimpleRouteLocator没有实现RefreshableRouteLocator接口,看来我们只能借鉴DiscoveryClientRouteLocator去改造SimpleRouteLocator使其具备刷新能力。
public interface RefreshableRouteLocator extends RouteLocator {
void refresh();
}
DiscoveryClientRouteLocator比SimpleRouteLocator多了两个功能,第一是从DiscoveryClient(如Eureka)发现路由信息,之前的架构图已经给大家解释清楚了,我们不想使用eureka这种侵入式的网关模块,所以忽略它,第二是实现了RefreshableRouteLocator接口,能够实现动态刷新。
对SimpleRouteLocator.class的源码加一些注释,方便大家阅读:
public class SimpleRouteLocator implements RouteLocator {
//配置文件中的路由信息配置
private ZuulProperties properties;
//路径正则配置器,即作用于path:/books/**
private PathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
private String dispatcherServletPath = "/";
private String zuulServletPath;
private AtomicReference<Map<String, ZuulRoute>> routes = new AtomicReference<>();
public SimpleRouteLocator(String servletPath, ZuulProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
if (servletPath != null && StringUtils.hasText(servletPath)) {
this.dispatcherServletPath = servletPath;
}
this.zuulServletPath = properties.getServletPath();
}
//路由定位器和其他组件的交互,是最终把定位的Routes以list的方式提供出去,核心实现
@Override
public List<Route> getRoutes() {
if (this.routes.get() == null) {
this.routes.set(locateRoutes());
}
List<Route> values = new ArrayList<>();
for (String url : this.routes.get().keySet()) {
ZuulRoute route = this.routes.get().get(url);
String path = route.getPath();
values.add(getRoute(route, path));
}
return values;
}
@Override
public Collection<String> getIgnoredPaths() {
return this.properties.getIgnoredPatterns();
}
//这个方法在网关产品中也很重要,可以根据实际路径匹配到Route来进行业务逻辑的操作,进行一些加工
@Override
public Route getMatchingRoute(final String path) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Finding route for path: " + path);
}
if (this.routes.get() == null) {
this.routes.set(locateRoutes());
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("servletPath=" + this.dispatcherServletPath);
log.debug("zuulServletPath=" + this.zuulServletPath);
log.debug("RequestUtils.isDispatcherServletRequest()="
+ RequestUtils.isDispatcherServletRequest());
log.debug("RequestUtils.isZuulServletRequest()="
+ RequestUtils.isZuulServletRequest());
}
String adjustedPath = adjustPath(path);
ZuulRoute route = null;
if (!matchesIgnoredPatterns(adjustedPath)) {
for (Entry<String, ZuulRoute> entry : this.routes.get().entrySet()) {
String pattern = entry.getKey();
log.debug("Matching pattern:" + pattern);
if (this.pathMatcher.match(pattern, adjustedPath)) {
route = entry.getValue();
break;
}
}
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("route matched=" + route);
}
return getRoute(route, adjustedPath);
}
private Route getRoute(ZuulRoute route, String path) {
if (route == null) {
return null;
}
String targetPath = path;
String prefix = this.properties.getPrefix();
if (path.startsWith(prefix) && this.properties.isStripPrefix()) {
targetPath = path.substring(prefix.length());
}
if (route.isStripPrefix()) {
int index = route.getPath().indexOf("*") - 1;
if (index > 0) {
String routePrefix = route.getPath().substring(0, index);
targetPath = targetPath.replaceFirst(routePrefix, "");
prefix = prefix + routePrefix;
}
}
Boolean retryable = this.properties.getRetryable();
if (route.getRetryable() != null) {
retryable = route.getRetryable();
}
return new Route(route.getId(), targetPath, route.getLocation(), prefix,
retryable,
route.isCustomSensitiveHeaders() ? route.getSensitiveHeaders() : null);
}
//注意这个类并没有实现refresh接口,但是却提供了一个protected级别的方法,旨在让子类不需要重复维护一个private AtomicReference<Map<String, ZuulRoute>> routes = new AtomicReference<>();也可以达到刷新的效果
protected void doRefresh() {
this.routes.set(locateRoutes());
}
//具体就是在这儿定位路由信息的,我们之后从数据库加载路由信息,主要也是从这儿改写
/**
* Compute a map of path pattern to route. The default is just a static map from the
* {@link ZuulProperties}, but subclasses can add dynamic calculations.
*/
protected Map<String, ZuulRoute> locateRoutes() {
LinkedHashMap<String, ZuulRoute> routesMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, ZuulRoute>();
for (ZuulRoute route : this.properties.getRoutes().values()) {
routesMap.put(route.getPath(), route);
}
return routesMap;
}
protected boolean matchesIgnoredPatterns(String path) {
for (String pattern : this.properties.getIgnoredPatterns()) {
log.debug("Matching ignored pattern:" + pattern);
if (this.pathMatcher.match(pattern, path)) {
log.debug("Path " + path + " matches ignored pattern " + pattern);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private String adjustPath(final String path) {
String adjustedPath = path;
if (RequestUtils.isDispatcherServletRequest()
&& StringUtils.hasText(this.dispatcherServletPath)) {
if (!this.dispatcherServletPath.equals("/")) {
adjustedPath = path.substring(this.dispatcherServletPath.length());
log.debug("Stripped dispatcherServletPath");
}
}
else if (RequestUtils.isZuulServletRequest()) {
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.zuulServletPath)
&& !this.zuulServletPath.equals("/")) {
adjustedPath = path.substring(this.zuulServletPath.length());
log.debug("Stripped zuulServletPath");
}
}
else {
// do nothing
}
log.debug("adjustedPath=" + path);
return adjustedPath;
}
}
重写过后的自定义路由定位器如下:
public class CustomRouteLocator extends SimpleRouteLocator implements RefreshableRouteLocator{
public final static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CustomRouteLocator.class);
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
private ZuulProperties properties;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate){
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
public CustomRouteLocator(String servletPath, ZuulProperties properties) {
super(servletPath, properties);
this.properties = properties;
logger.info("servletPath:{}",servletPath);
}
//父类已经提供了这个方法,这里写出来只是为了说明这一个方法很重要!!!
