Java POI读取、写入Excel Java利用POI读取、写入Excel的方法指南
Dreamer-1 人气:0前言
Apache POI [1] 是用Java编写的免费开源的跨平台的 Java API,Apache POI提供API给Java程式对Microsoft Office格式档案读和写的功能。POI为“Poor Obfuscation Implementation”的首字母缩写,意为“简洁版的模糊实现”。
做项目时经常有通过程序读取Excel数据,或是创建新的Excel并写入数据的需求;
网上很多经验教程里使用的POI版本都比较老了,一些API在新版里已经废弃,这里基于最新的Apache POI 4.0.1版本来总结一下整个读取和写入Excel的过程,希望能帮助到需要的人 ^_^
1. 准备工作
1.1 在项目中引入Apache POI相关类库
引入 Apache POI 和 Apache POI-OOXML 这两个类库,Maven坐标如下:
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId> <artifactId>poi</artifactId> <version>4.0.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId> <artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId> <version>4.0.1</version> </dependency>
2. 读取或写入Excel数据
2.1 示例程序结构说明
简单说明一下示例程序的整体结构:
- ExcelReader.java是实现读取Excel数据功能的类;
- ExcelWriter.java是创建新的Excel并向其中写入数据的类;
- ExcelDataVO.java封装了读取或写入时每一“行”的数据;
- MainTest.java是示例程序的入口类,其中演示了读取和写入Excel数据的整个过程;
2.2 读取数据
示例程序需要从桌面读取 readExample.xlsx 内的数据,readExample.xlsx 的内容如下:
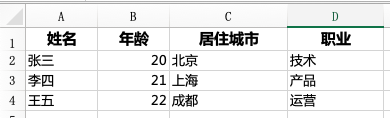
读取Excel时主要调用ExcelReader.java类来读取和解析Excel的具体内容,这里以读取系统文件的形式演示读取过程:(兼容 xls 和 xlsx)
2.2.1 主程序入口类代码:
/**
* Author: Dreamer-1
* Date: 2019-03-01
* Time: 10:13
* Description: 示例程序入口类
*/
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 设定Excel文件所在路径
String excelFileName = "/Users/Dreamer-1/Desktop/myBlog/java解析Excel/readExample.xlsx";
// 读取Excel文件内容
List<ExcelDataVO> readResult = ExcelReader.readExcel(excelFileName);
// todo 进行业务操作
}
}
读取和写入时封装每一“行”数据的ExcelDataVO.java代码如下:
/**
* Author: Dreamer-1
* Date: 2019-03-01
* Time: 11:33
* Description: 读取Excel时,封装读取的每一行的数据
*/
public class ExcelDataVO {
/**
* 姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 年龄
*/
private Integer age;
/**
* 居住地
*/
private String location;
/**
* 职业
*/
private String job;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getLocation() {
return location;
}
public void setLocation(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public String getJob() {
return job;
}
public void setJob(String job) {
this.job = job;
}
}
2.2.2 Excel解析类的代码:
/**
* Author: Dreamer-1
* Date: 2019-03-01
* Time: 10:21
* Description: 读取Excel内容
*/
public class ExcelReader {
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(ExcelReader.class.getName()); // 日志打印类
private static final String XLS = "xls";
private static final String XLSX = "xlsx";
/**
* 根据文件后缀名类型获取对应的工作簿对象
* @param inputStream 读取文件的输入流
* @param fileType 文件后缀名类型(xls或xlsx)
* @return 包含文件数据的工作簿对象
* @throws IOException
*/
public static Workbook getWorkbook(InputStream inputStream, String fileType) throws IOException {
Workbook workbook = null;
if (fileType.equalsIgnoreCase(XLS)) {
workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
} else if (fileType.equalsIgnoreCase(XLSX)) {
workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
}
return workbook;
}
/**
* 读取Excel文件内容
* @param fileName 要读取的Excel文件所在路径
* @return 读取结果列表,读取失败时返回null
*/
public static List<ExcelDataVO> readExcel(String fileName) {
Workbook workbook = null;
FileInputStream inputStream = null;
try {
// 获取Excel后缀名
String fileType = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf(".") + 1, fileName.length());
// 获取Excel文件
File excelFile = new File(fileName);
if (!excelFile.exists()) {
logger.warning("指定的Excel文件不存在!");
return null;
}
// 获取Excel工作簿
inputStream = new FileInputStream(excelFile);
workbook = getWorkbook(inputStream, fileType);
// 读取excel中的数据
List<ExcelDataVO> resultDataList = parseExcel(workbook);
return resultDataList;
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warning("解析Excel失败,文件名:" + fileName + " 错误信息:" + e.getMessage());
return null;
