基于Hadoop实现Knn算法 基于Hadoop实现Knn算法
Angelababy_huan 人气:0Knn算法的核心思想是如果一个样本在特征空间中的K个最相邻的样本中的大多数属于某一个类别,则该样本也属于这个类别,并具有这个类别上样本的特性。该方法在确定分类决策上只依据最邻近的一个或者几个样本的类别来决定待分样本所属的类别。Knn方法在类别决策时,只与极少量的相邻样本有关。由于Knn方法主要靠周围有限的邻近的样本,而不是靠判别类域的方法来确定所属类别的,因此对于类域的交叉或重叠较多的待分样本集来说,Knn方法较其他方法更为合适。
Knn算法流程如下:
1. 计算当前测试数据与训练数据中的每条数据的距离
2. 圈定距离最近的K个训练对象,作为测试对象的近邻
3. 计算这K个训练对象中出现最多的那个类别,并将这个类别作为当前测试数据的类别
以上流程是Knn的大致流程,按照这个流程实现的MR效率并不高,可以在这之上进行优化。在这里只写,跟着这个流程走的MR实现过程。
Mapper的设计:
由于测试数据相比于训练数据来说,会小很多,因此将测试数据用Java API读取,放到内存中。所以,在setup中需要对测试数据进行初始化。在map中,计算当前测试数据与每条训练数据的距离,Mapper的值类型为:<Object, Text, IntWritable,MyWritable>。map输出键类型为IntWritable,存放当前测试数据的下标,输出值类型为MyWritable,这是自定义值类型,其中存放的是距离以及与测试数据比较的训练数据的类别。
public class KnnMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, IntWritable,MyWritable> {
Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(KnnMapper.class);
private List<float[]> testData;
@Override
protected void setup(Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Configuration conf= context.getConfiguration();
conf.set("fs.defaultFS", "master:8020");
String testPath= conf.get("TestFilePath");
Path testDataPath= new Path(testPath);
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
this.testData = readTestData(fs,testDataPath);
}
@Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String[] line = value.toString().split(",");
float[] trainData = new float[line.length-1];
for(int i=0;i<trainData.length;i++){
trainData[i] = Float.valueOf(line[i]);
log.info("训练数据:"+line[i]+"类别:"+line[line.length-1]);
}
for(int i=0; i< this.testData.size();i++){
float[] testI = this.testData.get(i);
float distance = Outh(testI, trainData);
log.info("距离:"+distance);
context.write(new IntWritable(i), new MyWritable(distance, line[line.length-1]));
}
}
private List<float[]> readTestData(FileSystem fs,Path Path) throws IOException {
//补充代码完整
FSDataInputStream data = fs.open(Path);
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(data));
String line = "";
List<float[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
while ((line = bf.readLine()) != null) {
String[] items = line.split(",");
float[] item = new float[items.length];
for(int i=0;i<items.length;i++){
item[i] = Float.valueOf(items[i]);
}
list.add(item);
}
return list;
}
// 计算欧式距离
private static float Outh(float[] testData, float[] inData) {
float distance =0.0f;
for(int i=0;i<testData.length;i++){
distance += (testData[i]-inData[i])*(testData[i]-inData[i]);
}
distance = (float)Math.sqrt(distance);
return distance;
}
}
自定义值类型MyWritable如下:
public class MyWritable implements Writable{
private float distance;
private String label;
public MyWritable() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public MyWritable(float distance, String label){
this.distance = distance;
this.label = label;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.distance+","+this.label;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
out.writeFloat(distance);
out.writeUTF(label);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.distance = in.readFloat();
this.label = in.readUTF();
}
public float getDistance() {
return distance;
}
public void setDistance(float distance) {
this.distance = distance;
}
public String getLabel() {
return label;
}
public void setLabel(String label) {
this.label = label;
}
}
在Reducer端中,需要初始化参数K,也就是圈定距离最近的K个对象的K值。在reduce中需要对距离按照从小到大的距离排序,然后选取前K条数据,再计算这K条数据中,出现次数最多的那个类别并将这个类别与测试数据的下标相对应并以K,V的形式输出到HDFS上。
public class KnnReducer extends Reducer<IntWritable, MyWritable, IntWritable, Text> {
private int K;
@Override
protected void setup(Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.K = context.getConfiguration().getInt("K", 5);
}
@Override
/***
* key => 0
* values =>([1,lable1],[2,lable2],[3,label2],[2.5,lable2])
*/
protected void reduce(IntWritable key, Iterable<MyWritable> values,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
MyWritable[] mywrit = new MyWritable[K];
for(int i=0;i<K;i++){
mywrit[i] = new MyWritable(Float.MAX_VALUE, "-1");
}
// 找出距离最小的前k个
for (MyWritable m : values) {
float distance = m.getDistance();
String label = m.getLabel();
for(MyWritable m1: mywrit){
if (distance < m1.getDistance()){
m1.setDistance(distance);
m1.setLabel(label);
}
}
}
// 找出前k个中,出现次数最多的类别
String[] testClass = new String[K];
for(int i=0;i<K;i++){
testClass[i] = mywrit[i].getLabel();
}
String countMost = mostEle(testClass);
context.write(key, new Text(countMost));
}
public static String mostEle(String[] strArray) {
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < strArray.length; i++) {
String str = strArray[i];
if (map.containsKey(str)) {
int tmp = map.get(str);
map.put(str, tmp+1);
}else{
map.put(str, 1);
}
}
// 得到hashmap中值最大的键,也就是出现次数最多的类别
Collection<Integer> count = map.values();
int maxCount = Collections.max(count);
String maxString = "";
for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry: map.entrySet()){
if (maxCount == entry.getValue()) {
maxString = entry.getKey();
}
}
return maxString;
}
}
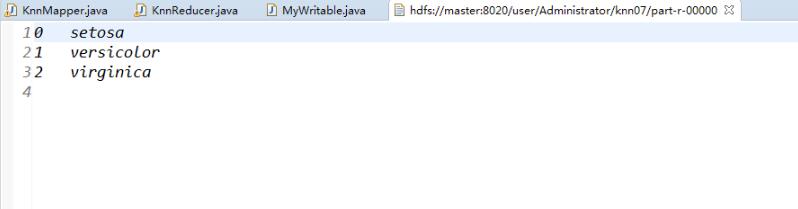
最后输出结果如下:
加载全部内容