nginx+tomcat实现Windows系统下的负载均衡搭建 nginx+tomcat实现Windows系统下的负载均衡搭建教程
天阴的时候 人气:0刚入行没多久就听过‘负载均衡'的大名,到现在因为工作接触的少,所以没什么太多的认识。但自己又对其非常的好奇,所以前两天通过查资料,在自己的笔记本上就搭建了一个超简单的案例(工作中没有时间,晚上到家了条件又不够,只能用自己的笔记本将就一下了,重在理解思想。。)
通俗点将,负载均衡就是因为访问流量太大,导致项目访问不流畅、甚至宕掉,所以通过一种分流的方式来缓解这种情况。

首先,安装两个tomcat,可以是同一个复制成两个,也可以下载两个不同版本的tomcat,我就是下载了两个不同版本的。下载地址:https://tomcat.apache.org/download-80.cgi
(这是8.0版本的,随便找两个不是特别老的版本的就行)。
然后启动两个tomcat,在启动前,先更改其中一个的端口号,使得两个tomcat启动时不会端口冲突,一个是本身的8080端口,一个是改成了9080端口。配好以后,打开cmd命令窗口,我的tomcat一个放在D:\software\apache-tomcat-8.5.24目录下,按照如下命令即可启动,启动成功会弹出另一个窗口,显示如下:

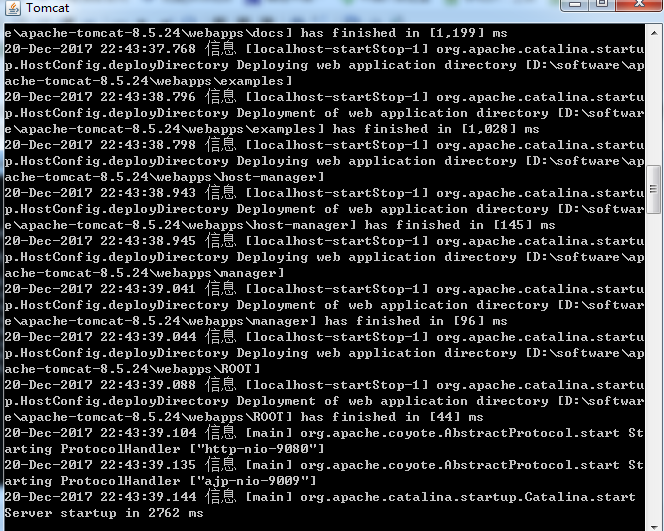
打开浏览器,输入http://localhost:9080/,出现如下界面即tomcat启动成功。另一个采用同样的步骤即可。

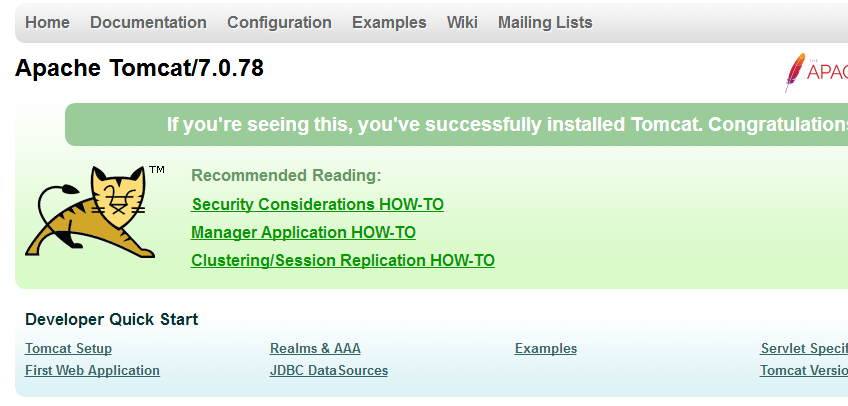
图1:tomcat8 图2:tomcat7
再之后,安装一个nginx,我装的是稳定版的nginx,下载地址:http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.12.2.zip,解压即可使用

在启动前,必须要对nginx进行一下配置才可实现负载均衡的功能,打开conf文件夹,下面有一个nginx.conf文件,配置如下:
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
gzip on;
#以下四行是新添加的,两个IP是两个tomcat的访问地址,weight表示分给该服务器的请求比重,两个都是1,则按照1:1来分配,
upstream netitcast.com{
server 127.0.0.1:8080 weight=1;
server 127.0.0.1:9080 weight=2;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
#一下两行是进行修改的,http://netitcast.com和上面添加的要保持一致
location / {
proxy_pass http://netitcast.com;
proxy_redirect default;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
还是打开cmd窗口,进入到以上目录,执行命令:start nginx 即启动成功,然后输入网址:http://localhost/index.jsp,不断的进行访问,就会发现,上方显示的图1和图2在交互的显示。因为以上的配置weight是以1:2的比重来分配的,所以9080端口的比重就大一些,访问到图一(9080端口)的几率就比较大,访问到图二(8080端口)的几率比较小,这个概率一个是三分之二,一个是三分之一。
当然,这只是一个简单的示例,在生产环境中开发,肯定还要解决许多问题,比如‘会话保持'等,这个以后明白了再来补充。写这个的目的就是让自己对负载均衡更加熟悉,希望大家以后一起努力,加油!!!
加载全部内容