} finally {
try {
if (null != workbook) {
workbook.close();
}
if (null != inputStream) {
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warning("关闭数据流出错!错误信息:" + e.getMessage());
return null;
}
}
}
/**
* 解析Excel数据
* @param workbook Excel工作簿对象
* @return 解析结果
*/
private static List<ExcelDataVO> parseExcel(Workbook workbook) {
List<ExcelDataVO> resultDataList = new ArrayList<>();
// 解析sheet
for (int sheetNum = 0; sheetNum < workbook.getNumberOfSheets(); sheetNum++) {
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(sheetNum);
// 校验sheet是否合法
if (sheet == null) {
continue;
}
// 获取第一行数据
int firstRowNum = sheet.getFirstRowNum();
Row firstRow = sheet.getRow(firstRowNum);
if (null == firstRow) {
logger.warning("解析Excel失败,在第一行没有读取到任何数据!");
}
// 解析每一行的数据,构造数据对象
int rowStart = firstRowNum + 1;
int rowEnd = sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows();
for (int rowNum = rowStart; rowNum < rowEnd; rowNum++) {
Row row = sheet.getRow(rowNum);
if (null == row) {
continue;
}
ExcelDataVO resultData = convertRowToData(row);
if (null == resultData) {
logger.warning("第 " + row.getRowNum() + "行数据不合法,已忽略!");
continue;
}
resultDataList.add(resultData);
}
}
return resultDataList;
}
/**
* 将单元格内容转换为字符串
* @param cell
* @return
*/
private static String convertCellValueToString(Cell cell) {
if(cell==null){
return null;
}
String returnValue = null;
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
case NUMERIC: //数字
Double doubleValue = cell.getNumericCellValue();
// 格式化科学计数法,取一位整数
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0");
returnValue = df.format(doubleValue);
break;
case STRING: //字符串
returnValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
break;
case BOOLEAN: //布尔
Boolean booleanValue = cell.getBooleanCellValue();
returnValue = booleanValue.toString();
break;
case BLANK: // 空值
break;
case FORMULA: // 公式
returnValue = cell.getCellFormula();
break;
case ERROR: // 故障
break;
default:
break;
}
return returnValue;
}
/**
* 提取每一行中需要的数据,构造成为一个结果数据对象
*
* 当该行中有单元格的数据为空或不合法时,忽略该行的数据
*
* @param row 行数据
* @return 解析后的行数据对象,行数据错误时返回null
*/
private static ExcelDataVO convertRowToData(Row row) {
ExcelDataVO resultData = new ExcelDataVO();
Cell cell;
int cellNum = 0;
// 获取姓名
cell = row.getCell(cellNum++);
String name = convertCellValueToString(cell);
resultData.setName(name);
// 获取年龄
cell = row.getCell(cellNum++);
String ageStr = convertCellValueToString(cell);
if (null == ageStr || "".equals(ageStr)) {
// 年龄为空
resultData.setAge(null);
} else {
resultData.setAge(Integer.parseInt(ageStr));
}
// 获取居住地
cell = row.getCell(cellNum++);
String location = convertCellValueToString(cell);
resultData.setLocation(location);
// 获取职业
cell = row.getCell(cellNum++);
String job = convertCellValueToString(cell);
resultData.setJob(job);
return resultData;
}
}
2.2.3 应用场景补充
一般我们会有这样的应用场景,即:在前台页面的文件上传入口上传本地的Excel文件到后台,后台收到Excel文件后进行解析并做对应的业务操作;
这里假设前台已经有了上传文件的入口,再简单贴一下后台的解析代码;
后台接收前台数据的Controller层代码示例:
@PostMapping("/uploadExcel")
public ResponseEntity<?> uploadImage(MultipartFile file) {
// 检查前台数据合法性
if (null == file || file.isEmpty()) {
logger.warning("上传的Excel商品数据文件为空!上传时间:" + new Date());
return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
try {
// 解析Excel
List<ExcelDataVO> parsedResult = ExcelReader.readExcel(file);
// todo 进行业务操作
return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.OK);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warning("上传的Excel商品数据文件为空!上传时间:" + new Date());
return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
}
ExcelReader.java中的 readExcel() 方法需要做一定的修改,代码如下:
/**
* 读取Excel文件内容
* @param file 上传的Excel文件
