C语言求解无向图顶点之间的所有最短路径 C语言求解无向图顶点之间的所有最短路径
uestcjerry 人气:0
思路一:
DFS,遇到终点之后进行记录
辅助存储:
std::vector<int> tempPath; std::vector<std::vector<int>> totalPath;
实现:
//查找无向图的所有最短路径,直接dfs就可以解决了
//记录保存这里用 vector<vector<int>> 插入失败,重新搞一下 OK
// 时间复杂度 O(N + E)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#define MAX 10
#define INF 999999
int graph[MAX + 1][MAX + 1];
int N, M; //node, edge
int nodeBook[MAX + 1];
int minPath = INF;
std::vector<int> pathNodeVec;
std::vector<std::vector<int>> allShortVec;
int startNode, endNode;
void dfs(int i, int step)
{
if (i == endNode) { //遇到终点,进行路径判定
if (step < minPath) {
std::cout << "step < minpath.., size = " << allShortVec.size() << std::endl;
minPath = step;
pathNodeVec.push_back(i);
for (auto &elem : pathNodeVec)
std::cout << elem << "\t";
std::cout << std::endl;
std::vector<int> tempVec = pathNodeVec;
allShortVec.clear(); //清空
allShortVec.push_back(tempVec); //存储
pathNodeVec.pop_back();
} else if (step == minPath) {
std::cout << "step == minpath.., size = " << allShortVec.size() << std::endl;
pathNodeVec.push_back(i);
for (auto &elem : pathNodeVec)
std::cout << elem << "\t";
std::cout << std::endl;
std::vector<int> tempVec = pathNodeVec;
allShortVec.push_back(tempVec); //存储当前路径
pathNodeVec.pop_back();
} else { ;}
return;
}
nodeBook[i] = 1;
pathNodeVec.push_back(i);
for (int x = 1; x <= N; x++) { //尝试所有可能性
if (x == i)
continue;
if (nodeBook[x] == 1)
continue;
if (graph[i][x] == INF)
continue;
dfs(x, step + 1);
}
nodeBook[i] = 0;
pathNodeVec.pop_back();
return ;
}
int main(void)
{
std::cin >> N >> M;
for (int x = 1; x <= N; x++)
nodeBook[x] = 0; //表示还没有访问
for (int x = 1; x <= N; ++x)
for (int y = 1; y <= N; ++y) {
if (x == y)
graph[x][y] = 0;
else
graph[x][y] = INF;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= M; ++i) {
int tempX, tempY, tempWeight;
std::cin >> tempX >> tempY >> tempWeight;
graph[tempX][tempY] = tempWeight;
}
std::cout << "please input start node & end node :" << std::endl;
std::cin >> startNode >> endNode;
pathNodeVec.clear();
allShortVec.clear();
dfs(startNode, 0);
std::cout << "all shortest path: \t";
std::cout << "size = " << allShortVec.size() << std::endl;
for (std::vector<std::vector<int>>::const_iterator it = allShortVec.begin(); it != allShortVec.end(); it++) {
for (std::vector<int>::const_iterator it2 = (*it).begin(); it2 != (*it).end(); it2++)
std::cout << (*it2) << "\t";
std::cout << std::endl;
}
getchar();
return 0;
}
时间分析:
O(V + E)
缺点:
可能会爆栈,我这里算86W点+414W边直接爆,小的没问题。
思路二:
BFS,位图/vector/.. 记录好每一步的路径即可
时间
O(V + E)
额外开销:
存储每一步的路径,如何维护好,尽量避免循环查找。
思路三:
1. 先求出起始点start到其余所有点的最短路径; Dijkstra
2. 然后以终点end为开始,反向进行dfs/bfs搜索;
每回退 i 层,判断值(path-i)与起点到当前点最短路径长度 temp 的比较;
二者相等,则继续(利用子问题的正确性); 若 (path-i) < temp ,则这个点不在最短路径上,放弃。
如图所示:
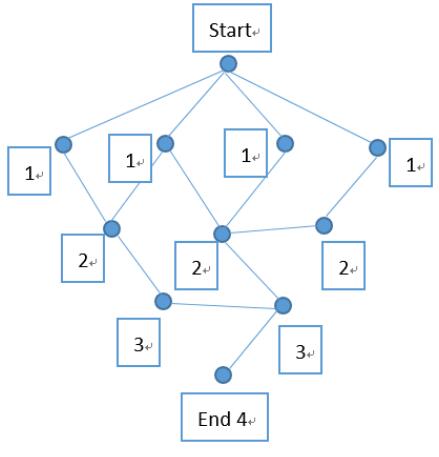
先求出start到其余所有点的最短路径;
然后从 end 点开始往回搜索;
end上面一个点,(path - 1 = 3)等于起始点到它的最短路径长 3,判断,是最短路径上的点,继续;
再往上搜索:
左边那个点3,因为此时(path - 2)= 2,而那个点的 temp=3,即 (path - i) < temp ,因此那个点一定不在 start 到 end 的最短路径上。
而上面那个点2,此时 (path - 2)= 2 , 而那个点 temp = 2, 即 (path - i) == temp , 因此它必然在 start 到 end 的最短路径上。继续搜索下去 。
重复这样的过程直到搜索完毕,最终得到两条最短路径。
加载全部内容