java走迷宫回溯算法 Java实现走迷宫回溯算法
Shower稻草人 人气:0想了解Java实现走迷宫回溯算法的相关内容吗,Shower稻草人在本文为您仔细讲解java走迷宫回溯算法的相关知识和一些Code实例,欢迎阅读和指正,我们先划重点:java走迷宫回溯算法,java走迷宫算法,java迷宫算法,下面大家一起来学习吧。
以一个M×N的长方阵表示迷宫,0和1分别表示迷宫中的通路和障碍。设计一个程序,对任意设定的迷宫,求出一条从入口到出口的通路,或得出没有通路的结论。
(1) 根据二维数组,输出迷宫的图形。
(2) 探索迷宫的四个方向:RIGHT为向右,DOWN向下,LEFT向左,UP向上,输出从入口到出口的行走路径。
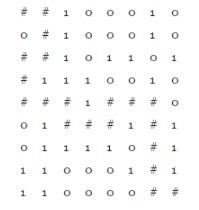
例子:
左上角(1,1)为入口,右下角(8,9)为出口。

可使用回溯方法,即从入口出发,顺着某一个方向进行探索,若能走通,则继续往前进;否则沿着原路退回,换一个方向继续探索,直至出口位置,求得一条通路。假如所有可能的通路都探索到而未能到达出口,则所设定的迷宫没有通路。
import java.util.*;
class Position{
public Position(){
}
public Position(int row, int col){
this.col = col;
this.row = row;
}
public String toString(){
return "(" + row + " ," + col + ")";
}
int row;
int col;
}
class Maze{
public Maze(){
maze = new int[15][15];
stack = new Stack<Position>();
p = new boolean[15][15];
}
/*
* 构造迷宫
*/
public void init(){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入迷宫的行数");
row = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入迷宫的列数");
col = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入" + row + "行" + col + "列的迷宫");
int temp = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < row; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < col; ++j) {
temp = scanner.nextInt();
maze[i][j] = temp;
p[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
/*
* 回溯迷宫,查看是否有出路
*/
public void findPath(){
// 给原始迷宫的周围家一圈围墙
int temp[][] = new int[row + 2][col + 2];
for(int i = 0; i < row + 2; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < col + 2; ++j) {
temp[0][j] = 1;
temp[row + 1][j] = 1;
temp[i][0] = temp[i][col + 1] = 1;
}
}
// 将原始迷宫复制到新的迷宫中
for(int i = 0; i < row; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < col; ++j) {
temp[i + 1][j + 1] = maze[i][j];
}
}
// 从左上角开始按照顺时针开始查询
int i = 1;
int j = 1;
p[i][j] = true;
stack.push(new Position(i, j));
while (!stack.empty() && (!(i == (row) && (j == col)))) {
if ((temp[i][j + 1] == 0) && (p[i][j + 1] == false)) {
p[i][j + 1] = true;
stack.push(new Position(i, j + 1));
j++;
} else if ((temp[i + 1][j] == 0) && (p[i + 1][j] == false)) {
p[i + 1][j] = true;
stack.push(new Position(i + 1, j));
i++;
} else if ((temp[i][j - 1] == 0) && (p[i][j - 1] == false)) {
p[i][j - 1] = true;
stack.push(new Position(i, j - 1));
j--;
} else if ((temp[i - 1][j] == 0) && (p[i - 1][j] == false)) {
p[i - 1][j] = true;
stack.push(new Position(i - 1, j));
i--;
} else {
stack.pop();
if(stack.empty()){
break;
}
i = stack.peek().row;
j = stack.peek().col;
}
}
Stack<Position> newPos = new Stack<Position>();
if (stack.empty()) {
System.out.println("没有路径");
} else {
System.out.println("有路径");
System.out.println("路径如下:");
while (!stack.empty()) {
Position pos = new Position();
pos = stack.pop();
newPos.push(pos);
}
}
/*
* 图形化输出路径
* */
String resault[][]=new String[row+1][col+1];
for(int k=0;k<row;++k){
for(int t=0;t<col;++t){
resault[k][t]=(maze[k][t])+"";
}
}
while (!newPos.empty()) {
Position p1=newPos.pop();
resault[p1.row-1][p1.col-1]="#";
}
for(int k=0;k<row;++k){
for(int t=0;t<col;++t){
System.out.print(resault[k][t]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
int maze[][];
private int row = 9;
private int col = 8;
Stack<Position> stack;
boolean p[][] = null;
}
class hello{
public static void main(String[] args){
Maze demo = new Maze();
demo.init();
demo.findPath();
}
}
运行示例:
请输入迷宫的行数
3
请输入迷宫的列数
3
请输入3行3列的迷宫
0 1 1
0 0 1
1 0 0
有路径
路径如下:

请输入迷宫的行数
9
请输入迷宫的列数
8
请输入9行8列的迷宫
0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1
0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1
0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1
1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
有路径
路径如下:
加载全部内容