// @Override
// protected void doRefresh() {
// super.doRefresh();
// }
@Override
public void refresh() {
doRefresh();
}
@Override
protected Map<String, ZuulRoute> locateRoutes() {
LinkedHashMap<String, ZuulRoute> routesMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, ZuulRoute>();
//从application.properties中加载路由信息
routesMap.putAll(super.locateRoutes());
//从db中加载路由信息
routesMap.putAll(locateRoutesFromDB());
//优化一下配置
LinkedHashMap<String, ZuulRoute> values = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (Map.Entry<String, ZuulRoute> entry : routesMap.entrySet()) {
String path = entry.getKey();
// Prepend with slash if not already present.
if (!path.startsWith("/")) {
path = "/" + path;
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getPrefix())) {
path = this.properties.getPrefix() + path;
if (!path.startsWith("/")) {
path = "/" + path;
}
}
values.put(path, entry.getValue());
}
return values;
}
private Map<String, ZuulRoute> locateRoutesFromDB(){
Map<String, ZuulRoute> routes = new LinkedHashMap<>();
List<ZuulRouteVO> results = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from gateway_api_define where enabled = true ",new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(ZuulRouteVO.class));
for (ZuulRouteVO result : results) {
if(org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils.isBlank(result.getPath()) || org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils.isBlank(result.getUrl()) ){
continue;
}
ZuulRoute zuulRoute = new ZuulRoute();
try {
org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils.copyProperties(result,zuulRoute);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("=============load zuul route info from db with error==============",e);
}
routes.put(zuulRoute.getPath(),zuulRoute);
}
return routes;
}
public static class ZuulRouteVO {
/**
* The ID of the route (the same as its map key by default).
*/
private String id;
/**
* The path (pattern) for the route, e.g. /foo/**.
*/
private String path;
/**
* The service ID (if any) to map to this route. You can specify a physical URL or
* a service, but not both.
*/
private String serviceId;
/**
* A full physical URL to map to the route. An alternative is to use a service ID
* and service discovery to find the physical address.
*/
private String url;
/**
* Flag to determine whether the prefix for this route (the path, minus pattern
* patcher) should be stripped before forwarding.
*/
private boolean stripPrefix = true;
/**
* Flag to indicate that this route should be retryable (if supported). Generally
* retry requires a service ID and ribbon.
*/
private Boolean retryable;
private Boolean enabled;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public String getServiceId() {
return serviceId;
}
public void setServiceId(String serviceId) {
this.serviceId = serviceId;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public boolean isStripPrefix() {
return stripPrefix;
}
public void setStripPrefix(boolean stripPrefix) {
this.stripPrefix = stripPrefix;
}
public Boolean getRetryable() {
return retryable;
}
public void setRetryable(Boolean retryable) {
this.retryable = retryable;
}
public Boolean getEnabled() {
return enabled;
}
public void setEnabled(Boolean enabled) {
this.enabled = enabled;
}
}
}
配置这个自定义的路由定位器:
@Configuration
public class CustomZuulConfig {
@Autowired
ZuulProperties zuulProperties;
@Autowired
ServerProperties server;
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Bean
public CustomRouteLocator routeLocator() {
CustomRouteLocator routeLocator = new CustomRouteLocator(this.server.getServletPrefix(), this.zuulProperties);
routeLocator.setJdbcTemplate(jdbcTemplate);
return routeLocator;
}
}
现在容器启动时,就可以从数据库和配置文件中一起加载路由信息了,离动态路由还差最后一步,就是实时刷新,前面已经说过了,默认的ZuulConfigure已经配置了事件监听器,我们只需要发送一个事件就可以实现刷新了。
public class RefreshRouteService {
@Autowired
ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;
@Autowired
RouteLocator routeLocator;
public void refreshRoute() {
RoutesRefreshedEvent routesRefreshedEvent = new RoutesRefreshedEvent(routeLocator);
publisher.publishEvent(routesRefreshedEvent);
}
}
具体的刷新流程其实就是从数据库重新加载了一遍,有人可能会问,为什么不自己是手动重新加载Locator.dorefresh?非要用事件去刷新。这牵扯到内部的zuul内部组件的工作流程,不仅仅是Locator本身的一个变量,具体想要了解的还得去看源码。
到这儿我们就实现了动态路由了,所以的实例代码和建表语句我会放到github上,下载的时候记得给我star QAQ !!!
加载全部内容