* @return 读取结果列表,读取失败时返回null
*/
public static List<ExcelDataVO> readExcel(MultipartFile file) {
Workbook workbook = null;
try {
// 获取Excel后缀名
String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename();
if (fileName == null || fileName.isEmpty() || fileName.lastIndexOf(".") < 0) {
logger.warning("解析Excel失败,因为获取到的Excel文件名非法!");
return null;
}
String fileType = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf(".") + 1, fileName.length());
// 获取Excel工作簿
workbook = getWorkbook(file.getInputStream(), fileType);
// 读取excel中的数据
List<ExcelDataVO> resultDataList = parseExcel(workbook);
return resultDataList;
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warning("解析Excel失败,文件名:" + file.getOriginalFilename() + " 错误信息:" + e.getMessage());
return null;
} finally {
try {
if (null != workbook) {
workbook.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warning("关闭数据流出错!错误信息:" + e.getMessage());
return null;
}
}
}
2.3 写入数据
写入数据时主要调用ExcelWriter.java来创建Excel工作簿对象并写入数据,这里以写入系统文件数据为例演示写入的过程:
2.3.1 主程序入口类代码
/**
* Author: Dreamer-1
* Date: 2019-03-01
* Time: 10:13
* Description: 示例程序入口类
*/
public class MainTest {
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(MainTest.class.getName());
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建需要写入的数据列表
List<ExcelDataVO> dataVOList = new ArrayList<>(2);
ExcelDataVO dataVO = new ExcelDataVO();
dataVO.setName("小明");
dataVO.setAge(18);
dataVO.setLocation("广州");
dataVO.setJob("大学生");
ExcelDataVO dataVO2 = new ExcelDataVO();
dataVO2.setName("小花");
dataVO2.setAge(19);
dataVO2.setLocation("深圳");
dataVO2.setJob("大学生");
dataVOList.add(dataVO);
dataVOList.add(dataVO2);
// 写入数据到工作簿对象内
Workbook workbook = ExcelWriter.exportData(dataVOList);
// 以文件的形式输出工作簿对象
FileOutputStream fileOut = null;
try {
String exportFilePath = "/Users/Dreamer-1/Desktop/myBlog/java解析Excel/writeExample.xlsx";
File exportFile = new File(exportFilePath);
if (!exportFile.exists()) {
exportFile.createNewFile();
}
fileOut = new FileOutputStream(exportFilePath);
workbook.write(fileOut);
fileOut.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warning("输出Excel时发生错误,错误原因:" + e.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
if (null != fileOut) {
fileOut.close();
}
if (null != workbook) {
workbook.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.warning("关闭输出流时发生错误,错误原因:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
2.3.2 写入Excel类的代码
ExcelWriter.java类中,你可以根据实际需要替换 CELL_HEADS 列头的信息,然后重写 convertDataToRow 方法,转换你自己的行数据;
/**
* Author: Dreamer-1
* Date: 2019-03-01
* Time: 11:09
* Description: 生成Excel并写入数据
*/
public class ExcelWriter {
private static List<String> CELL_HEADS; //列头
static{
// 类装载时就载入指定好的列头信息,如有需要,可以考虑做成动态生成的列头
CELL_HEADS = new ArrayList<>();
CELL_HEADS.add("姓名");
CELL_HEADS.add("年龄");
CELL_HEADS.add("居住城市");
CELL_HEADS.add("职业");
}
/**
* 生成Excel并写入数据信息
* @param dataList 数据列表
* @return 写入数据后的工作簿对象
*/
public static Workbook exportData(List<ExcelDataVO> dataList){
// 生成xlsx的Excel
Workbook workbook = new SXSSFWorkbook();
// 如需生成xls的Excel,请使用下面的工作簿对象,注意后续输出时文件后缀名也需更改为xls
//Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
// 生成Sheet表,写入第一行的列头
Sheet sheet = buildDataSheet(workbook);
//构建每行的数据内容
int rowNum = 1;
for (Iterator<ExcelDataVO> it = dataList.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) {
ExcelDataVO data = it.next();
if (data == null) {
continue;
}
//输出行数据
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNum++);
convertDataToRow(data, row);
}
return workbook;
}
/**
* 生成sheet表,并写入第一行数据(列头)
* @param workbook 工作簿对象
* @return 已经写入列头的Sheet
*/
private static Sheet buildDataSheet(Workbook workbook) {
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
// 设置列头宽度
for (int i=0; i<CELL_HEADS.size(); i++) {
sheet.setColumnWidth(i, 4000);
}
// 设置默认行高
sheet.setDefaultRowHeight((short) 400);
// 构建头单元格样式
CellStyle cellStyle = buildHeadCellStyle(sheet.getWorkbook());
// 写入第一行各列的数据
Row head = sheet.createRow(0);
for (int i = 0; i < CELL_HEADS.size(); i++) {
Cell cell = head.createCell(i);
cell.setCellValue(CELL_HEADS.get(i));
cell.setCellStyle(cellStyle);
}
return sheet;
}
/**
* 设置第一行列头的样式
* @param workbook 工作簿对象
* @return 单元格样式对象
*/
private static CellStyle buildHeadCellStyle(Workbook workbook) {
CellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle();
//对齐方式设置
style.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
//边框颜色和宽度设置
style.setBorderBottom(BorderStyle.THIN);
style.setBottomBorderColor(IndexedColors.BLACK.getIndex()); // 下边框
style.setBorderLeft(BorderStyle.THIN);
style.setLeftBorderColor(IndexedColors.BLACK.getIndex()); // 左边框
style.setBorderRight(BorderStyle.THIN);
style.setRightBorderColor(IndexedColors.BLACK.getIndex()); // 右边框
style.setBorderTop(BorderStyle.THIN);
style.setTopBorderColor(IndexedColors.BLACK.getIndex()); // 上边框
//设置背景颜色
style.setFillForegroundColor(IndexedColors.GREY_25_PERCENT.getIndex());
style.setFillPattern(FillPatternType.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
//粗体字设置
Font font = workbook.createFont();
font.setBold(true);
style.setFont(font);
return style;
}
/**
* 将数据转换成行
* @param data 源数据
* @param row 行对象
* @return
*/
private static void convertDataToRow(ExcelDataVO data, Row row){
int cellNum = 0;
Cell cell;
// 姓名
cell = row.createCell(cellNum++);
cell.setCellValue(null == data.getName() ? "" : data.getName());
// 年龄
cell = row.createCell(cellNum++);
if (null != data.getAge()) {
cell.setCellValue(data.getAge());
} else {
cell.setCellValue("");
}
// 所在城市
cell = row.createCell(cellNum++);
cell.setCellValue(null == data.getLocation() ? "" : data.getLocation());
// 职业
cell = row.createCell(cellNum++);
cell.setCellValue(null == data.getJob() ? "" : data.getJob());
}
}
示例程序运行后将会在指定的系统路径下生成 writeExample.xlsx文件,其内容如下:

2.3.3 应用场景补充
一般写入Excel时会有这样的场景:前台页面上有一个导出按钮,点击后将后台某张表里的数据以Excel的形式导出,导出的Excel文件通过浏览器下载到用户系统中;
这里默认前台页面已经有相应的按钮功能,给出对应的Controller层代码供参考:
@GetMapping("/exportExcel")
public void exportExcel(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
Workbook workbook = null;
OutputStream out = null;
try {
// todo 根据业务需求获取需要写入Excel的数据列表 dataList
// 生成Excel工作簿对象并写入数据
workbook = ExcelWriter.exportData(dataList);
// 写入Excel文件到前端
if(null != workbook){
String excelName = "示例Excel导出";
String fileName = excelName + DateUtil.format(new Date(), DateUtil.SHORT_DATE) + ".xlsx";
fileName = new String(fileName.getBytes("UTF-8"),"iso8859-1");
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + fileName);
response.setContentType("application/x-download");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.addHeader("Pargam", "no-cache");
response.addHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache");
response.flushBuffer();
out = response.getOutputStream();
workbook.write(out);
out.flush();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.WARNING("写入Excel过程出错!错误原因:" + e.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
if (null != workbook) {
workbook.close();
}
if (null != out) {
out.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.WARNING("关闭workbook或outputStream出错!");
}
}
}
// 前台页面发送请求到后台Controller时的JS代码可参考: var url = "/exportExcel"; window.location=url;
3. 源码下载
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流,谢谢大家对的支持。
加载全部内容